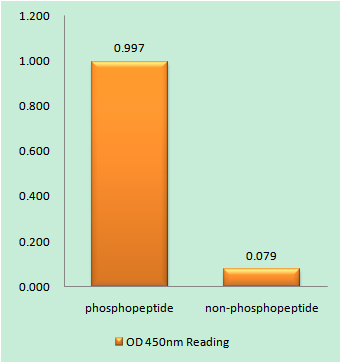
Catalog: KA1780C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$470.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
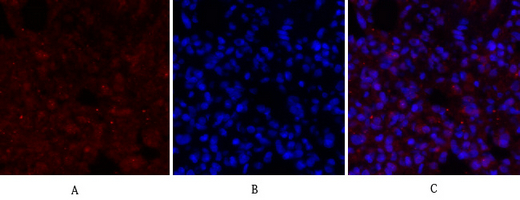
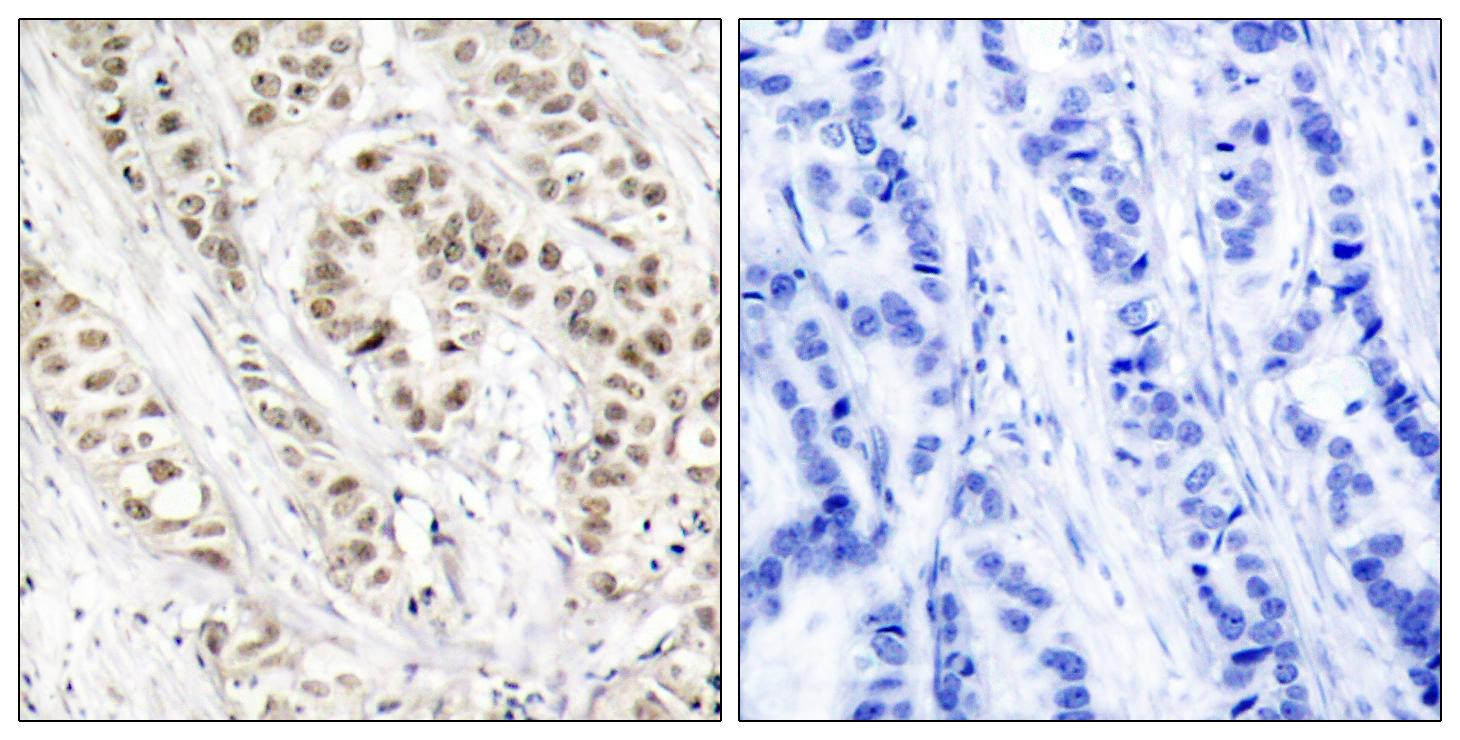
Reactivity
Human
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
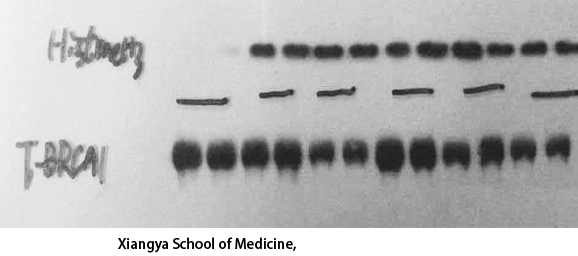
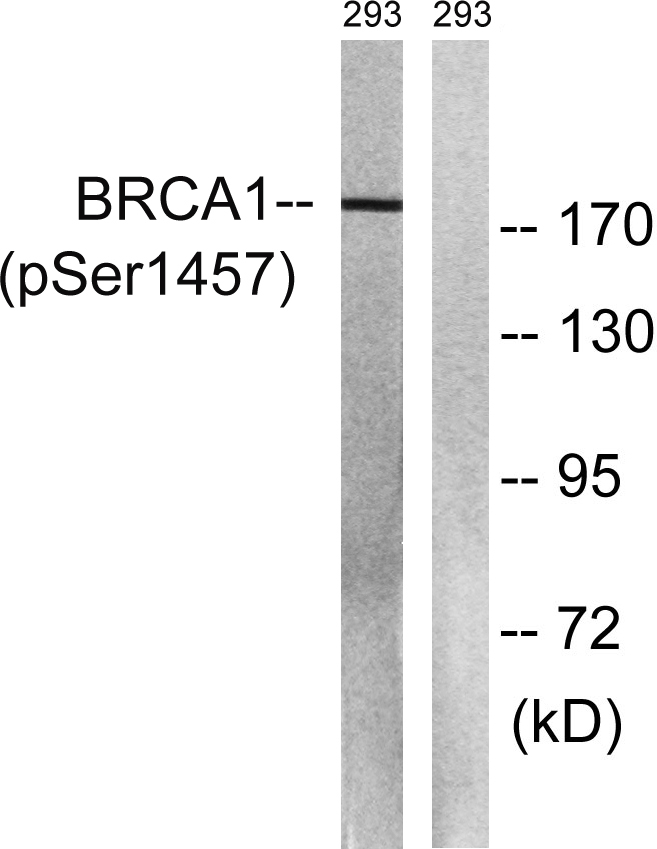
Phospho
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Phospho
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
BRCA1 RNF53
show all
Other Name:
BRCA1 ;
RNF53 ;
Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein ;
RING finger protein 53
RNF53 ;
Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein ;
RING finger protein 53
show all
Database Link:
Background:
disease:Defects in BRCA1 are a cause of genetic susceptibility to breast cancer (BC) [MIM:113705, 114480]. BC is an extremely common malignancy, affecting one in eight women during their lifetime. A positive family history has been identified as major contributor to risk of development of the disease, and this link is striking for early-onset breast cancer. Mutations in BRCA1 are thought to be responsible for 45% of inherited breast cancer. Moreover, BRCA1 carriers have a 4-fold increased risk of colon cancer, whereas male carriers face a 3-fold increased risk of prostate cancer. Cells lacking BRCA1 show defects in DNA repair by homologous recombination.,disease:Defects in BRCA1 are a cause of genetic susceptibility to ovarian cancer [MIM:113705].,disease:Defects in BRCA1 are a cause of susceptibility to familial breast-ovarian cancer type 1 (BROVCA1) [MIM:604370]. Mutations in BRCA1 are thought to be responsible for more than 80% of inherited breast-ovarian cancer.,domain:The BRCT domains recognize and bind phosphorylated pSXXF motif on proteins. The interaction with the phosphorylated pSXXF motif of FAM175A/Abraxas, recruits BRCA1 at DNA damage sites.,domain:The RING-type zinc finger domain interacts with BAP1.,function:The BRCA1-BARD1 heterodimer coordinates a diverse range of cellular pathways such as DNA damage repair, ubiquitination and transcriptional regulation to maintain genomic stability. Acts by mediating ubiquitin E3 ligase activity that is required for its tumor suppressor function. Plays a central role in DNA repair by facilitating cellular response to DNA repair. Required for appropriate cell cycle arrests after ionizing irradiation in both the S-phase and the G2 phase of the cell cycle. Involved in transcriptional regulation of P21 in response to DNA damage. Required for FANCD2 targeting to sites of DNA damage. May function as a transcriptional regulator. Inhibits lipid synthesis by binding to inactive phosphorylated ACACA and preventing its dephosphorylation.,online information:BRCA1 entry,online information:The Singapore human mutation and polymorphism database,pathway:Protein modification; protein ubiquitination.,polymorphism:There is evidence that the presence of the rare form of Gln-356-Arg and Leu-871-Pro polymorphisms may be associated with an increased risk for developing ovarian cancer.,PTM:Phosphorylated in response to IR, UV, and various stimuli that cause checkpoint activation, probably by ATM or ATR.,similarity:Contains 1 RING-type zinc finger.,similarity:Contains 2 BRCT domains.,subcellular location:Localizes at sites of DNA damage at double-strand breaks (DSBs); recruitment to DNA damage sites is mediated by the BRCA1-A complex.,subunit:Part of the BRCA1-associated genome surveillance complex (BASC), which contains BRCA1, MSH2, MSH6, MLH1, ATM, BLM, PMS2 