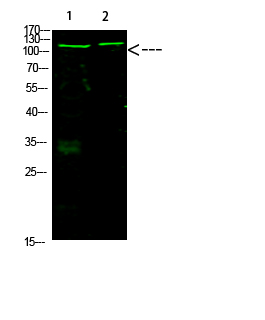
Catalog: KA4266C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
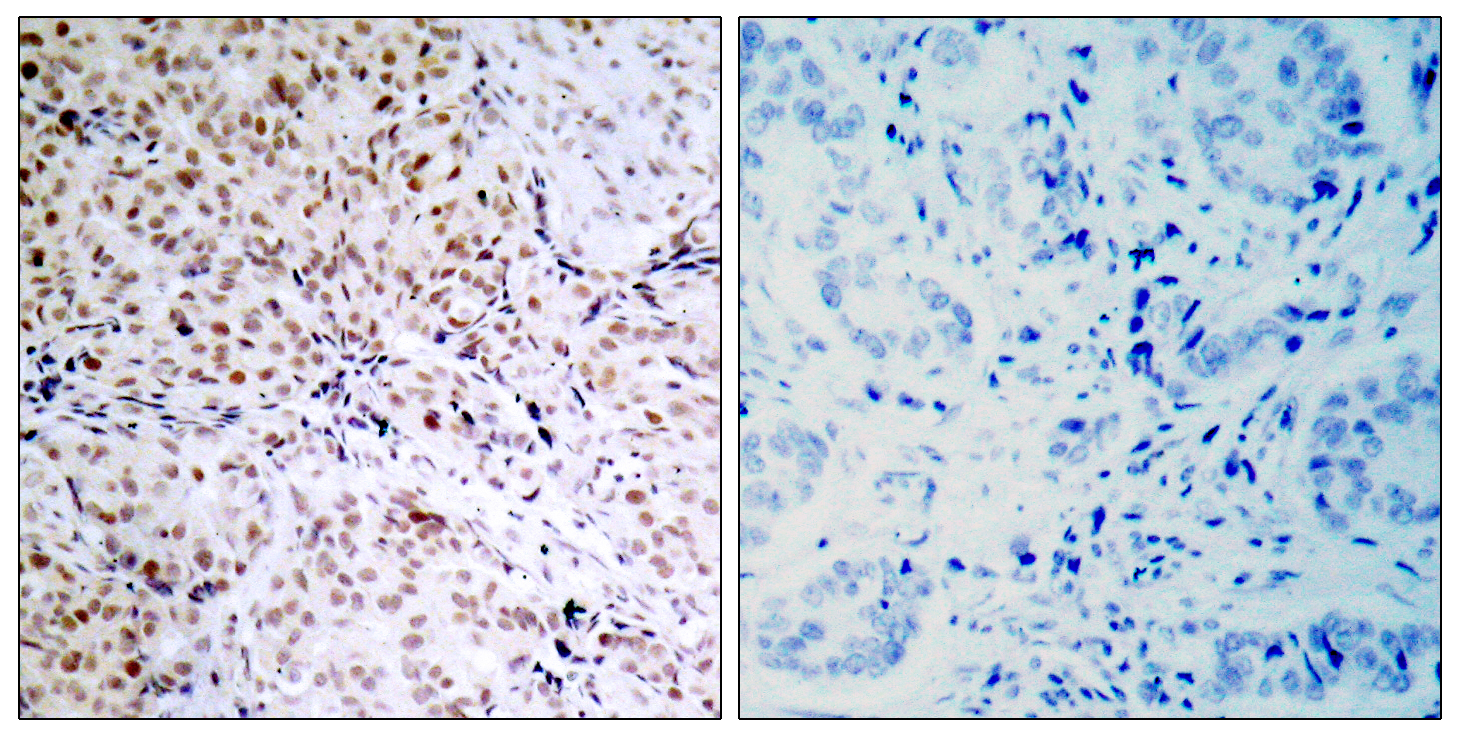
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Unmodified
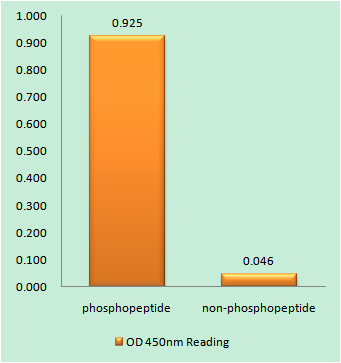
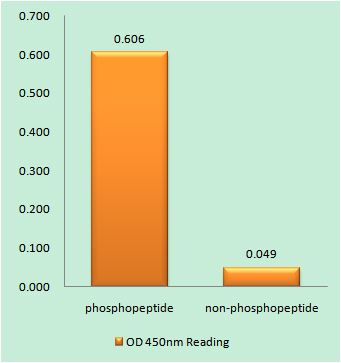
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
RB1
show all
Other Name:
Retinoblastoma-associated protein ;
p105-Rb ;
pRb ;
Rb ;
pp110 ;
p105-Rb ;
pRb ;
Rb ;
pp110 ;
show all
Database Link:
Background:
disease:Defects in RB1 are a cause of bladder cancer [MIM:109800].,disease:Defects in RB1 are a cause of osteogenic sarcoma [MIM:259500].,disease:Defects in RB1 are the cause of childhood cancer retinoblastoma (RB) [MIM:180200]. RB is a congenital malignant tumor that arises from the nuclear layers of the retina. It occurs in about 1:20'000 live births and represents about 2% of childhood malignancies. It is bilateral in about 30% of cases. Although most RB appear sporadically, about 20% are transmitted as an autosomal dominant trait with incomplete penetrance. The diagnosis is usually made before the age of 2 years when strabismus or a gray to yellow reflex from pupil ("cat eye") is investigated.,function:Key regulator of entry into cell division that acts as a tumor suppressor. Acts as a transcription repressor of E2F1 target genes. The underphosphorylated, active form of RB1 interacts with E2F1 and represses its transcription activity, leading to cell cycle arrest. Directly involved in heterochromatin formation by maintaining overall chromatin structure and, in particular, that of constitutive heterochromatin by stabilizing histone methylation. Recruits and targets histone methyltransferases SUV39H1, SUV420H1 and SUV420H2, leading to epigenetic transcriptional repression. Controls histone H4 'Lys-20' trimethylation. Inhibits the intrinsic kinase activity of TAF1. In case of viral infections, interactions with SV40 large T antigen, HPV E7 protein or adenovirus E1A protein induce the disassembly of RB1-E2F1 complex thereby disrupting RB1's activity.,online information:RB1 mutation db,online information:Retinoblastoma protein entry,PTM:Phosphorylated in G1, thereby releasing E2F1 which is then able to activate cell growth. Dephosphorylated at the late M phase. SV40 large T antigen, HPV E7 and adenovirus E1A bind to the underphosphorylated, active form of pRb.,similarity:Belongs to the retinoblastoma protein (RB) family.,subunit:Interacts with ATAD5 (By similarity). The hypophosphorylated form interacts with and sequesters the E2F1 transcription factor. The unphosphorylated form interacts with ARID3B, KDM5A, SUV39H1, MJD2A/JHDM3A and THOC1. Interacts with the N-terminal domain of TAF1. Interacts with AATF, DNMT1, LIN9, LMNA, SUV420H1, SUV420H2, PELP1 and TMPO-alpha. May interact with NDC80. Interacts with EID1 and UBR4. Interacts with ARID4A and KDM5B. Interacts with E4F1. Interacts with adenovirus E1A protein, HPV E7 protein and SV40 large T antigen.,tissue specificity:Expressed in the retina.,
show all
Function:
cell cycle checkpoint, G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle, regulation of transcription of G1/S-phase of mitotic cell cycle,negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, mitotic cell cycle, M phase, regulation of cell growth, immune system development, regulation of myeloid leukocyte differentiation, positive regulation of myeloid leukocyte differentiation, chromatin organization, chromatin remodeling, transcription, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, negative regulation of protein kinase activity,cell cycle, cell cycle arrest, regulation of S phase of mitotic cell cycle, intracellular signaling cascade, regulation of mitotic cell cycle, negative regulation of cell proliferation, regulation of cell size, negative regulation of biosynthetic process, positive regulation of biosynthetic process, positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process,negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, regulation