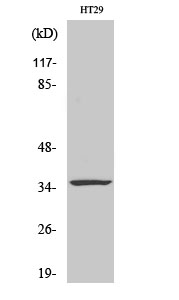
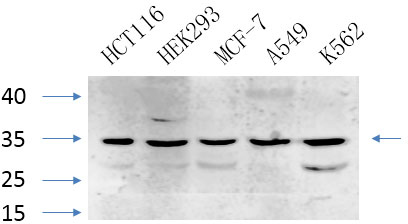
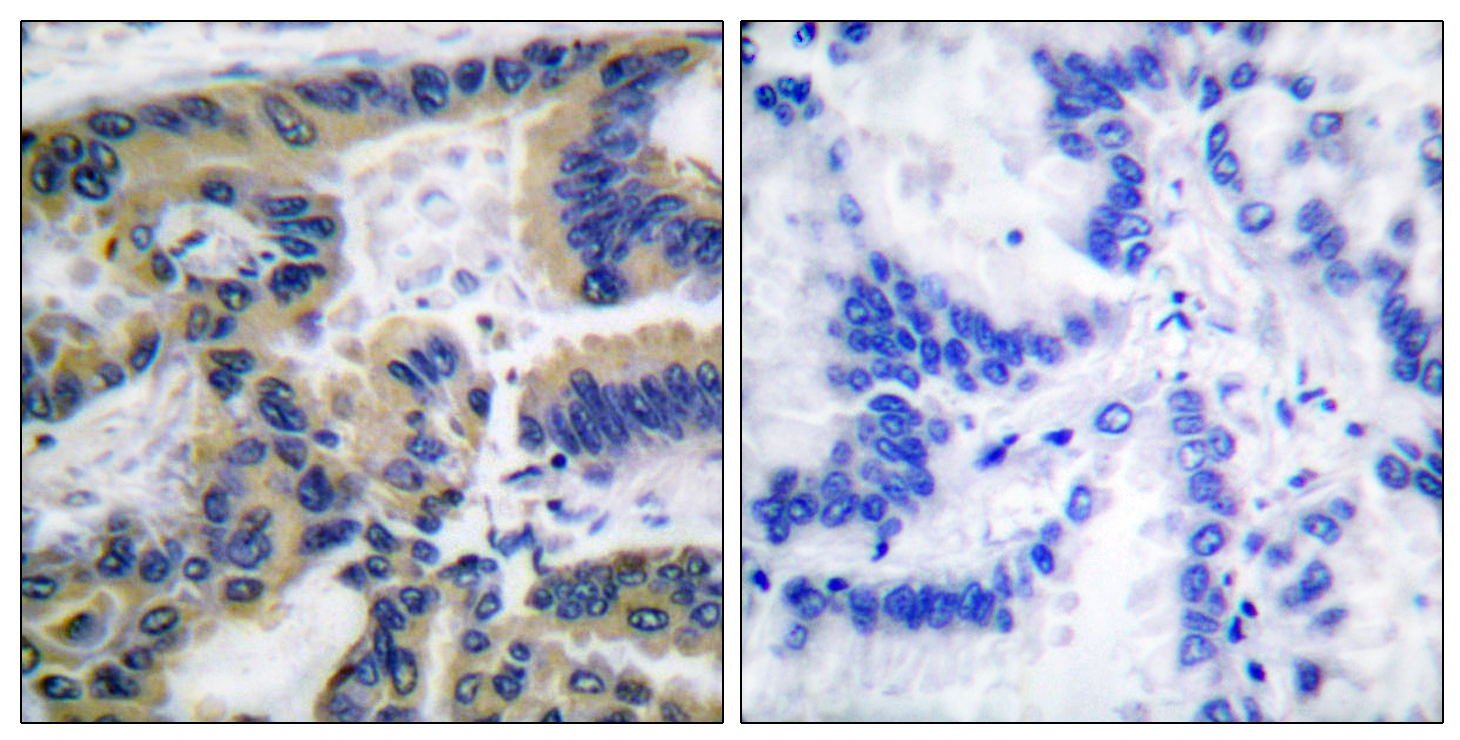
Catalog: KA3939C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Reactivity
Human, Mouse
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Unmodified
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
CASP7
show all
Other Name:
Caspase-7 ;
CASP-7 ;
Apoptotic protease Mch-3 ;
CMH-1 ;
ICE-like apoptotic protease 3 ;
ICE-LAP3 ;
[Cleaved into: Caspase-7 subunit p20 ;
Caspase-7 subunit p11]
CASP-7 ;
Apoptotic protease Mch-3 ;
CMH-1 ;
ICE-like apoptotic protease 3 ;
ICE-LAP3 ;
[Cleaved into: Caspase-7 subunit p20 ;
Caspase-7 subunit p11]
show all
Background:
catalytic activity:Strict requirement for an Asp residue at position P1 and has a preferred cleavage sequence of Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-|-.,enzyme regulation:Inhibited by isatin sulfonamides.,function:Involved in the activation cascade of caspases responsible for apoptosis execution. Cleaves and activates sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs). Proteolytically cleaves poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) at a '216-Asp-|-Gly-217' bond. Overexpression promotes programmed cell death.,PTM:Cleavages by granzyme B or caspase-10 generate the two active subunits. Propeptide domains can also be cleaved efficiently by caspase-3. Active heterodimers between the small subunit of caspase-7 and the large subunit of caspase-3, and vice versa, also occur.,similarity:Belongs to the peptidase C14A family.,subunit:Heterotetramer that consists of two anti-parallel arranged heterodimers, each one formed by a 20 kDa (p20) and a 11 kDa (p11) subunit.,tissue specificity:Highly expressed in lung, skeletal muscle, liver, kidney, spleen and heart, and moderately in testis. No expression in the brain.,
show all
Function:
release of cytochrome c from mitochondria, proteolysis, apoptosis, mitochondrion organization, heart development,cell death, apoptotic mitochondrial changes, response to radiation, response to UV, response to light stimulus,response to abiotic stimulus, programmed cell death, death,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Cytoplasm.
show all
Signaling Pathway
Cellular Processes >> Cell growth and death >> Apoptosis
Cellular Processes >> Cell growth and death >> Apoptosis - multiple species
Organismal Systems >> Immune system >> Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> Pathways in cancer
Human Diseases >> Neurodegenerative disease >> Alzheimer disease
Human Diseases >> Neurodegenerative disease >> Pathways of neurodegeneration - multiple diseases
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> TNF signaling pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA3939C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}