and the RAD50-MRE11-NBN protein complex. This association could be a dynamic process changing throughout the cell cycle and within subnuclear domains. Component of the BRCA1-A complex, at least composed of the BRCA1, BARD1, UIMC1/RAP80, FAM175A/Abraxas, BRCC3/BRCC36, BRE/BRCC45 and MERIT40/NBA1. Interacts (via BRCT domains) with FAM175A/Abraxas and RBBP8. Associates with RNA polymerase II holoenzyme. Interacts with SMC1A and COBRA1/NELFB. Interacts (via BRCT domains) with BRIP1. Interacts with FANCD2 (ubiquitinated). Interacts with BAP1. Interacts with DCLRE1C/Artemis and CLSPN. Interacts with H2AFX (phosphorylated on 'Ser-140'). Interacts with CHEK1/CHK1. Interacts with BRCC3. Interacts (via BRCT domains) with ACACA (phosphorylated); the interaction prevents dephosphorylation of ACACA.,tissue specificity:Isoform 1 and isoform 3 are widely expressed. Isoform 3 is reduced or absent in several breast and ovarian cancer cell lines.,
show all
Function:
cell cycle checkpoint, DNA damage checkpoint, microtubule cytoskeleton organization, double-strand break repair via homologous recombination, recombinational repair, DNA metabolic process, DNA replication, DNA repair, regulation of DNA repair, postreplication repair, double-strand break repair, DNA recombination, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase III promoter, proteolysis, fatty acid metabolic process, fatty acid biosynthetic process, apoptosis, induction of apoptosis, response to DNA damage stimulus, DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in transcription of p21 class mediator, cytoskeleton organization, microtubule-based process, cell cycle,chromosome segregation, centrosome cycle, intracellular signaling cascade, dosage compensation, cell death, lipid biosynthetic process, induction of apoptosis by intracellular signals, DNA damage response, signal transduction resulting in induction of apoptosis, dosage compensation, by inactivation of X chromosome, macromolecule catabolic process, response to radiation, response to abiotic stimulus, response to endogenous stimulus, response to hormone stimulus, embryonic development ending in birth or egg hatching, negative regulation of biosynthetic process, positive regulation of biosynthetic process, response to organic substance, response to ionizing radiation, positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, regulation of cell cycle process, regulation of cellular ketone metabolic process, positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process,negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, positive regulation of gene expression, negative regulation of gene expression, negative regulation of organelle organization, regulation of centrosome duplication, regulation of cell death, positive regulation of cell death, negative regulation of cell cycle process, programmed cell death, induction of programmed cell death, organic acid biosynthetic process, death, negative regulation of transcription, protein ubiquitination, regulation of lipid metabolic process, regulation of fatty acid metabolic process, modification-dependent protein catabolic process, cell cycle process, protein catabolic process, DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator, steroid hormone receptor signaling pathway, androgen receptor signaling pathway, intracellular receptor-mediated signaling pathway, microtubule organizing center organization, negative regulation of cellular biosynthetic process, positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process, regulation of protein ubiquitination, positive