Catalog: YP1665
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
200μL
$600.00
In stock
0
100μL
$340.00
In stock
0
50μL
$190.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Target
NFAT2
Host Species
Rabbit
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
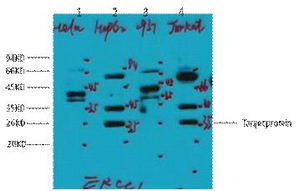
Applications
WB
MW
104kD (Calculated)
Conjugate/Modification
Phospho
Detailed Information
Recommended Dilution Ratio
WB 1:500-2000
Formulation
Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
Specificity
This antibody detects endogenous levels of NFAT2 (Phospho-Ser172) at Human, Mouse,Rat.The name of modified sites may be influenced by many factors, such as species (the modified site was not originally found in human samples) and the change of protein sequence (the previous protein sequence is incomplete, and the protein sequence may be prolonged with the development of protein sequencing technology). When naming, we will use the "numbers" in historical reference to keep the sites consistent with the reports. The antibody binds to the following modification sequence (lowercase letters are modification sites):LsPAS
Purification
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit serum by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
Storage
-15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
Concentration
1 mg/ml
MW(Calculated)
104kD
Modification
Phospho
Clonality
Polyclonal
Isotype
IgG
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Immunogen:
Synthesized peptide derived from human NFAT2 (Phospho-Ser172)
show all
Specificity:
This antibody detects endogenous levels of NFAT2 (Phospho-Ser172) at Human, Mouse,Rat.The name of modified sites may be influenced by many factors, such as species (the modified site was not originally found in human samples) and the change of protein sequence (the previous protein sequence is incomplete, and the protein sequence may be prolonged with the development of protein sequencing technology). When naming, we will use the "numbers" in historical reference to keep the sites consistent with the reports. The antibody binds to the following modification sequence (lowercase letters are modification sites):LsPAS
show all
Gene Name:
NFATC1 NFAT2 NFATC
show all
Protein Name:
NFAT2 (Phospho-Ser172)
show all
Other Name:
Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1 ;
NF-ATc1 ;
NFATc1 ;
NFAT transcription complex cytosolic component ;
NF-ATc ;
NFATc ;
NF-ATc1 ;
NFATc1 ;
NFAT transcription complex cytosolic component ;
NF-ATc ;
NFATc ;
show all
Background:
The product of this gene is a component of the nuclear factor of activated T cells DNA-binding transcription complex. This complex consists of at least two components: a preexisting cytosolic component that translocates to the nucleus upon T cell receptor (TCR) stimulation, and an inducible nuclear component. Proteins belonging to this family of transcription factors play a central role in inducible gene transcription during immune response. The product of this gene is an inducible nuclear component. It functions as a major molecular target for the immunosuppressive drugs such as cyclosporin A. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified for this gene. Different isoforms of this protein may regulate inducible expression of different cytokine genes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013],
show all
Function:
Alternative products:Isoform C-alpha and isoform C-beta are the strongest activator of gene transcription, followed by isoform A-alpha and isoform A-beta, whereas isoform B-alpha and isoform B-beta are the weakest. Isoform B-alpha, isoform B-beta, isoform C-alpha and isoform C-beta, both present in T-cells, can modulate their transcriptional activity,Domain:Isoforms C have a C-terminal part with an additional trans-activation domain, TAD-B, which acts as a transcriptional activator. Isoforms B have a shorter C-terminal part without complete TAD-B which acts as a transcriptional repressor.,Domain:Rel Similarity Domain (RSD) allows DNA-binding and cooperative interactions with AP1 factors.,Domain:The N-terminal transactivation domain (TAD-A) binds to and is activated by Cbp/p300. The dephosphorylated form contains two unmasked nuclear localization signals (NLS), which allow translocation of the protein to the nucleus.,Function:Plays a role in the inducible expression of cytokine genes in T-cells, especially in the induction of the IL-2 or IL-4 gene transcription. Also controls gene expression in embryonic cardiac cells. Could regulate not only the activation and proliferation but also the differentiation and programmed death of T-lymphocytes as well as lymphoid and non-lymphoid cells.,induction:Only isoforms A are inducibly expressed in T lymphocytes upon activation of the T-cell receptor (TCR) complex. Induced after co-addition of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and ionomycin. Also induced after co-addition of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) and ionomycin. Weakly induced with PMA, ionomycin and cyclosporin A.,PTM:Phosphorylated by NFATC-kinase; dephosphorylated by calcineurin.,similarity:Contains 1 RHD (Rel-like) domain.,subcellular location:Cytoplasmic for the phosphorylated form and nuclear after activation that is controlled by calcineurin-mediated dephosphorylation. Rapid nuclear exit of NFATC is thought to be one mechanism by which cells distinguish between sustained and