Catalog: YM0512
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
200μL
$600.00
3 weeks
0
100μL
$350.00
3 weeks
0
50μL
$210.00
3 weeks
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Target
PDGFR-β
Host Species
Mouse
Reactivity
Human, Mouse
Applications
WB, ELISA
MW
135-180kD (Observed)
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Recommended Dilution Ratio
WB 1:500-1:2000; ELISA 1:10000; Not yet tested in other applications.
Formulation
Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
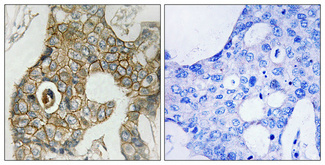
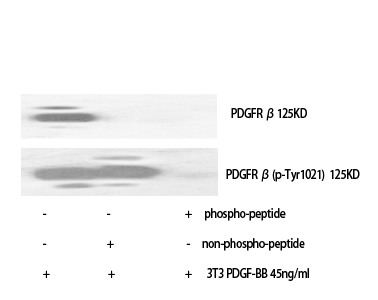
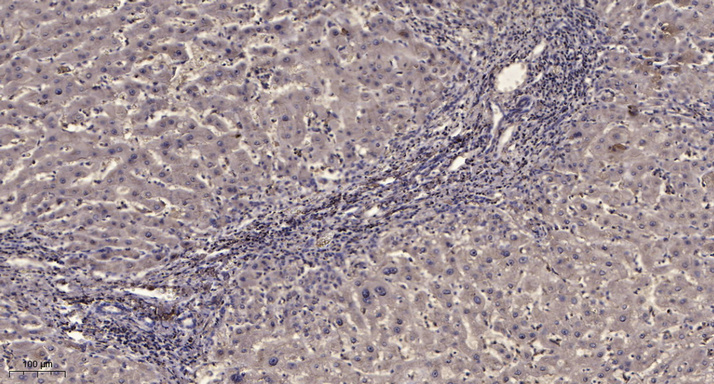
Specificity
PDGFR-β Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of PDGFR-β protein.
Purification
Affinity purification
Storage
-15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
MW(Observed)
135-180kD
Modification
Unmodified
Clonality
Monoclonal
Clone Number
15F3
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Immunogen:
Purified recombinant fragment of human PDGFR-β expressed in E. Coli.
show all
Specificity:
PDGFR-β Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of PDGFR-β protein.
show all
Gene Name:
PDGFRB PDGFR PDGFR1
show all
Protein Name:
Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta
show all
Other Name:
PDGFRB ;
PDGFR ;
PDGFR1 ;
Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta ;
PDGF-R-beta ;
PDGFR-beta ;
Beta platelet-derived growth factor receptor ;
Beta-type platelet-derived growth factor receptor ;
CD140 antigen-like family member B ;
Platelet-deri
PDGFR ;
PDGFR1 ;
Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta ;
PDGF-R-beta ;
PDGFR-beta ;
Beta platelet-derived growth factor receptor ;
Beta-type platelet-derived growth factor receptor ;
CD140 antigen-like family member B ;
Platelet-deri
show all
Background:
This gene encodes a cell surface tyrosine kinase receptor for members of the platelet-derived growth factor family. These growth factors are mitogens for cells of mesenchymal origin. The identity of the growth factor bound to a receptor monomer determines whether the functional receptor is a homodimer or a heterodimer, composed of both platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha and beta polypeptides. This gene is flanked on chromosome 5 by the genes for granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and macrophage-colony stimulating factor receptor; all three genes may be implicated in the 5-q syndrome. A translocation between chromosomes 5 and 12, that fuses this gene to that of the translocation, ETV6, leukemia gene, results in chronic myeloproliferative disorder with eosinophilia. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
show all
Function:
Catalytic activity:ATP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine = ADP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine phosphate.,Disease:A chromosomal aberration involving PDGFRB is a cause in many instances of chronic myeloproliferative disorder with eosinophilia (MPE) [MIM:131440]. Translocation t(5;12) with ETV6 on chromosome 12 creating an PDGFRB-ETV6 fusion protein.,Disease:A chromosomal aberration involving PDGFRB is found in a form of chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML). Translocation t(5;12)(q33;p13) with EVT6/TEL. It is characterized by abnormal clonal myeloid proliferation and by progression to acute myelogenous leukemia (AML).,Disease:A chromosomal aberration involving PDGFRB may be a cause of acute myelogenous leukemia. Translocation t(5;14)(q33;q32) with TRIP11. The fusion protein may be involved in clonal evolution of leukemia and eosinophilia.,Disease:A chromosomal