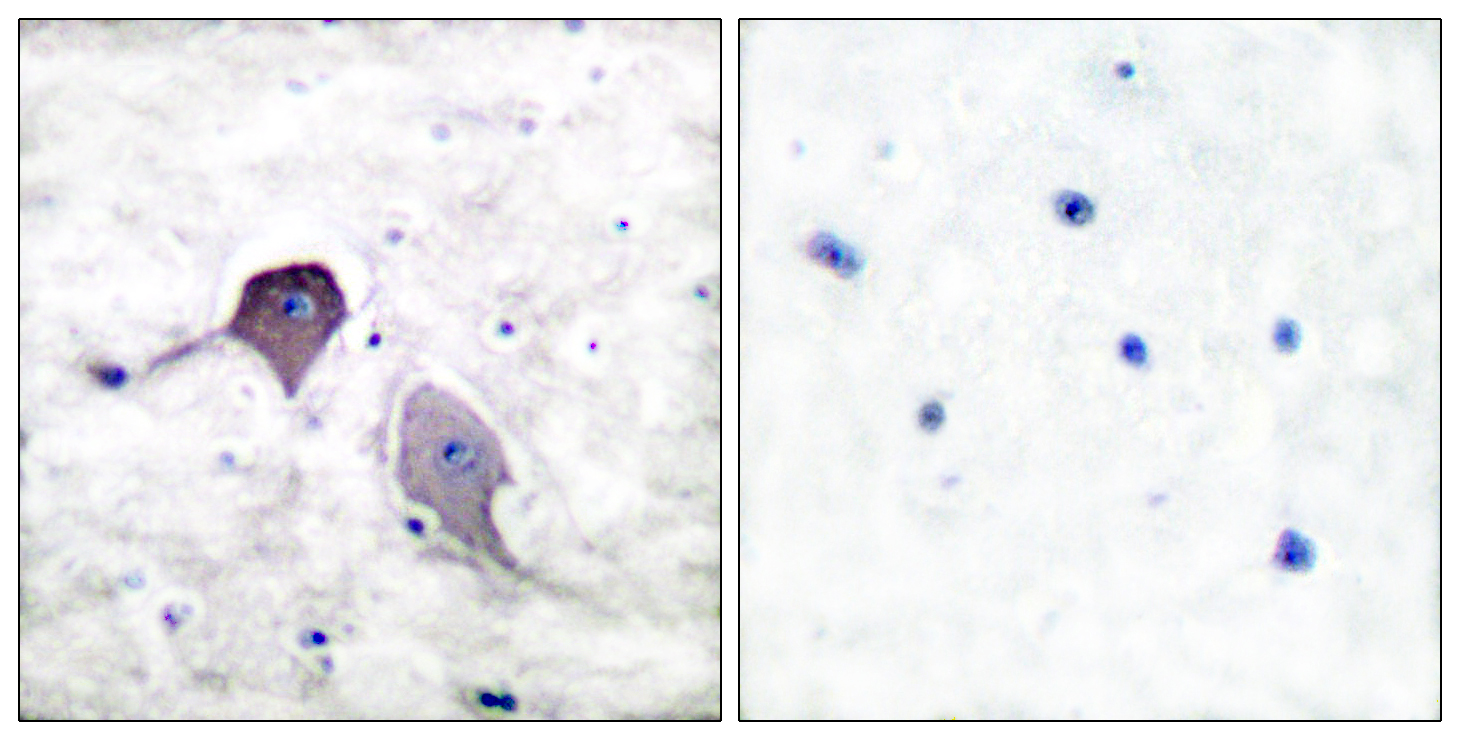
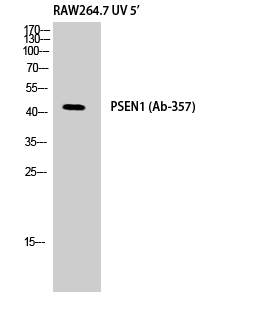
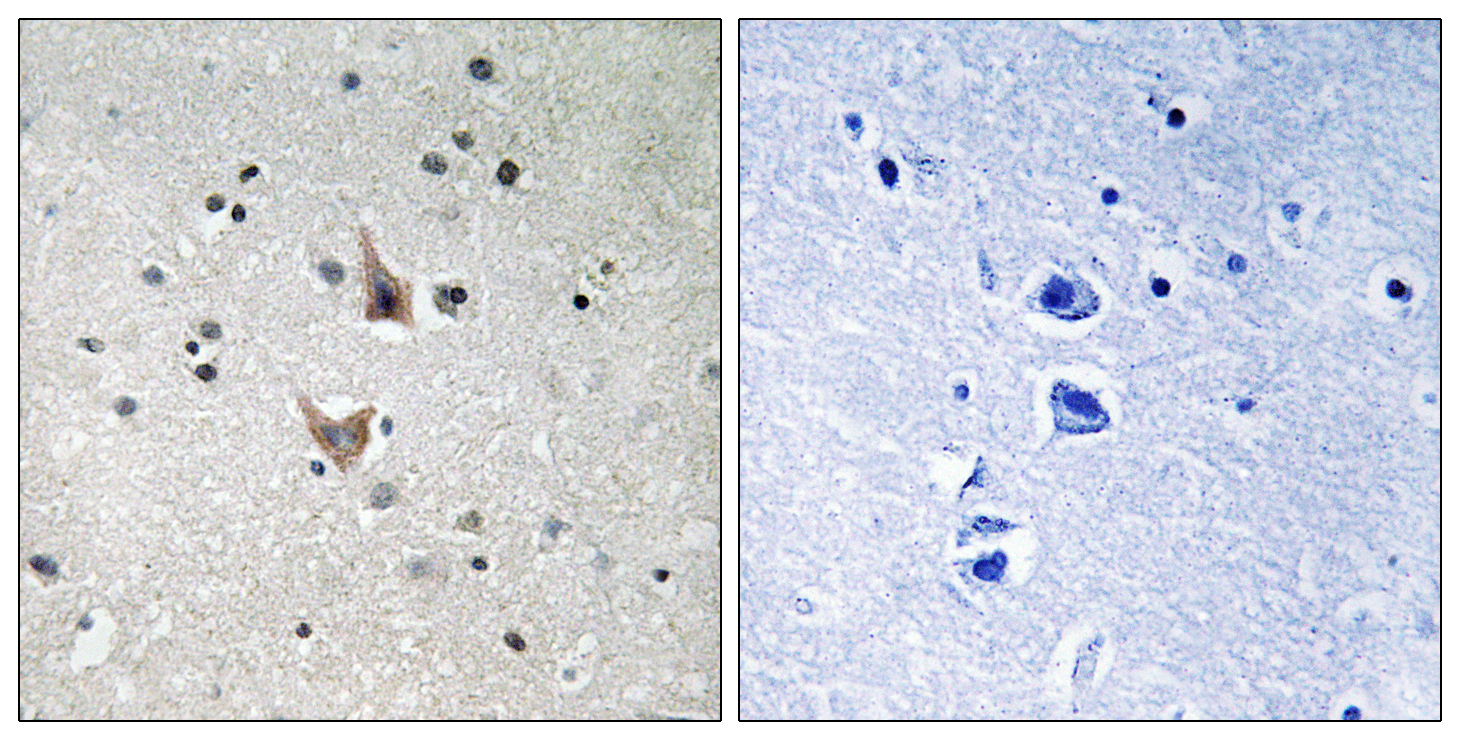
Catalog: KA1757C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$470.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Phospho
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Phospho
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
PSEN1
show all
Other Name:
Presenilin-1 ;
PS-1 ;
Protein S182 ;
[Cleaved into: Presenilin-1 NTF subunit ;
Presenilin-1 CTF subunit ;
Presenilin-1 CTF12 ;
PS1-CTF12 ;
]
PS-1 ;
Protein S182 ;
[Cleaved into: Presenilin-1 NTF subunit ;
Presenilin-1 CTF subunit ;
Presenilin-1 CTF12 ;
PS1-CTF12 ;
]
show all
Database Link:
Background:
disease:Defects in PSEN1 are a cause of Alzheimer disease type 3 (AD3) [MIM:607822]. AD3 is a familial early-onset form of Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer disease is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive dementia, loss of cognitve abilities, and deposition of fibrillar amyloid proteins as intraneuronal neurofibrillary tangles, extracellular amyloid plaques and vascular amyloid deposits. The major constituent of these plaques is the neurotoxic amyloid-beta-APP 40-42 peptide (s), derived proteolytically from the transmembrane precursor protein APP by sequential secretase processing. The cytotoxic C-terminal fragments (CTFs) and the caspase-cleaved products such as C31 derived from APP, are also implicated in neuronal death.,disease:Defects in PSEN1 are a cause of frontotemporal dementia [MIM:600274].,domain:The PAL motif is required for normal active site conformation.,function:Probable catalytic subunit of the gamma-secretase complex, an endoprotease complex that catalyzes the intramembrane cleavage of integral membrane proteins such as Notch receptors and APP (beta-amyloid precursor protein). Requires the other members of the gamma-secretase complex to have a protease activity. May play a role in intracellular signaling and gene expression or in linking chromatin to the nuclear membrane. Stimulates cell-cell adhesion though its association with the E-cadherin/catenin complex. Under conditions of apoptosis or calcium influx, cleaves E-cadherin promoting the disassembly of the E-cadherin/catenin complex and increasing the pool of cytoplasmic beta-catenin, thus negatively regulating Wnt signaling. May also play a role in hematopoiesis.,online information:Presenilins