transient calcium signals. The subcellular localization of NFATC plays a key role in the regulation of gene transcription.,subunit:Member of the multicomponent NFATC transcription complex that consists of at least two components, a pre-existing cytoplasmic component NFATC2 and an inducible nuclear component NFATC1. Other members such as NFATC4, NFATC3 or members of the activating protein-1 family, MAF, GATA4 and Cbp/p300 can also bind the complex. NFATC proteins bind to DNA as monomers.,tissue specificity:Expressed in thymus, peripheral leukocytes as T-cells and spleen. Isoforms A are preferentially expressed in effector T-cells (thymus and peripheral leukocytes) whereas isoforms B and isoforms C are preferentially expressed in naive T-cells (spleen). Isoforms B are expressed in naive T-cells after first antigen exposure and isoforms A are expressed in effector T-cells after second antigen exposure.,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Cytoplasm . Nucleus . Cytoplasmic for the phosphorylated form and nuclear after activation that is controlled by calcineurin-mediated dephosphorylation. Rapid nuclear exit of NFATC is thought to be one mechanism by which cells distinguish between sustained and transient calcium signals. The subcellular localization of NFATC plays a key role in the regulation of gene transcription (PubMed:16511445). Nuclear translocation of NFATC1 is enhanced in the presence of TNFSF11. Nuclear translocation is decreased in the presence of FBN1 which can bind and sequester TNFSF11 (By similarity). .
show all
Tissue Expression:
Expressed in thymus, peripheral leukocytes as T-cells and spleen. Isoforms A are preferentially expressed in effector T-cells (thymus and peripheral leukocytes) whereas isoforms B and isoforms C are preferentially expressed in naive T-cells (spleen). Isoforms B are expressed in naive T-cells after first antigen exposure and isoforms A are expressed in effector T-cells after second antigen exposure. Isoforms IA are widely expressed but not detected in liver nor pancreas, neural expression is strongest in corpus callosum. Isoforms IB are expressed mostly in muscle, cerebellum, placenta and thymus, neural expression in fetal and adult brain, strongest in corpus callosum.
show all
Research Areas:
>>MAPK signaling pathway ;
>>cGMP-PKG signaling pathway ;
>>cAMP signaling pathway ;
>>Cellular senescence ;
>>Wnt signaling pathway ;
>>Osteoclast differentiation ;
>>C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway ;
>>Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity ;
>>Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation ;
>>Th17 cell differentiation ;
>>T cell receptor signaling pathway ;
>>B cell receptor signaling pathway ;
>>Oxytocin signaling pathway ;
>>AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications ;
>>Yersinia infection ;
>>Hepatitis B ;
>>Human cytomegalovirus infection ;
>>Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection ;
>>Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection ;
>>Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection ;
>>PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer ;
>>Inflammatory bowel disease ;
>>Lipid and atherosclerosis
>>cGMP-PKG signaling pathway ;
>>cAMP signaling pathway ;
>>Cellular senescence ;
>>Wnt signaling pathway ;
>>Osteoclast differentiation ;
>>C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway ;
>>Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity ;
>>Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation ;
>>Th17 cell differentiation ;
>>T cell receptor signaling pathway ;
>>B cell receptor signaling pathway ;
>>Oxytocin signaling pathway ;
>>AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications ;
>>Yersinia infection ;
>>Hepatitis B ;
>>Human cytomegalovirus infection ;
>>Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection ;
>>Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection ;
>>Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection ;
>>PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer ;
>>Inflammatory bowel disease ;
>>Lipid and atherosclerosis
show all
Signaling Pathway
Cellular Processes >> Cell growth and death >> Cellular senescence
Organismal Systems >> Immune system >> Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity
Organismal Systems >> Immune system >> T cell receptor signaling pathway
Organismal Systems >> Immune system >> Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation
Organismal Systems >> Immune system >> Th17 cell differentiation
Organismal Systems >> Immune system >> B cell receptor signaling pathway
Organismal Systems >> Endocrine system >> Oxytocin signaling pathway
Organismal Systems >> Development and regeneration >> Osteoclast differentiation
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer
Human Diseases >> Immune disease >> Inflammatory bowel disease
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> MAPK signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Wnt signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Calcium signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> cAMP signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> cGMP-PKG signaling pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: YP1665
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
200μL
$600.00
In stock
0
100μL
$340.00
In stock
0
50μL
$190.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}