of cell cycle process, positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, positive regulation of gene expression, negative regulation of gene expression, negative regulation of cell cycle process, negative regulation of transcription, chromatin modification, regulation of lipid metabolic process, regulation of phosphate metabolic process,cell cycle process, cell cycle phase, hemopoiesis, myeloid cell differentiation, erythrocyte differentiation, negative regulation of cell growth, steroid hormone receptor signaling pathway, androgen receptor signaling pathway,intracellular receptor-mediated signaling pathway, negative regulation of cellular biosynthetic process, positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process, regulation of cellular component size, regulation of S phase, negative regulation of kinase activity, erythrocyte homeostasis, regulation of growth, regulation of cell proliferation, regulation of phosphorylation, homeostatic process, muscle cell differentiation, negative regulation of catalytic activity, enucleate erythrocyte differentiation, regulation of kinase activity, regulation of lipid kinase activity, negative regulation of molecular function, myoblast differentiation, regulation of transcription, positive regulation of cell differentiation,regulation of myeloid cell differentiation, positive regulation of myeloid cell differentiation, regulation of macrophage differentiation, positive regulation of macrophage differentiation, negative regulation of S phase of mitotic cell cycle,negative regulation of cell cycle, negative regulation of cell size, regulation of protein kinase activity, negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, negative regulation of growth, negative regulation of mitotic cell cycle, negative regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process, positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process, positive regulation of transcription, positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter,hemopoietic or lymphoid organ development, homeostasis of number of cells, positive regulation of developmental process, striated muscle cell differentiation, negative regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process, positive regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process, regulation of phosphorus metabolic process, regulation of RNA metabolic process, negative regulation of RNA metabolic process, positive regulation of RNA metabolic process,chromosome organization, cell division, G1 phase, interphase, interphase of mitotic cell cycle, regulation of transferase activity, negative regulation of transferase activity, regulation of cell cycle,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Nucleus . During keratinocyte differentiation, acetylation by KAT2B/PCAF is required for nuclear localization. .
show all
Tissue Expression:
Signaling Pathway
Cellular Processes >> Cell growth and death >> Cell cycle
Cellular Processes >> Cell growth and death >> Cellular senescence
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> Pathways in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Pancreatic cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Hepatocellular carcinoma
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Gastric cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Glioma
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Chronic myeloid leukemia
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Melanoma
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Bladder cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Prostate cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Breast cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Small cell lung cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Non-small cell lung cancer
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA4266C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}