
Catalog: KA3085C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Unmodified
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
GJA1 GJAL
show all
Other Name:
GJA1 ;
GJAL ;
Gap junction alpha-1 protein ;
Connexin-43 ;
Cx43 ;
Gap junction 43 kDa heart protein
GJAL ;
Gap junction alpha-1 protein ;
Connexin-43 ;
Cx43 ;
Gap junction 43 kDa heart protein
show all
Database Link:
Background:
caution:PubMed:11741837 reported 2 mutations (Phe-11 and Ala-24) linked to non-syndromic autosomal recessive deafness (DFNBG). These mutations have subsequently been shown (PubMed:12457340) to involve the pseudogene of connexin-43 located on chromosome 5.,caution:PubMed:7715640 reported a mutation Pro-364 linked to congenital heart diseases. This was later shown (PubMed:8873667) to be an artifact.,disease:Defects in GJA1 are a cause of hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) [MIM:241550]. HLHS refers to the abnormal development of the left-sided cardiac structures, resulting in obstruction to blood flow from the left ventricular outflow tract. In addition, the syndrome includes underdevelopment of the left ventricle, aorta, and aortic arch, as well as mitral atresia or stenosis.,disease:Defects in GJA1 are the cause of autosomal dominant oculodentodigital dysplasia (ODDD) [MIM:164200]; also known as oculodentoosseous dysplasia. ODDD is a highly penetrant syndrome presenting with craniofacial (ocular, nasal, dental) and limb dysmorphisms, spastic paraplegia, and neurodegeneration. Craniofacial anomalies tipically include a thin nose with hypoplastic alae nasi, small anteverted nares, prominent columnella, and microcephaly. Brittle nails and hair abnormalities of hypotrichosis and slow growth are present. Ocular defects include microphthalmia, microcornea, cataracts, glaucoma, and optic atrophy. Syndactyly type III and conductive deafness can occur in some cases. Cardiac abnormalities are observed in rare instances.,disease:Defects in GJA1 may be the cause of syndactyly type III (SDTY3) [MIM:186100]. Syndactyly is an autosomal dominant trait and is the most common congenital anomaly of the hand or foot. It is marked by persistence of the webbing between adjacent digits, so they are more or less completely attached. In this type there is usually complete and bilateral syndactyly between the fourth and fifth fingers. Usually it is soft tissue syndactyly but occasionally the distal phalanges are fused. The fifth finger is short with absent or rudimentary middle phalanx. The feet are not affected.,function:One gap junction consists of a cluster of closely packed pairs of transmembrane channels, the connexons, through which materials of low MW diffuse from one cell to a neighboring cell.,function:One gap junction consists of a cluster of closely packed pairs of transmembrane channels, the connexons, through which materials of low MW diffuse from one cell to a neighboring cell. May play a critical role in the physiology of hearing by participating in the recycling of potassium to the cochlear endolymph.,similarity:Belongs to the connexin family.,similarity:Belongs to the connexin family. Alpha-type (group II) subfamily.,subunit:A connexon is composed of a hexamer of connexins.,subunit:A connexon is composed of a hexamer of connexins. Interacts with SGSM3. Interacts with KIAA1432/CIP150.,tissue specificity:Expressed in the heart and fetal cochlea.,
show all
Function:
cell morphogenesis, muscle system process, protein complex assembly, nucleotide transport, apoptosis, muscle contraction, cell-cell junction assembly, cell-cell signaling, heart development, cell death, negative regulation of cell proliferation, response to pH, response to abiotic stimulus, regulation of catabolic process, positive regulation of catabolic process, positive regulation of signal transduction, vascular transport, positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, regulation of protein kinase cascade, positive regulation of cell communication, positive regulation of protein kinase cascade, regulation of metal ion transport, programmed cell death, purine nucleotide transport, ATP transport, purine ribonucleotide transport, nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid transport, gap junction assembly, death, cell projection organization, neuron differentiation, neuron projection development, cellular component morphogenesis, cell part morphogenesis, cell junction assembly, cell junction organization, regulation of cell proliferation, regulation of protein catabolic process, regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade, positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade, regulation of ion transport, macromolecular complex subunit organization, cell-cell junction organization, positive regulation of protein catabolic process, neuron development,neuron projection morphogenesis, cell projection morphogenesis, positive regulation of protein metabolic process,protein oligomerization, adenine nucleotide transport, regulation of calcium ion transport, macromolecular complex assembly, protein complex biogenesis,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Cell junction, gap junction . Endoplasmic reticulum . Localizes at the intercalated disk (ICD) in cardiomyocytes and the proper localization at ICD is dependent on TMEM65. .
show all
Tissue Expression:
Signaling Pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA3085C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$330.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}









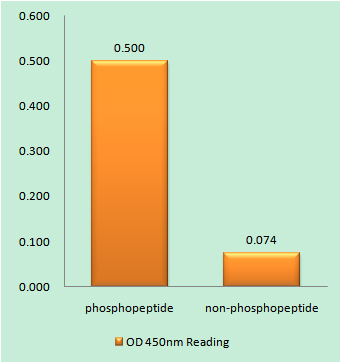
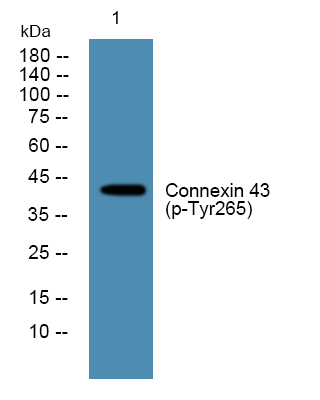
.jpg)







