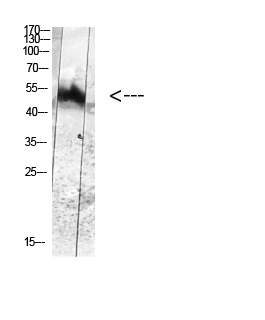
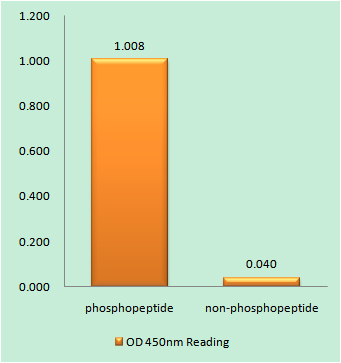
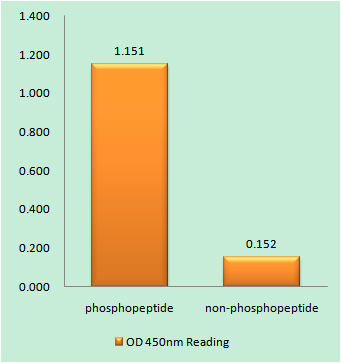
Catalog: KA3143C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Reactivity
Human
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Unmodified
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
MDM2
show all
Other Name:
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Mdm2 ;
Double minute 2 protein ;
Hdm2 ;
Oncoprotein Mdm2 ;
p53-binding protein Mdm2 ;
Double minute 2 protein ;
Hdm2 ;
Oncoprotein Mdm2 ;
p53-binding protein Mdm2 ;
show all
Background:
disease:Seems to be amplified in certain tumors (including soft tissue sarcomas, osteosarcomas and gliomas). A higher frequency of splice variants lacking p53 binding domain sequences was found in late-stage and high-grade ovarian and bladder carcinomas. Four of the splice variants show loss of p53 binding.,domain:Region I is sufficient for binding p53 and inhibiting its G1 arrest and apoptosis functions. It also binds p73 and E2F1. Region II contains most of a central acidic region required for interaction with ribosomal protein L5 and a putative C4-type zinc finger. The RING finger domain which coordinates two molecules of zinc interacts specifically with RNA whether or not zinc is present and mediates the heterooligomerization with MDM4. It is also essential for its ubiquitin ligase E3 activity toward p53 and itself.,function:Inhibits TP53/p53- and TP73/p73-mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by binding its transcriptional activation domain. Functions as a ubiquitin ligase E3, in the presence of E1 and E2, toward p53 and itself. Permits the nuclear export of p53 and targets it for proteasome-mediated proteolysis.,induction:By DNA damage.,miscellaneous:MDM2 RING finger mutations that failed to ubiquitinate p53 in vitro did not target p53 for degradation when expressed in cells.,online information:Mdm2 entry,PTM:Auto-ubiquitinated; which leads to proteasomal degradation.,PTM:Phosphorylated in response to ionizing radiation in an ATM-dependent manner.,similarity:Belongs to the MDM2/MDM4 family.,similarity:Contains 1 RanBP2-type zinc finger.,similarity:Contains 1 RING-type zinc finger.,similarity:Contains 1 SWIB domain.,subcellular location:Expressed predominantly in the nucleoplasm. Interaction with ARF(P14) results in the localization of both proteins to the nucleolus. The nucleolar localization signals in both ARF(P14) and MDM2 may be necessary to allow efficient nucleolar localization of both proteins.,subunit:Binds p53, p73, ARF(P14), ribosomal protein L5 and specifically to RNA. Can interact also with retinoblastoma protein (RB), E1A-associated protein EP300 and the E2F1 transcription factor. Forms a ternary complex with TP53/p53 and WWOX. Interacts with CDKN2AIP, MTBP, TBRG1, USP7, PYHIN1 and UBXN6. Isoform Mdm2-F does not interact with TP53/p53. Interacts with and ubiquitinates HIV-1 Tat.,tissue specificity:Ubiquitous. Isoform Mdm2-A, isoform Mdm2-B, isoform Mdm2-C, isoform Mdm2-D, isoform Mdm2-E, isoform Mdm2-F and isoform Mdm2-G are observed in a range of cancers but absent in normal tissues.,
show all
Function:
G1 phase of mitotic cell cycle, negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, mitotic cell cycle,regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, protein complex assembly, proteolysis, ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process, cell cycle, traversing start control point of mitotic cell cycle, regulation of mitotic cell cycle, positive regulation of cell proliferation, macromolecule catabolic process, negative regulation of biosynthetic process, regulation of catabolic process, positive regulation of catabolic process, negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, negative regulation of gene expression, negative regulation of transcription, protein ubiquitination, modification-dependent protein catabolic process, cell cycle process,cell cycle phase, regulation of proteolysis, protein catabolic process, negative regulation of cellular biosynthetic process, regulation of cellular catabolic process, positive regulation of cellular catabolic process, regulation of cellular protein metabolic process, positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process, regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process, positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process, protein modification by small protein conjugation, regulation of cell proliferation, regulation of protein catabolic process, protein ubiquitination during ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process, modification-dependent macromolecule catabolic process, macromolecular complex subunit organization, cellular protein catabolic process, cellular macromolecule catabolic process, regulation of transcription, positive regulation of protein catabolic process, positive regulation of cell cycle, positive regulation of proteolysis, negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, negative regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process, negative regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process, positive regulation of protein metabolic process, regulation of RNA metabolic process, negative regulation of RNA metabolic process, G1 phase, interphase, interphase of mitotic cell cycle, proteolysis involved in cellular protein catabolic process, regulation of cell cycle, macromolecular complex assembly, protein complex biogenesis, protein modification by small protein conjugation or removal,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Nucleus, nucleoplasm. Cytoplasm . Nucleus, nucleolus. Nucleus . Expressed predominantly in the nucleoplasm. Interaction with ARF(P14) results in the localization of both proteins to the nucleolus. The nucleolar localization signals in both ARF(P14) and MDM2 may be necessary to allow efficient nucleolar localization of both proteins. Colocalizes with RASSF1 isoform A in the nucleus.
show all
Signaling Pathway
Cellular Processes >> Cell growth and death >> Cell cycle
Cellular Processes >> Cell growth and death >> p53 signaling pathway
Cellular Processes >> Cell growth and death >> Cellular senescence
Organismal Systems >> Endocrine system >> Thyroid hormone signaling pathway
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> Pathways in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> Transcriptional misregulation in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> MicroRNAs in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Glioma
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Chronic myeloid leukemia
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Melanoma
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Bladder cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Prostate cancer
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> FoxO signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> PI3K-Akt signaling pathway
Genetic Information Processing >> Folding, sorting and degradation >> Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA3143C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}