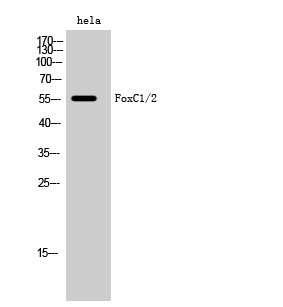
Catalog: KA3698C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Unmodified
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
FOXC1/FOXC2
show all
Background:
disease:Defects in FOXC1 are a cause of Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome (ARS) [MIM:601090]; also known as Axenfeld syndrome or Axenfeld anomaly. It is characterized by posterior corneal embryotoxon, prominent Schwalbe line and iris adhesion to the Schwalbe line. Other features may be hypertelorism (wide spacing of the eyes), hypoplasia of the malar bones, congenital absence of some teeth and mental retardation. When associated with tooth anomalies, the disorder is known as Rieger syndrome. Glaucoma is a progressive blinding condition that occurs in approximately half of patients with Axenfeld-Rieger malformations.,disease:Defects in FOXC1 are a cause of Peters anomaly [MIM:604229]. Peters anomaly consists of a central corneal leukoma, absence of the posterior corneal stroma and Descemet membrane, and a variable degree of iris and lenticular attachments to the central aspect of the posterior cornea.,disease:Defects in FOXC1 are the cause of iridogoniodysgenesis anomaly (IGDA) [MIM:601631]. IGDA is an autosomal dominant phenotype characterized by iris hypoplasia, goniodysgenesis, and juvenile glaucoma.,function:Binding of FREAC-3 and FREAC-4 to their cognate sites results in bending of the DNA at an angle of 80-90 degrees.,similarity:Contains 1 fork-head DNA-binding domain.,subunit:Monomer.,tissue specificity:Expressed in all tissues and cell lines examined.,
show all
Function:
skeletal system development, ossification, ovarian follicle development, blood vessel development, eye development,urogenital system development, metanephros development, ureteric bud development, in utero embryonic development, formation of primary germ layer, mesoderm formation, kidney development, vasculature development,lymph vessel development, blood vessel remodeling, reproductive developmental process, heart morphogenesis,circulatory system process, vascular process in circulatory system, polysaccharide metabolic process, aminoglycan metabolic process, transcription, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, anti-apoptosis, cell motion, cell surface receptor linked signal transduction, enzyme linked receptor protein signaling pathway, transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway, Notch signaling pathway, gamete generation, regulation of mitotic cell cycle, gastrulation, sensory organ development,mesoderm development, heart development, muscle organ development, sex differentiation, blood circulation, cell proliferation, germ cell migration, gonad development, female gonad development, embryonic development ending in birth or egg hatching, positive regulation of biosynthetic process, positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, positive regulation of gene expression, regulation of cell death, mesenchymal cell development, neural crest cell development, neural crest cell differentiation, striated muscle tissue development, striated muscle cell proliferation, cell migration, sexual reproduction, ovulation cycle process, extracellular matrix organization, collagen fibril organization, glycosaminoglycan metabolic process, positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process, multicellular organism reproduction, lacrimal gland development, muscle cell proliferation, embryonic heart tube development, regulation of tube size, organ growth, exocrine system development, tube development, growth, regulation of growth, odontogenesis of dentine-containing tooth,odontogenesis, ovulation cycle, regulation of apoptosis, chordate embryonic development, camera-type eye development, extracellular structure organization, negative regulation of apoptosis, regulation of programmed cell death, negative regulation of programmed cell death, development of primary sexual characteristics, regulation of transcription, negative regulation of cell cycle, positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, negative regulation of mitotic cell cycle, positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process,positive regulation of transcription, positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, development of primary female sexual characteristics, regulation of organ growth, female sex differentiation, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway, mesoderm morphogenesis, paraxial mesoderm development, paraxial mesoderm morphogenesis, paraxial mesoderm formation, rhythmic process, blood vessel morphogenesis, embryonic morphogenesis, reproductive structure development, reproductive process in a multicellular organism, reproductive cellular process, tissue morphogenesis, gland development, cardiac muscle tissue development, mesenchymal cell differentiation, tissue remodeling, artery morphogenesis, cell motility, regulation of blood vessel size, positive regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process, regulation of RNA metabolic process, positive regulation of RNA metabolic process, localization of cell, regulation of cell cycle, cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis, ventricular cardiac muscle morphogenesis, cardiac muscle tissue growth, cardiac muscle cell proliferation, bone development, muscle tissue morphogenesis, heart growth, mesenchyme development, muscle tissue development, negative regulation of cell death,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Nucleus . Colocalizes with PITX2 isoform 3 in the nucleus at subnuclear chromatine regions (PubMed:16449236). Colocalizes with CBX5 to a heterochromatin-rich region of the nucleus (PubMed:15684392). Colocalizes with GLI2 in the nucleus (By similarity). .
show all
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA3698C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}