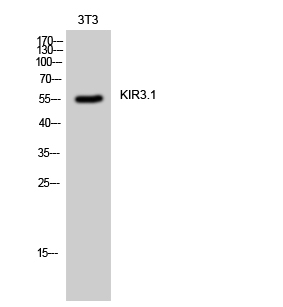
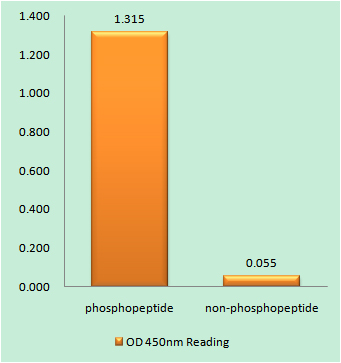
Catalog: KA4105C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Unmodified
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
KCNJ3
show all
Other Name:
G protein-activated inward rectifier potassium channel 1 ;
GIRK-1 ;
Inward rectifier K ;
+ ;
channel Kir3.1 ;
Potassium channel, inwardly rectifying subfamily J member 3 ;
GIRK-1 ;
Inward rectifier K ;
+ ;
channel Kir3.1 ;
Potassium channel, inwardly rectifying subfamily J member 3 ;
show all
Background:
function:This potassium channel is controlled by G proteins. Inward rectifier potassium channels are characterized by a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into the cell rather than out of it. Their voltage dependence is regulated by the concentration of extracellular potassium; as external potassium is raised, the voltage range of the channel opening shifts to more positive voltages. The inward rectification is mainly due to the blockage of outward current by internal magnesium. This receptor plays a crucial role in regulating the heartbeat.,similarity:Belongs to the inward rectifier-type potassium channel family.,subunit:Associates with GIRK2, GIRK3 or GIRK4 to form a G-protein activated heteromultimer pore-forming unit. The resulting inward current is much larger.,
show all
Function:
ion transport, cation transport, potassium ion transport, monovalent inorganic cation transport, metal ion transport,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
show all
Signaling Pathway
Organismal Systems >> Endocrine system >> Estrogen signaling pathway
Organismal Systems >> Endocrine system >> Oxytocin signaling pathway
Organismal Systems >> Nervous system >> Glutamatergic synapse
Organismal Systems >> Nervous system >> Cholinergic synapse
Organismal Systems >> Nervous system >> Dopaminergic synapse
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA4105C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}