regulation of protein ubiquitination, regulation of protein modification process, positive regulation of protein modification process, DNA integrity checkpoint, G2/M transition DNA damage checkpoint, G2/M transition checkpoint,regulation of cellular protein metabolic process, positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process, protein modification by small protein conjugation, regulation of microtubule-based process, regulation of organelle organization, cellular response to stress, regulation of gene expression, epigenetic, regulation of cell proliferation,regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic process, DNA damage response, signal transduction, DNA damage response, signal transduction resulting in transcription, regulation of apoptosis, chordate embryonic development, positive regulation of apoptosis, regulation of programmed cell death, positive regulation of programmed cell death, response to estrogen stimulus, modification-dependent macromolecule catabolic process, cellular protein catabolic process,cellular macromolecule catabolic process, regulation of transcription, negative regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic process, positive regulation of DNA repair, negative regulation of lipid metabolic process, positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, negative regulation of fatty acid metabolic process, negative regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process, positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process, positive regulation of transcription, carboxylic acid biosynthetic process, regulation of centriole replication, negative regulation of centriole replication, regulation of centrosome cycle, negative regulation of centrosome cycle, regulation of lipid biosynthetic process, response to steroid hormone stimulus, positive regulation of response to stimulus, regulation of DNA metabolic process, positive regulation of DNA metabolic process, negative regulation of lipid biosynthetic process, negative regulation of cellular component organization, negative regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process, positive regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process, positive regulation of protein metabolic process, regulation of RNA metabolic process, positive regulation of RNA metabolic process,centrosome organization, regulation of cytoskeleton organization, negative regulation of cytoskeleton organization,proteolysis involved in cellular protein catabolic process, regulation of cell cycle, regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization, protein modification by small protein conjugation or removal, regulation of cellular response to stress,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Nucleus . Chromosome . Cytoplasm . Localizes at sites of DNA damage at double-strand breaks (DSBs); recruitment to DNA damage sites is mediated by ABRAXAS1 and the BRCA1-A complex (PubMed:26778126). Translocated to the cytoplasm during UV-induced apoptosis (PubMed:20160719). .; [Isoform 3]: Cytoplasm.; [Isoform 5]: Cytoplasm .
show all
Signaling Pathway
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> MicroRNAs in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Breast cancer
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> PI3K-Akt signaling pathway
Genetic Information Processing >> Folding, sorting and degradation >> Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA1780C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$470.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}