Catalog: KA3420C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Unmodified
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
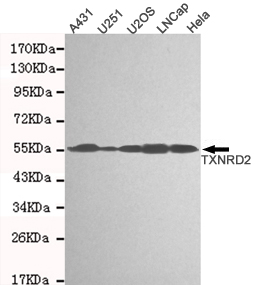
TXNRD2
show all
Other Name:
TXNRD2 ;
KIAA1652 ;
TRXR2 ;
Thioredoxin reductase 2 ;
mitochondrial ;
Selenoprotein Z ;
SelZ ;
TR-beta ;
Thioredoxin reductase TR3
KIAA1652 ;
TRXR2 ;
Thioredoxin reductase 2 ;
mitochondrial ;
Selenoprotein Z ;
SelZ ;
TR-beta ;
Thioredoxin reductase TR3
show all
Database Link:
Background:
catalytic activity:Thioredoxin + NADP(+) = thioredoxin disulfide + NADPH.,cofactor:FAD.,function:Maintains thioredoxin in a reduced state. Implicated in the defenses against oxidative stress. May play a role in redox-regulated cell signaling.,miscellaneous:The active site is a redox-active disulfide bond. The selenocysteine residue is essential for enzymatic activity.,sequence caution:Translated as Sec.,similarity:Belongs to the class-I pyridine nucleotide-disulfide oxidoreductase family.,subunit:Homodimer.,tissue specificity:Highly expressed in the prostate, ovary, liver, testis, uterus, colon and small intestine. Intermediate levels in brain, skeletal muscle, heart and spleen. Low levels in placenta, pancreas, thymus and peripheral blood leukocytes. According to PubMed:10608886, high levels in kidney, whereas according to PubMed:9923614 levels are low.,
show all
Function:
response to reactive oxygen species, response to oxygen radical, response to oxidative stress, response to inorganic substance, response to metal ion, response to selenium ion, cellular homeostasis, homeostatic process, cell redox homeostasis, oxidation reduction,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Mitochondrion .
show all
Signaling Pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA3420C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}








.jpg)