Catalog: KA3119C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Unmodified
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
HDAC5
show all
Other Name:
Histone deacetylase 5 ;
HD5 ;
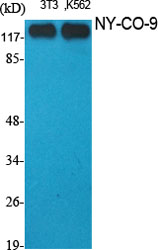
Antigen NY-CO-9 ;
HD5 ;
Antigen NY-CO-9 ;
show all
Background:
catalytic activity:Hydrolysis of an N(6)-acetyl-lysine residue of a histone to yield a deacetylated histone.,domain:The nuclear export sequence mediates the shuttling between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.,function:Responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). Histone deacetylation gives a tag for epigenetic repression and plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events. Histone deacetylases act via the formation of large multiprotein complexes. Involved in muscle maturation by repressing transcription of myocyte enhancer MEF2C. During muscle differentiation, it shuttles into the cytoplasm, allowing the expression of myocyte enhancer factors.,PTM:Phosphorylated by CaMK at Ser-259 and Ser-498. The phosphorylation is required for the export to the cytoplasm.,PTM:Ubiquitinated. Polyubiquitination however does not lead to its degradation.,similarity:Belongs to the histone deacetylase family. Type 2 subfamily.,subcellular location:Shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. In muscle cells, it shuttles into the cytoplasm during myocyte differentiation. The export to cytoplasm depends on the interaction with a 14-3-3 chaperone protein and is due to its phosphorylation at Ser-259 and Ser-498 by CaMK.,subunit:Interacts with AHRR (By similarity). Interacts with BCOR, HDAC7, HDAC9, CTBP1, MEF2C, NCOR2, NRIP1, PHB2 and a 14-3-3 chaperone protein. Interacts with KDM5B.,tissue specificity:Ubiquitous.,
show all
Function:
negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, cell activation, immune system development,leukocyte differentiation, muscle system process, chromatin organization, chromatin remodeling, chromatin silencing,transcription, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter,protein amino acid deacetylation, defense response, inflammatory response, heart development, response to wounding, response to endogenous stimulus, response to hormone stimulus, negative regulation of biosynthetic process, positive regulation of biosynthetic process, response to organic substance, regulation of specific transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, positive regulation of specific transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter,negative regulation of specific transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, regulation of endothelial cell migration, negative regulation of endothelial cell migration, positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process,negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, positive regulation of gene expression, negative regulation of gene expression, regulation of myotube differentiation, negative regulation of myotube differentiation, cardiac muscle adaptation, striated muscle adaptation, muscle hypertrophy, striated muscle hypertrophy, cardiac muscle hypertrophy, regulation of striated muscle tissue development, gene silencing, negative regulation of transcription,negative regulation of angiogenesis, chromatin modification, covalent chromatin modification, histone modification,histone deacetylation, hemopoiesis, lymphocyte differentiation, B cell differentiation, regulation of cell migration,negative regulation of cell migration, negative regulation of cellular biosynthetic process, positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process, negative regulation of gene-specific transcription, regulation of gene-specific transcription,response to insulin stimulus, cellular response to insulin stimulus, cellular response to hormone stimulus, regulation of locomotion, negative regulation of locomotion, regulation of gene expression, epigenetic, B cell activation, positive regulation of gene-specific transcription, positive regulation of DNA binding, regulation of protein binding, response to peptide hormone stimulus, muscle adaptation, regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration, negative regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration, positive regulation of molecular function, leukocyte activation,regulation of transcription, negative regulation of cell differentiation, regulation of angiogenesis, negative regulation of gene expression, epigenetic, negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, negative regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process, positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process, positive regulation of transcription, positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, lymphocyte activation, hemopoietic or lymphoid organ development, regulation of muscle development, regulation of skeletal muscle tissue development, regulation of skeletal muscle fiber development, regulation of transcription factor activity,positive regulation of transcription factor activity, regulation of binding, positive regulation of binding, regulation of DNA binding, regulation of muscle cell differentiation, negative regulation of muscle cell differentiation, regulation of striated muscle cell differentiation, negative regulation of striated muscle cell differentiation, negative regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process, positive regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process, regulation of RNA metabolic process, negative regulation of RNA metabolic process, positive regulation of RNA metabolic process,regulation of cell motion, negative regulation of cell motion, chromosome organization, regulation of cell development,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. In muscle cells, it shuttles into the cytoplasm during myocyte differentiation. The export to cytoplasm depends on the interaction with a 14-3-3 chaperone protein and is due to its phosphorylation at Ser-259 and Ser-498 by AMPK, CaMK1 and SIK1.
show all
Tissue Expression:
show all
Signaling Pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA3119C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}