mutations,PTM:After endoproteolysis, the C-terminal fragment (CTF) is phosphorylated on serine residues by PKA and/or PKC. Phosphorylation on Ser-346 inhibits endoproteolysis.,PTM:Heterogeneous proteolytic processing generates N-terminal (NTF) and C-terminal (CTF) fragments of approximately 35 and 20 kDa, respectively. During apoptosis, the C-terminal fragment (CTF) is further cleaved by caspase-3 to produce the fragment, PS1-CTF12.,similarity:Belongs to the peptidase A22A family.,subcellular location:Bound to NOTCH1 also at the cell surface. Colocalizes with CDH1/2 at sites of cell-cell contact. Colocalizes with CTNNB1 in the endoplasmic reticulum and the proximity of the plasma membrane. Also present in azurophil granules of neutrophils.,subunit:Homodimer. Component of the gamma-secretase complex, a complex composed of a presenilin homodimer (PSEN1 or PSEN2), nicastrin (NCSTN), APH1 (APH1A or APH1B) and PEN2. Such minimal complex is sufficient for secretase activity. Other components which are associated with the complex include SLC25A64, SLC5A7, PHB and PSEN1 isoform 3. Predominantly heterodimer of a N-terminal (NTF) and a C-terminal (CTF) endoproteolytical fragment. Associates with proteolytic processed C-terminal fragments C83 and C99 of the amyloid precursor protein (APP). Associates with NOTCH1. Component of cadherin/catenin adhesion complexes through direct binding to CDH1 or CDH2. Interaction with CDH1 stabilizes the complex and stimulates cell-cell aggregation. Interaction with CDH2 is essential for trafficking of CDH2 from the endoplasmic reticulum to the plasma membrane. Interacts with CTNND2, CTNNB1, HERPUD1, FLNA, FLNB, MTCH1, PKP4 and PARL. Interacts through its N-terminus with isoform 3 of GFAP. Interacts with DOCK3.,tissue specificity:Expressed in a wide range of tissues including various regions of the brain, liver, spleen and lymph nodes.,
show all
Function:
autophagic vacuole formation, MAPKKK cascade, activation of MAPKK activity, skeletal system development, regulation of neurotransmitter levels, blood vessel development, cell fate specification, somitogenesis, neuron migration, cell activation, regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation, negative regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation, positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation, hair follicle development, vasculature development, heart looping, hemopoietic progenitor cell