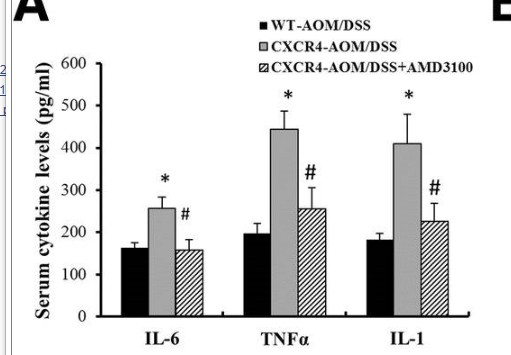
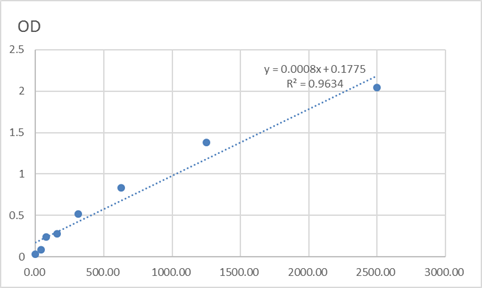
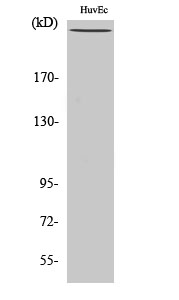Catalog: KA4098C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Unmodified
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
FLNA
show all
Other Name:
Filamin-A ;
FLN-A ;
Actin-binding protein 280 ;
ABP-280 ;
Alpha-filamin ;
Endothelial actin-binding protein ;
Filamin-1 ;
Non-muscle filamin ;
FLN-A ;
Actin-binding protein 280 ;
ABP-280 ;
Alpha-filamin ;
Endothelial actin-binding protein ;
Filamin-1 ;
Non-muscle filamin ;
show all
Background:
disease:Defects in FLNA are associated with cerebrofrontofacial syndrome [MIM:608578]. This syndrome consists of a phenotype of male PVNH, with relatively normal development, no epilepsy or other neurological abnormality, severe constipation, and facial dysmorphism and without a discernible skeletal phenotype.,disease:Defects in FLNA are the cause of frontometaphyseal dysplasia (FMD) [MIM:305620]. FMD is a congenital bone disease characterized by supraorbital hyperostosis, deafness and digital anomalies.,disease:Defects in FLNA are the cause of Melnick-Needles syndrome (MNS) [MIM:309350]. MNS is a severe congenital bone disorder characterized by typical facies (exophthalmos, full cheeks, micrognathia and malalignment of teeth), flaring of the metaphyses of long bones, s-like curvature of bones of legs, irregular constrictions in the ribs, and sclerosis of base of skull.,disease:Defects in FLNA are the cause of otopalatodigital syndrome type 1 (OPD1) [MIM:311300]. OPD1 is an X-linked dominant multiple congenital anomalies disease mainly characterized by a generalized skeletal dysplasia, mild mental retardation, hearing loss, cleft palate, and typical facial anomalies. OPD1 belongs to a group of X-linked skeletal dysplasias known as oto-palato-digital syndrome spectrum disorders that also include OPD2, Melnick-Needles syndrome (MNS), and frontometaphyseal dysplasia (FMD). Remodeling of the cytoskeleton is central to the modulation of cell shape and migration. FLNA is a widely expressed protein that regulates re-organization of the actin cytoskeleton by interacting with integrins, transmembrane receptor complexes and second messengers. Males with OPD1 have cleft palate, malformations of the ossicles causing deafness and milder bone and limb defects than those associated with OPD2. Obligate female carriers of mutations causing both OPD1 and OPD2 have variable (often milder) expression of a similar phenotypic spectrum.,disease:Defects in FLNA are the cause of otopalatodigital syndrome type 2 (OPD2) [MIM:304120]; also known as cranioorodigital syndrome. OPD2 is a congenital bone disorder that is characterized by abnormally modeled, bowed bones, small or absent first digits and, more variably, cleft palate, posterior fossa brain anomalies, omphalocele and cardiac defects.,disease:Defects in FLNA are the cause of periventricular nodular heterotopia type 1 (PVNH1) [MIM:300049]; also called nodular heterotopia, bilateral periventricular (NHBP or BPNH). PVNH is a developmental disorder characterized by the presence of periventricular nodules of cerebral gray matter, resulting from a failure of neurons to migrate normally from the lateral ventricular proliferative zone, where they are formed, to the cerebral cortex. PVNH1 is an X-linked dominant form. Heterozygous females have normal intelligence but suffer from seizures and various manifestations outside the central nervous system, especially related to the vascular system. Hemizygous affected males die in the prenatal or perinatal period.,disease:Defects in FLNA are the cause of periventricular nodular heterotopia type 4 (PVNH4) [MIM:300537]; also known as periventricular heterotopia Ehlers-Danlos variant. PVNH4 is characterized by nodular brain heterotopia, joint hypermobility and development of aortic dilatation in early adulthood.,disease:Defects in FLNA are the cause of X-linked congenital idiopathic intestinal pseudoobstruction (CIIPX) [MIM:300048]. CIIPX is characterized by a severe abnormality of gastrointestinal motility due to primary qualitative defects of enteric ganglia and nerve fibers. Affected individuals manifest recurrent signs of intestinal obstruction in the absence of any mechanical lesion.,domain:Comprised of a NH2-terminal actin-binding domain, 24 internally homologous repeats and two hinge regions. Repeat 24 and the second hinge domain are important for dimer formation.,function:Promotes orthogonal branching of actin filaments and links actin filaments to membrane glycoproteins. Anchors various transmembrane proteins to the actin cytoskeleton and serves as a scaffold for a wide range of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Interaction with FLNA may allow neuroblast migration from the ventricular zone into the cortical plate. Tethers cell surface-localized furin, modulates its rate of internalization and directs its intracellular trafficking.,PTM:Phosphorylated upon DNA damage, probably by ATM or ATR (By similarity). Phosphorylation extent changes in response to cell activation.,PTM:The N-terminus is blocked.,similarity:Belongs to the filamin family.,similarity:Contains 1 actin-binding domain.,similarity:Contains 2 CH (calponin-homology) domains.,similarity:Contains 24 filamin repeats.,subunit:Interacts with PDLIM2 (By similarity). Homodimer. Interacts with FCGR1A, FLNB, FURIN, HSPB7, INPPL1, KCND2, MYOT, MYOZ1, ARHGAP24, PSEN1, PSEN2 and ECSCR. Interacts also with various other binding partners in addition to filamentous actin.,tissue specificity:Ubiquitous.,
