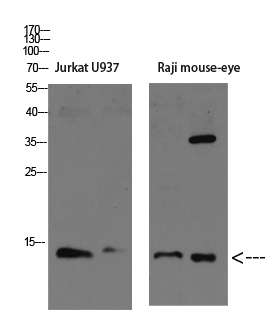
Catalog: YM4849
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
200μL
$600.00
In stock
0
100μL
$340.00
In stock
0
40μL
$190.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Target
TCL1
Host Species
Mouse
Reactivity
Human,
Applications
IHC, WB, IF, ELISA
MW
13kD (Calculated)
13kD (Observed)
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Recommended Dilution Ratio
IHC 1:200-1000; WB 1:500-2000; IF 1:100-500; ELISA 1:1000-5000
Formulation
PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300, 0.05%BSA
Specificity
The antibody can specifically recognize human TCL1 protein.
Purification
Protein G
Storage
-15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
MW(Calculated)
13kD
MW(Observed)
13kD
Modification
Unmodified
Clonality
Monoclonal
Clone Number
ABT234
Isotype
IgG2a,Kappa
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Immunogen:
Synthesized peptide derived from human TCL1 AA range: 50-114
show all
Specificity:
The antibody can specifically recognize human TCL1 protein.
show all
Gene Name:
TCL1A TCL1
show all
Protein Name:
TCL1
show all
Other Name:
Anti TCL1A ;
Lymphoma/leukemia, T-cell ;
Oncogene TCL-1 ;
Oncogene TCL1 ;
P14 TCL1 ;
P14 TCL1 protein ;
Protein p14 TCL1 ;
T cell leukemia 1 ;
T cell lymphoma 1 ;
T cell lymphoma 1A ;
T-cell leukemia/lymphoma 1A ;
T-cell leukemia/lymphoma protein 1A ;
TCL 1 protein ;
TCL1 ;
TCL1 oncogene ;
TCL1 PEN ;
Tcl1a ;
TCL1A ;
TCL1A_HUMAN
Lymphoma/leukemia, T-cell ;
Oncogene TCL-1 ;
Oncogene TCL1 ;
P14 TCL1 ;
P14 TCL1 protein ;
Protein p14 TCL1 ;
T cell leukemia 1 ;
T cell lymphoma 1 ;
T cell lymphoma 1A ;
T-cell leukemia/lymphoma 1A ;
T-cell leukemia/lymphoma protein 1A ;
TCL 1 protein ;
TCL1 ;
TCL1 oncogene ;
TCL1 PEN ;
Tcl1a ;
TCL1A ;
TCL1A_HUMAN
show all
Background:
TCL1 belongs to the proto oncogene family. It promotes the nuclear translocation of AKT1 by activating the phosphorylation of AKT1, AKT2 and Akt3, so as to promote cell proliferation and survival and stabilize mitochondrial membrane potential. The encoded protein is involved in embryonic development, T cell carcinogenesis, pre lymphocyte carcinogenesis and B cell carcinogenesis.
show all
Function:
Disease:Chromosomal aberrations activating TCL1A are found in chronic T-cell leukemias (T-CLL). Translocation t(14;14)(q11;q32); translocation t(7;14)(q35;q32); inversion inv(14)(q11;q32) that involves the T-cell receptor alpha/delta locuses.,Function:Enhances the phosphorylation and activation of AKT1, AKT2 and AKT3. Promotes nuclear translocation of AKT1. Enhances cell proliferation, stabilizes mitochondrial membrane potential and promotes cell survival.,similarity:Belongs to the TCL1 family.,subcellular location:Microsomal fraction.,subunit:Homodimer. Interacts with AKT1, AKT2 and AKT3 (via PH domain). Interacts with PNPT1; the interaction has no effect on PNPT1 exonuclease activity.,tissue specificity:Restricted in the T-cell lineage to immature thymocytes and activated peripheral lymphocytes. Preferentially expressed early in T- and B-lymphocyte differentiation.,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Cytoplasmic, Nuclear
show all
Tissue Expression:
Restricted in the T-cell lineage to immature thymocytes and activated peripheral lymphocytes. Preferentially expressed early in T- and B-lymphocyte differentiation.
show all
Research Areas:
>>PI3K-Akt signaling pathway
show all
Signaling Pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: YM4849
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
200μL
$600.00
In stock
0
100μL
$340.00
In stock
0
40μL
$190.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}