Catalog: YT7934
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
200μL
$450.00
In stock
0
100μL
$280.00
In stock
0
40μL
$150.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
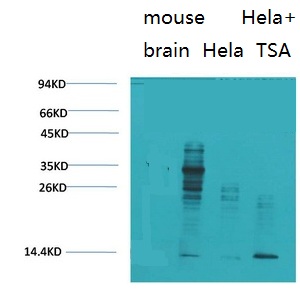
Target
SWS
Host Species
Rabbit
Reactivity
Human, Rat, Mouse,
Applications
WB, ELISA, IHC
MW
38kD (Observed)
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Recommended Dilution Ratio
WB 1:500-2000; IHC 1:50-300; ELISA 1:2000-20000
Formulation
Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
Specificity
This antibody detects endogenous levels of Human SWS
Purification
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
Storage
-15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
Concentration
1 mg/ml
MW(Observed)
38kD
Modification
Unmodified
Clonality
Polyclonal
Isotype
IgG
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Immunogen:
Synthesized peptide derived from human SWS
show all
Specificity:
This antibody detects endogenous levels of Human SWS
show all
Gene Name:
OPN1SW BCP
show all
Protein Name:
Short-wave-sensitive opsin 1 (Blue cone photoreceptor pigment) (Blue-sensitive opsin) (BOP)
show all
Other Name:
Short-wave-sensitive opsin 1 ;
Blue cone photoreceptor pigment ;
Blue-sensitive opsin ;
BOP ;
Blue cone photoreceptor pigment ;
Blue-sensitive opsin ;
BOP ;
show all
Database Link:
Background:
This gene belongs to the G-protein coupled receptor 1 family, opsin subfamily. It encodes the blue cone pigment gene which is one of three types of cone photoreceptors responsible for normal color vision. Defects in this gene are the cause of tritan color blindness (tritanopia). Affected individuals lack blue and yellow sensory mechanisms while retaining those for red and green. Defective blue vision is characteristic. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
show all
Function:
Disease:Defects in OPN1SW are the cause of tritan color blindness (tritanopia) [MIM:190900].,Function:Visual pigments are the light-absorbing molecules that mediate vision. They consist of an apoprotein, opsin, covalently linked to cis-retinal.,online information:Retina International's Scientific Newsletter,PTM:Phosphorylated on some or all of the serine and threonine residues present in the C-terminal region.,similarity:Belongs to the G-protein coupled receptor 1 family.,similarity:Belongs to the G-protein coupled receptor 1 family. Opsin subfamily.,tissue specificity:The three color pigments are found in the cone photoreceptor cells.,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Photoreceptor inner segment . Cell projection, cilium, photoreceptor outer segment . Cytoplasm, perinuclear region .
show all
Tissue Expression:
The three color pigments are found in the cone photoreceptor cells (PubMed:2937147). Expressed throughout the epidermis and dermis, primarily in the stratum granulosum in the facial and abdominal skin (at protein level) (PubMed:30168605). Expressed in dermal fibroblasts (at protein level) (PubMed:31380578). Expressed in melanocytes (at protein level) (PubMed:31730232).
show all
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: YT7934
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
200μL
$450.00
In stock
0
100μL
$280.00
In stock
0
40μL
$150.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}