show all
Function:
regulation of nucleotide metabolic process, protein complex assembly, cytoskeleton organization, actin filament organization, cell surface receptor linked signal transduction, enzyme linked receptor protein signaling pathway,transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway, signal complex assembly, G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway, G-protein signaling, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger, G-protein signaling, coupled to cAMP nucleotide second messenger, inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity by G-protein signaling, negative regulation of adenylate cyclase activity, inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity by dopamine receptor signaling pathway, dopamine receptor signaling pathway, intracellular signaling cascade, protein localization,regulation of catabolic process, negative regulation of catabolic process, positive regulation of signal transduction,negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression, regulation of protein kinase cascade, positive regulation of cell communication, positive regulation of protein kinase cascade,vesicle-mediated transport, endosome transport, second-messenger-mediated signaling, cAMP-mediated signaling,cyclic-nucleotide-mediated signaling, actin filament-based process, actin cytoskeleton organization, regulation of cyclic nucleotide metabolic process, regulation of cyclic nucleotide biosynthetic process, regulation of nucleotide biosynthetic process, regulation of cAMP metabolic process, regulation of cAMP biosynthetic process, regulation of cyclase activity,negative regulation of cyclase activity, actin cytoskeleton reorganization, regulation of protein stability, regulation of intracellular transport, positive regulation of intracellular transport, maintenance of protein location in cell, regulation of protein localization, regulation of intracellular protein transport, protein localization at cell surface, cellular protein localization, cellular macromolecular complex subunit organization, cellular macromolecular complex assembly,regulation of protein catabolic process, negative regulation of protein catabolic process, regulation of protein import into nucleus, positive regulation of protein import into nucleus, regulation of transcription factor import into nucleus,positive regulation of transcription factor import into nucleus, negative regulation of catalytic activity, receptor metabolic process, receptor clustering, regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade, positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade, negative regulation of DNA binding, negative regulation of transcription factor activity, cellular protein complex assembly, macromolecular complex subunit organization, negative regulation of molecular function, early endosome to late endosome transport, establishment of protein localization, maintenance of protein location, regulation of transcription, regulation of adenylate cyclase activity, regulation of nucleocytoplasmic transport, positive regulation of nucleocytoplasmic transport, intracellular transport, protein stabilization, positive regulation of transport, negative regulation of transport, regulation of transcription factor activity, regulation of binding, negative regulation of binding, regulation of DNA binding, cytoplasmic sequestering of protein, positive regulation of protein transport, regulation of protein transport, negative regulation of protein transport, maintenance of location, negative regulation of protein metabolic process, regulation of lyase activity, negative regulation of lyase activity, maintenance of location in cell, actin crosslink formation, regulation of cellular localization, macromolecular complex assembly, regulation of establishment of protein localization, protein complex biogenesis, cellular macromolecule localization,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Cytoplasm, cell cortex . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton . Perikaryon . Cell projection, growth cone . Colocalizes with CPMR1 in the central region of DRG neuron growth cone (By similarity). Following SEMA3A stimulation of DRG neurons, colocalizes with F-actin (By similarity). .
show all
Tissue Expression:
show all
Signaling Pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA4098C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}