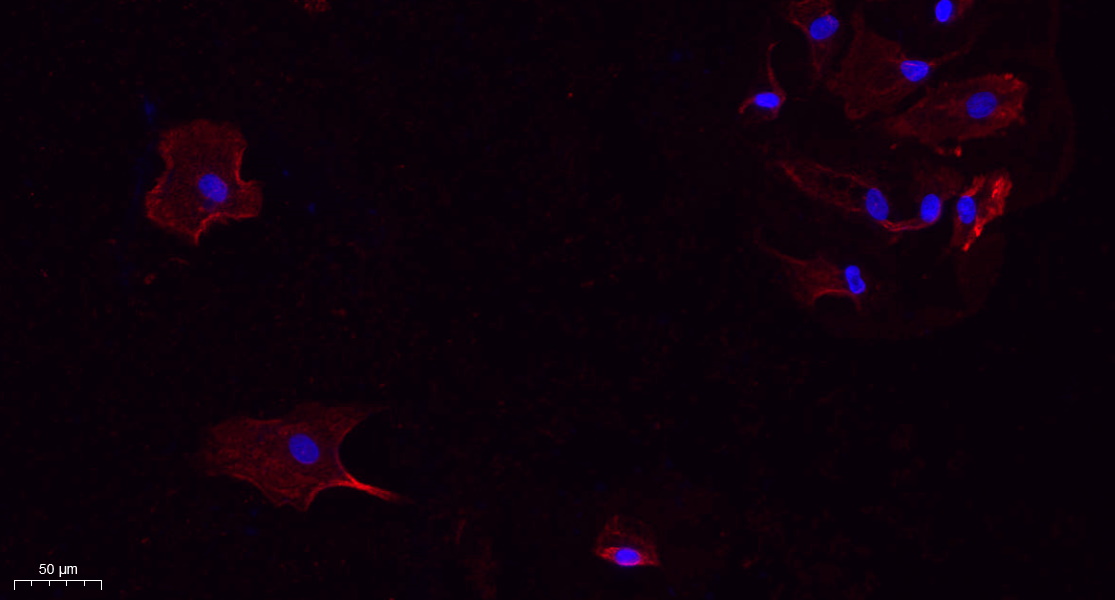
Catalog: KA3449C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Unmodified
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
TNFSF11
show all
Other Name:
Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11 ;
Osteoclast differentiation factor ;
ODF ;
Osteoprotegerin ligand ;
OPGL ;
Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand ;
RANKL ;
TNF-related activation-induced cytokine ;
TRANCE ;
CD antigen CD254 ;
[Cleaved into: Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11, membrane form ;
Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11, soluble form]
Osteoclast differentiation factor ;
ODF ;
Osteoprotegerin ligand ;
OPGL ;
Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand ;
RANKL ;
TNF-related activation-induced cytokine ;
TRANCE ;
CD antigen CD254 ;
[Cleaved into: Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11, membrane form ;
Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11, soluble form]
show all
Background:
disease:Defects in TNFSF11 are the cause of osteopetrosis autosomal recessive type 2 (OPTB2) [MIM:259710]; also known as osteoclast-poor osteopetrosis. Osteopetrosis is a rare genetic disease characterized by abnormally dense bone, due to defective resorption of immature bone. The disorder occurs in two forms: a severe autosomal recessive form occurring in utero, infancy, or childhood, and a benign autosomal dominant form occurring in adolescence or adulthood. Autosomal recessive osteopetrosis is usually associated with normal or elevated amount of non-functional osteoclasts. OPTB2 is characterized by paucity of osteoclasts, suggesting a molecular defect in osteoclast development.,function:Cytokine that binds to TNFRSF11B/OPG and to TNFRSF11A/RANK. Osteoclast differentiation and activation factor. Augments the ability of dendritic cells to stimulate naive T-cell proliferation. May be an important regulator of interactions between T-cells and dendritic cells and may play a role in the regulation of the T-cell-dependent immune response. May also play an important role in enhanced bone-resorption in humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy.,induction:Up-regulated by T-cell receptor stimulation.,PTM:The soluble form of isoform 1 derives from the membrane form by proteolytic processing (By similarity). The cleavage may be catalyzed by ADAM17.,similarity:Belongs to the tumor necrosis factor family.,subunit:Homotrimer.,tissue specificity:Highest in the peripheral lymph nodes, weak in spleen, peripheral blood Leukocytes, bone marrow, heart, placenta, skeletal muscle, stomach and thyroid.,
show all
Function:
skeletal system development, ossification, tissue homeostasis, immune system development, leukocyte differentiation,myeloid leukocyte differentiation, regulation of myeloid leukocyte differentiation, positive regulation of myeloid leukocyte differentiation, protein complex assembly, immune response, response to radiation, response to abiotic stimulus, hemopoiesis, myeloid cell differentiation, osteoclast differentiation, regulation of homeostatic process,positive regulation of homeostatic process, regulation of tissue remodeling, positive regulation of tissue remodeling,homeostatic process, macromolecular complex subunit organization, regulation of bone resorption, bone resorption,positive regulation of cell differentiation, regulation of myeloid cell differentiation, positive regulation of myeloid cell differentiation, regulation of osteoclast differentiation, positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation, positive regulation of bone resorption, bone remodeling, regulation of bone remodeling, positive regulation of bone remodeling, hemopoietic or lymphoid organ development, tissue remodeling, multicellular organismal homeostasis,positive regulation of developmental process, positive regulation of multicellular organismal process, protein oligomerization, protein homooligomerization, anatomical structure homeostasis, bone development, macromolecular complex assembly, protein complex biogenesis,
show all
Cellular Localization:
[Isoform 1]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein.; [Isoform 3]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein.; [Isoform 2]: Cytoplasm .; [Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11, soluble form]: Secreted .
show all
Signaling Pathway
Organismal Systems >> Endocrine system >> Prolactin signaling pathway
Organismal Systems >> Development and regeneration >> Osteoclast differentiation
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Breast cancer
Human Diseases >> Immune disease >> Rheumatoid arthritis
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> NF-kappa B signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signaling molecules and interaction >> Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA3449C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}