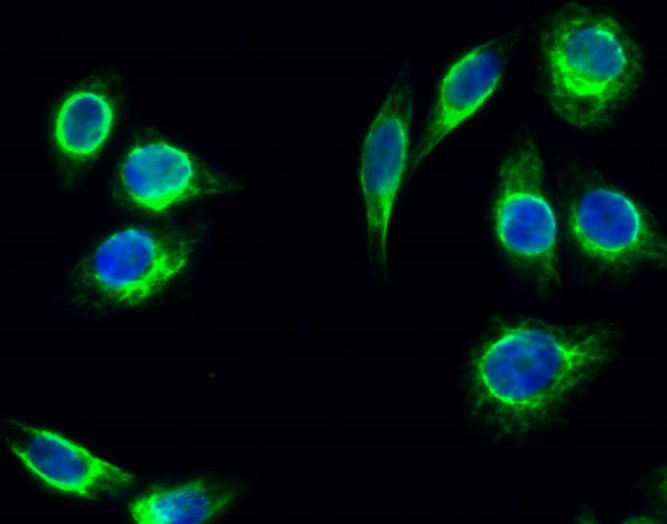
Catalog: KA3876C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Unmodified
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
TSG101
show all
Other Name:
TSG101 ;
Tumor susceptibility gene 101 protein ;
ESCRT-I complex subunit TSG101
Tumor susceptibility gene 101 protein ;
ESCRT-I complex subunit TSG101
show all
Database Link:
Background:
alternative products:Additional isoforms seem to exist. Several shorter isoforms are detected in primary breast cancers and other tumors,domain:The coiled coil domain may interact with stathmin.,domain:The UEV domain binds ubiquitin and P-[ST]-A-P peptide motif independently.,domain:The UEV domain is required for the interaction of the complex with ubiquitin. It also mediates the interaction with PTAP/PSAP motifs of HIV-1 P6 protein and human spumaretrovirus Gag protein.,function:Component of the ESCRT-I complex, a regulator of vesicular trafficking process. Binds to ubiquitinated cargo proteins and is required for the sorting of endocytic ubiquitinated cargos into multivesicular bodies (MVBs). Mediates the association between the ESCRT-0 and ESCRT-I complex. Required for completion of cytokinesis; the function requires CEP55. May be involved in cell growth and differentiation. Acts as a negative growth regulator. Involved in the budding of many viruses through an interaction with viral proteins that contain a late-budding motif P-[ST]-A-P. This interaction is essential for viral particle budding of numerous retroviruses.,PTM:Monoubiquitinated at multiple sites by LRSAM1. Ubiquitination inactivates it, possibly by regulating its shuttling between an active membrane-bound protein and an inactive soluble form.,similarity:Belongs to the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme family. UEV subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 SB (steadiness box) domain.,similarity:Contains 1 UEV (ubiquitin E2 variant) domain.,subcellular location:Mainly cytoplasmic. Membrane-associated when active and soluble when inactive. Depending on the stage of the cell cycle, detected in the nucleus. Colocalized with CEP55 in the midbody during cytokinesis.,subunit:Component of the ESCRT-I complex (endosomal sorting complex required for transport I) which consists of TSG101, VPS28, a VPS37 protein (VPS37A to -D) and a FAM125/MVB12 protein (FAM125A or -B) in a 1:1:1:1 stoechiometry. Interacts with VPS37A, VPS37B and VPS37C. Interacts with ubiquitin, stathmin, GMCL, DMAP1 and AATF (By similarity). Interacts with HGS; the interaction mediates the association with the ESCRT-0 complex. Interacts with GGA1 and GGA3. Interacts (via UEV domain) with PDCD6IP/AIP1. Interacts with VPS28, SNF8 and VPS36. Self-associates. Interacts with FAM125A/MVB12A; the association appears to be mediated by the TSG101-VPS37 binary subcomplex. Interacts with VPS37D. Interacts with LRSAM1. Interacts with CEP55; the interaction is required for cytokinesis but not for viral budding. Interacts with HIV-1 p6. Interacts with human spumavirus Gag. Interacts with HTLV-1 Gag. Interacts with Ebola virus VP40. Interacts with EIAV p9; the interaction has been shown in vitro.,tissue specificity:Heart, brain, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal, kidney and pancreas.,
show all
Function:
regulation of cell growth, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, proteolysis, ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process, protein monoubiquitination, cell cycle, cell cycle arrest, ectoderm development, protein localization,negative regulation of cell proliferation, epidermis development, macromolecule catabolic process, negative regulation of biosynthetic process, epidermal cell differentiation, negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process,negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, negative regulation of gene expression, protein transport,viral reproduction, negative regulation of transcription, protein ubiquitination, viral infectious cycle, viral assembly, maturation, egress, and release, release of virus from host, modification-dependent protein catabolic process, cell cycle process, viral reproductive process, protein catabolic process, keratinocyte differentiation, epithelial cell differentiation, negative regulation of cellular biosynthetic process, protein modification by small protein conjugation,regulation of growth, regulation of cell proliferation, ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the multivesicular body sorting pathway, modification-dependent macromolecule catabolic process, cellular protein catabolic process, cellular macromolecule catabolic process, establishment of protein localization, regulation of transcription, negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, negative regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process, non-lytic viral release, non-lytic virus budding, negative regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process, regulation of RNA metabolic process, negative regulation of RNA metabolic process, cell division, proteolysis involved in cellular protein catabolic process, epithelium development, protein modification by small protein conjugation or removal,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Cytoplasm . Early endosome membrane ; Peripheral membrane protein ; Cytoplasmic side . Late endosome membrane ; Peripheral membrane protein. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome . Midbody, Midbody ring . Nucleus . Mainly cytoplasmic. Membrane-associated when active and soluble when inactive. Nuclear localization is cell cycle-dependent. Interaction with CEP55 is required for localization to the midbody during cytokinesis. .
show all
Tissue Expression:
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA3876C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}