aberration involving PDGFRB may be a cause of juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia. Translocation t(5;17)(q33;p11.2) with SPECC1.,Disease:A chromosomal aberration involving PDGFRB may be the cause of a myeloproliferative disorder (MBD) associated with eosinophilia. Translocation t(1;5)(q23;q33) that forms a PDE4DIP-PDGFRB fusion protein.,Function:Receptor that binds specifically to PDGFB and PDGFD and has a tyrosine-protein kinase activity. Phosphorylates Tyr residues at the C-terminus of PTPN11 creating a binding site for the SH2 domain of GRB2.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. CSF-1/PDGF receptor subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 protein kinase domain.,similarity:Contains 5 Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains.,subunit:Homodimer, and heterodimer with PDGFRA. Interacts with APS. The autophosphorylated form interacts directly with SHB and with PIK3C2B, maybe indirectly.,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cytoplasmic vesicle. Lysosome lumen. After ligand binding, the autophosphorylated receptor is ubiquitinated and internalized, leading to its degradation.
show all
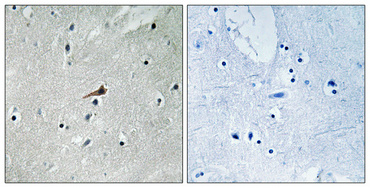
Tissue Expression:
Brain,Spleen,
show all
Research Areas:
>>EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance ;
>>MAPK signaling pathway ;
>>Ras signaling pathway ;
>>Rap1 signaling pathway ;
>>Calcium signaling pathway ;
>>Phospholipase D signaling pathway ;
>>PI3K-Akt signaling pathway ;
>>Focal adhesion ;
>>Gap junction ;
>>JAK-STAT signaling pathway ;
>>Regulation of actin cytoskeleton ;
>>Human papillomavirus infection ;
>>Pathways in cancer ;
>>MicroRNAs in cancer ;
>>Glioma ;
>>Prostate cancer ;
>>Melanoma ;
>>Central carbon metabolism in cancer ;
>>Choline metabolism in cancer
>>MAPK signaling pathway ;
>>Ras signaling pathway ;
>>Rap1 signaling pathway ;
>>Calcium signaling pathway ;
>>Phospholipase D signaling pathway ;
>>PI3K-Akt signaling pathway ;
>>Focal adhesion ;
>>Gap junction ;
>>JAK-STAT signaling pathway ;
>>Regulation of actin cytoskeleton ;
>>Human papillomavirus infection ;
>>Pathways in cancer ;
>>MicroRNAs in cancer ;
>>Glioma ;
>>Prostate cancer ;
>>Melanoma ;
>>Central carbon metabolism in cancer ;
>>Choline metabolism in cancer
show all
Signaling Pathway
Cellular Processes >> Cellular community - eukaryotes >> Focal adhesion
Cellular Processes >> Cellular community - eukaryotes >> Gap junction
Cellular Processes >> Cell motility >> Regulation of actin cytoskeleton
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> Pathways in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> MicroRNAs in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> Central carbon metabolism in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Glioma
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Melanoma
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Prostate cancer
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> MAPK signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Ras signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Rap1 signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> JAK-STAT signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Calcium signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Phospholipase D signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> PI3K-Akt signaling pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: YM0512
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
200μL
$600.00
3 weeks
0
100μL
$350.00
3 weeks
0
50μL
$210.00
3 weeks
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}