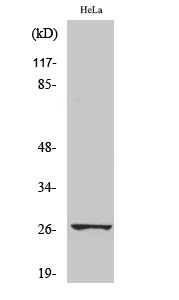
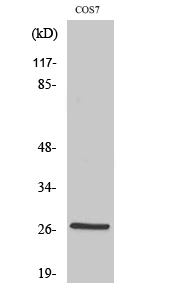
Catalog: KA4124C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Unmodified
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
HSPB1 HSP27 HSP28
show all
Other Name:
Heat shock protein beta-1 ;
HspB1 ;
28 kDa heat shock protein ;
Estrogen-regulated 24 kDa protein ;
Heat shock 27 kDa protein ;
HSP 27 ;
Stress-responsive protein 27 ;
SRP27 ;
HspB1 ;
28 kDa heat shock protein ;
Estrogen-regulated 24 kDa protein ;
Heat shock 27 kDa protein ;
HSP 27 ;
Stress-responsive protein 27 ;
SRP27 ;
show all
Database Link:
Background:
disease:Defects in HSPB1 are a cause of distal hereditary motor neuronopathy type 2B (HMN2B) [MIM:608634]. Distal hereditary motor neuronopathies constitute a heterogeneous group of neuromuscular disorders caused by selective impairment of motor neurons in the anterior horn of the spinal cord, without sensory deficit in the posterior horn. The overall clinical picture consists of a classical distal muscular atrophy syndrome in the legs without clinical sensory loss. The disease starts with weakness and wasting of distal muscles of the anterior tibial and peroneal compartments of the legs. Later on, weakness and atrophy may expand to the proximal muscles of the lower limbs and/or to the distal upper limbs.,disease:Defects in HSPB1 are the cause of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2F (CMT2F) [MIM:606595]. CMT2F is a form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, the most common inherited disorder of the peripheral nervous system. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is classified in two main groups on the basis of electrophysiologic properties and histopathology: primary peripheral demyelinating neuropathy or CMT1, and primary peripheral axonal neuropathy or CMT2. Neuropathies of the CMT2 group are characterized by signs of axonal regeneration in the absence of obvious myelin alterations, normal or slightly reduced nerve conduction velocities, and progressive distal muscle weakness and atrophy. Nerve conduction velocities are normal or slightly reduced. CMT2F onset is between 15 and 25 years with muscle weakness and atrophy usually beginning in feet and legs (peroneal distribution). Upper limb involvement occurs later. CMT2F inheritance is autosomal dominant.,function:Involved in stress resistance and actin organization.,induction:Expressed in response to environmental stresses such as heat shock, or estrogen stimulation in MCF-7 cells.,PTM:Phosphorylated in MCF-7 cells on exposure to protein kinase C activators and heat shock.,similarity:Belongs to the small heat shock protein (HSP20) family.,subcellular location:Cytoplasmic in interphase cells. Colocalizes with mitotic spindles in mitotic cells. Translocates to the nucleus during heat shock.,subunit:Interacts with TGFB1I1 (By similarity). Associates with alpha- and beta-tubulin, microtubules and CRYAB. Interacts with HSPB8 and HSPBAP1.,tissue specificity:Detected in all tissues tested: skeletal muscle, heart, aorta, large intestine, small intestine, stomach, esophagus, bladder, adrenal gland, thyroid, pancreas, testis, adipose tissue, kidney, liver, spleen, cerebral cortex, blood serum and cerebrospinal fluid. Highest levels are found in the heart and in tissues composed of striated and smooth muscle.,
show all
Function:
regulation of translation, regulation of translational initiation, anti-apoptosis, cell motion, response to unfolded protein, cell death, response to temperature stimulus, response to heat, response to abiotic stimulus, response to organic substance, posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression, regulation of cell death, death, regulation of cellular protein metabolic process, regulation of apoptosis, negative regulation of apoptosis, regulation of programmed cell death, negative regulation of programmed cell death, response to protein stimulus, negative regulation of cell death,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Cytoplasm . Nucleus . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle . Cytoplasmic in interphase cells. Colocalizes with mitotic spindles in mitotic cells. Translocates to the nucleus during heat shock and resides in sub-nuclear structures known as SC35 speckles or nuclear splicing speckles. .
show all
Signaling Pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA4124C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}