Catalog: KA3354C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Reactivity
Human, Mouse
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Unmodified
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
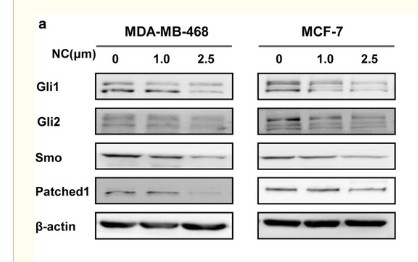
PTCH1
show all
Protein Name:
Protein patched homolog 1
show all
Other Name:
PTCH1 ;
PTCH ;
Protein patched homolog 1 ;
PTC ;
PTC1
PTCH ;
Protein patched homolog 1 ;
PTC ;
PTC1
show all
Background:
developmental stage:In the embryo, found in all major target tissues of sonic hedgehog, such as the ventral neural tube, somites, and tissues surrounding the zone of polarizing activity of the limb bud.,disease:Defects in PTCH1 are a cause of sporadic basal cell carcinoma (BCC) [MIM:605462].,disease:Defects in PTCH1 are probably the cause of basal cell nevus syndrome (BCNS) [MIM:109400]; also known as Gorlin syndrome or Gorlin-Goltz syndrome. BCNS is an autosomal dominant disease characterized by nevoid basal cell carcinomas (NBCCS) and developmental abnormalities such as rib and craniofacial alterations, polydactyly, syndactyly, and spina bifida. In addition, the patients suffer from a multitude of tumors like basal cell carcinomas (BCC), fibromas of the ovaries and heart, cysts of the skin, jaws and mesentery, as well as medulloblastomas and meningiomas. PTCH1 is also mutated in squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Could also be associated with large body size observed in BCNS patients.,disease:Defects in PTCH1 are the cause of holoprosencephaly type 7 (HPE7) [MIM:610828]. Holoprosencephaly (HPE) [MIM:236100] is the most common structural anomaly of the brain, in which the developing forebrain fails to correctly separate into right and left hemispheres. Holoprosencephaly is genetically heterogeneous and associated with several distinct facies and phenotypic variability.,function:Acts as a receptor for sonic hedgehog (SHH), indian hedgehog (IHH) and desert hedgehog (DHH). Associates with the smoothened protein (SMO) to transduce the hedgehog's proteins signal. Seems to have a tumor suppressor function, as inactivation of this protein is probably a necessary, if not sufficient step for tumorigenesis.,PTM:Glycosylation is necessary for SHH binding.,similarity:Belongs to the patched family.,similarity:Contains 1 SSD (sterol-sensing) domain.,subunit:Interacts with SNX17.,tissue specificity:In the adult, expressed in brain, lung, liver, heart, placenta, skeletal muscle, pancreas and kidney. Expressed in tumor cells but not in normal skin.,
show all
Function:
embryonic epithelial tube formation, neural tube formation, neural tube closure, morphogenesis of an epithelium,regionalization, heart morphogenesis, cell surface receptor linked signal transduction, smoothened signaling pathway,pattern specification process, ectoderm development, heart development, response to nutrient, cell proliferation,negative regulation of cell proliferation, epidermis development, regulation of smoothened signaling pathway,response to mechanical stimulus, response to abiotic stimulus, response to endogenous stimulus, response to hormone stimulus, embryonic development ending in birth or egg hatching, dorsal/ventral pattern formation, response to extracellular stimulus, response to organic substance, primary neural tube formation, response to organic cyclic substance, morphogenesis of embryonic epithelium, protein processing, neural tube patterning, dorsal/ventral neural tube patterning, neural tube development, embryonic limb morphogenesis, mammary gland development, response to nutrient levels, response to estradiol stimulus, response to retinoic acid, response to vitamin A, response to vitamin,carbohydrate homeostasis, appendage morphogenesis, limb morphogenesis, embryonic appendage morphogenesis,hindlimb morphogenesis, tube lumen formation, tube morphogenesis, tube development, regulation of growth,regulation of multicellular organism growth, negative regulation of multicellular organism growth, regulation of cell proliferation, response to drug, homeostatic process, glucose homeostasis, chordate embryonic development,keratinocyte proliferation, response to estrogen stimulus, negative regulation of growth, response to steroid hormone stimulus, embryonic morphogenesis, tissue morphogenesis, gland development, appendage development, chemical homeostasis, regulation of epithelial cell proliferation, negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation, negative regulation of multicellular organismal process, protein maturation, limb development, epithelium development,epithelial tube morphogenesis, tube closure,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein .
show all
Signaling Pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA3354C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}