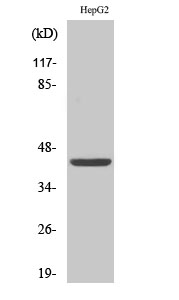
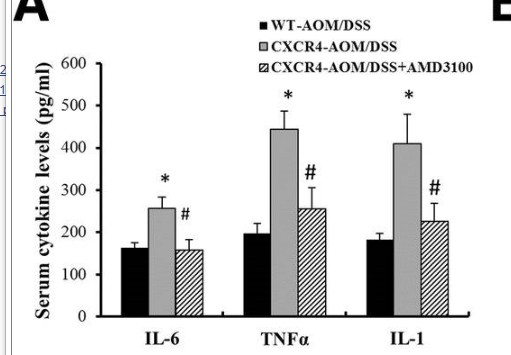
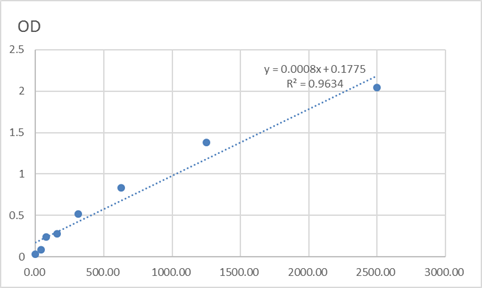
Catalog: KA3257C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Unmodified
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
FGFR1OP
show all
Other Name:
FGFR1OP ;
FOP ;
FGFR1 oncogene partner
FOP ;
FGFR1 oncogene partner
show all
Database Link:
Background:
disease:A chromosomal aberration involving FGFR1OP may be a cause of stem cell myeloproliferative disorder (MPD). Translocation t(6;8)(q27;p11) with FGFR1. MPD is characterized by myeloid hyperplasia, eosinophilia and T-cell or B-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma. In general it progresses to acute myeloid leukemia. The fusion proteins FGFR1OP-FGFR1 or FGFR1-FGFR1OP may exhibit constitutive kinase activity and be responsible for the transforming activity.,function:Required for anchoring microtubules to the centrosomes.,similarity:Contains 1 LisH domain.,subcellular location:Associated with gamma-tubulin.,subunit:Homodimer. Part of a ternary complex that contains CEP350, FGFR1OP and MAPRE1. Interacts directly with CEP350 and MAPRE1.,tissue specificity:Ubiquitous. Highly expressed in heart, liver, muscle, kidney, intestine, colon, adrenal gland, prostate, testis, and pancreas.,
show all
Function:
microtubule cytoskeleton organization, cytoskeleton organization, microtubule-based process, protein localization,positive regulation of cell proliferation, maintenance of protein location in cell, microtubule anchoring, regulation of cell proliferation, maintenance of protein location, maintenance of location, maintenance of location in cell,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome, centriole . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, cilium basal body . Associated with gamma-tubulin (PubMed:16314388). Localizes on both mother and daughter centrioles (PubMed:28625565, PubMed:28428259). Localizes to an axial position on the mother centriole (PubMed:28625565). Localizes to the distal end of the centriole partly on the subdistal appendage region (PubMed:28659385). .
show all
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA3257C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}