Catalog: YM0621
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
200μL
$600.00
3 weeks
0
100μL
$350.00
3 weeks
0
50μL
$210.00
3 weeks
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Target
TLR2
Host Species
Mouse
Reactivity
Human
Applications
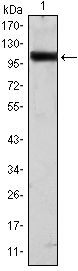
WB, ELISA
MW
90kD (Calculated)
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Recommended Dilution Ratio
WB 1:500-1:2000; ELISA 1:10000; Not yet tested in other applications.
Formulation
Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
Specificity
TLR2 Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of TLR2 protein.
Purification
Affinity purification
Storage
-15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
MW(Calculated)
90kD
Modification
Unmodified
Clonality
Monoclonal
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Immunogen:
Purified recombinant fragment of human TLR2 expressed in E. Coli.
show all
Specificity:
TLR2 Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of TLR2 protein.
show all
Gene Name:
TLR2
show all
Protein Name:
Toll-like receptor 2
show all
Other Name:
TLR2 ;
TIL4 ;
Toll-like receptor 2 ;
Toll/interleukin-1 receptor-like protein 4 ;
CD antigen CD282
TIL4 ;
Toll-like receptor 2 ;
Toll/interleukin-1 receptor-like protein 4 ;
CD antigen CD282
show all
Background:
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) family which plays a fundamental role in pathogen recognition and activation of innate immunity. TLRs are highly conserved from Drosophila to humans and share structural and functional similarities. This protein is a cell-surface protein that can form heterodimers with other TLR family members to recognize conserved molecules derived from microorganisms known as pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). Activation of TLRs by PAMPs leads to an up-regulation of signaling pathways to modulate the host's inflammatory response. This gene is also thought to promote apoptosis in response to bacterial lipoproteins. This gene has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several autoimmune diseases. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016],
show all
Function:
Function:Cooperates with LY96 to mediate the innate immune response to bacterial lipoproteins and other microbial cell wall components. Cooperates with TLR1 to mediate the innate immune response to bacterial lipoproteins or lipopeptides. Acts via MYD88 and TRAF6, leading to NF-kappa-B activation, cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response. May also promote apoptosis in response to lipoproteins. Recognizes mycoplasmal macrophage-activating lipopeptide-2kD (MALP-2), soluble tuberculosis factor (STF), phenol-soluble modulin (PSM) and B.burgdorferi outer surface protein A lipoprotein (OspA-L) cooperatively with TLR6.,polymorphism:Genetic variations in TLR2 are associated with suceptibility to leprosy [MIM:246300]. Leprosy is a chronic disease associated with depressed cellular (but not humoral) immunity, the bacterium requires a lower temperature than 37 degrees Celsius and thrives particularly in peripheral Schwann cells and macrophages. The Trp-677 polymorphism in the intracellular domain of TLR2 has a role in susceptibility to lepromatous leprosy. Wild-type TLR2 mediates CD14-enhanced Mycobacterium leprae-dependent activation of NFKB1, but TLR2 containing the Trp-677 polymorphism did not. The impaired function of the Trp-677 polymorphism provides a molecular mechanism for the poor cellular immune response associated with lepromatous leprosy.,PTM:Glycosylation of Asn-442 is critical for secretion of the N-terminal ectodomain of TLR2.,similarity:Belongs to the Toll-like receptor family.,similarity:Contains 1 TIR domain.,similarity:Contains 14 LRR (leucine-rich) repeats.,subunit:Interacts with LY96, TLR1 and TLR6 (via extracellular domain). Binds MYD88 (via TIR domain). Interacts with TICAM1. Ligand binding induces the formation of a heterodimer with TLR1.,tissue specificity:Highly expressed in peripheral blood leukocytes, in particular in monocytes, in bone marrow, lymph node and in spleen. Also detected in lung and in fetal liver. Levels are low in other tissues.,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein . Cytoplasmic vesicle, phagosome membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein . Membrane raft . Does not reside in lipid rafts before stimulation but accumulates increasingly in the raft upon the presence of the microbial ligand. In response to diacylated lipoproteins, TLR2:TLR6 heterodimers are recruited in lipid rafts, this recruitment determines the intracellular targeting to the Golgi apparatus. Triacylated lipoproteins induce the same mechanism for TLR2:TLR1 heterodimers. .
show all
Tissue Expression:
Highly expressed in peripheral blood leukocytes, in particular in monocytes, in bone marrow, lymph node and in spleen. Also detected in lung and in fetal liver. Levels are low in other tissues.
show all
Research Areas:
>>Phagosome ;
>>PI3K-Akt signaling pathway ;
>>Neutrophil extracellular trap formation ;
>>Toll-like receptor signaling pathway ;
>>Salmonella infection ;
>>Legionellosis ;
>>Leishmaniasis ;
>>Chagas disease ;
>>Malaria ;
>>Toxoplasmosis ;
>>Amoebiasis ;
>>Tuberculosis ;
>>Hepatitis B ;
>>Measles ;
>>Herpes simplex virus 1 infection ;
>>Epstein-Barr virus infection ;
>>Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection ;
>>Coronavirus disease - COVID-19 ;
>>Proteoglycans in cancer ;
>>PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer ;
>>Inflammatory bowel disease ;
>>Rheumatoid arthritis ;
>>Lipid and atherosclerosis
>>PI3K-Akt signaling pathway ;
>>Neutrophil extracellular trap formation ;
>>Toll-like receptor signaling pathway ;
>>Salmonella infection ;
>>Legionellosis ;
>>Leishmaniasis ;
>>Chagas disease ;
>>Malaria ;
>>Toxoplasmosis ;
>>Amoebiasis ;
>>Tuberculosis ;
>>Hepatitis B ;
>>Measles ;
>>Herpes simplex virus 1 infection ;
>>Epstein-Barr virus infection ;
>>Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection ;
>>Coronavirus disease - COVID-19 ;
>>Proteoglycans in cancer ;
>>PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer ;
>>Inflammatory bowel disease ;
>>Rheumatoid arthritis ;
>>Lipid and atherosclerosis
show all
Signaling Pathway
Cellular Processes >> Transport and catabolism >> Phagosome
Organismal Systems >> Immune system >> Neutrophil extracellular trap formation
Organismal Systems >> Immune system >> Toll-like receptor signaling pathway
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer
Human Diseases >> Immune disease >> Rheumatoid arthritis
Human Diseases >> Immune disease >> Inflammatory bowel disease
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> PI3K-Akt signaling pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: YM0621
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
200μL
$600.00
3 weeks
0
100μL
$350.00
3 weeks
0
50μL
$210.00
3 weeks
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}