differentiation, activation of immune response, cell activation during immune response, lymphocyte activation during immune response, T cell activation during immune response,leukocyte activation during immune response, immune response-activating cell surface receptor signaling pathway,immune system development, leukocyte differentiation, myeloid leukocyte differentiation, positive regulation of immune system process, immune response-activating signal transduction, immune response-regulating signal transduction, immune response-regulating cell surface receptor signaling pathway, generation of a signal involved in cell-cell signaling, regionalization, heart morphogenesis, protein amino acid phosphorylation, negative regulation of protein kinase activity, protein amino acid glycosylation, proteolysis, membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis,glycoprotein catabolic process, phosphorus metabolic process, phosphate metabolic process, ion transport, cation transport, anion transport, neurotransmitter transport, mitochondrial transport, amino acid transport, cellular ion homeostasis, cellular calcium ion homeostasis, cellular metal ion homeostasis, exocytosis, vesicle targeting,autophagy, apoptosis, anti-apoptosis, induction of apoptosis, cell motion, immune response, response to DNA damage stimulus, response to oxidative stress, vacuole organization, chromosome segregation, cell adhesion, cell surface receptor linked signal transduction, regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor activity, Notch signaling pathway,Notch receptor processing, intracellular signaling cascade, protein kinase cascade, cell-cell signaling, synaptic transmission, neurotransmitter secretion, pattern specification process, ectoderm development, heart development,behavior, learning or memory, memory, protein localization, cell death, cell proliferation, epidermis development,induction of apoptosis by extracellular signals, macromolecule catabolic process, glycoprotein metabolic process,glycoprotein biosynthetic process, cellular response to starvation, post-embryonic development, embryonic development ending in birth or egg hatching, anterior/posterior pattern formation, dorsal/ventral pattern formation,response to extracellular stimulus, regulation of receptor activity, positive regulation of phosphorus metabolic process,negative regulation of phosphorus metabolic process, positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process,negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, negative regulation of cell development, regulation of cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation, regulation of cell death, positive regulation of cell death, regulation of neuron projection development, programmed cell death, induction of programmed cell death, protein transport,organic cation transport, quaternary ammonium group transport, organic anion transport, acidic amino acid transport,L-glutamate transport, amine transport, organic acid transport, organic alcohol transport, choline transport, synaptic vesicle exocytosis, synaptic vesicle targeting, vesicle-mediated transport, macroautophagy, death, phosphorylation,cell-cell adhesion, cell migration, protein processing, regulation of phosphate metabolic process, transmission of nerve impulse, cellular homeostasis, neural tube patterning, telencephalon development, pallium development,developmental maturation, cerebral cortex cell migration, Cajal-Retzius cell differentiation, forebrain cell migration,cerebral cortex neuron differentiation, dorsal/ventral neural tube patterning, neural tube development, cerebral cortex development, telencephalon cell migration, molting cycle process, hair cycle process, regulation of cell morphogenesis,biological adhesion, cellular cation homeostasis, cellular di-, tri-valent inorganic cation homeostasis, hemopoiesis,myeloid cell differentiation, protein catabolic process, neuron differentiation, embryonic limb morphogenesis, forebrain development, membrane protein intracellular domain proteolysis, regulation of cell projection organization, negative regulation of cell projection organization, regulation of protein modification process, negative regulation of protein modification process, positive regulation of protein modification process, regulation of neurological system process,response to nutrient levels, cellular response to extracellular stimulus, cellular response to nutrient levels, activation of protein kinase activity, regulation of cellular protein metabolic process, negative regulation of cellular protein metabolic process, positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process, endoplasmic reticulum calcium ion homeostasis, secretion by cell, cellular response to stress, membrane protein proteolysis, negative regulation of kinase activity, positive regulation of kinase activity, appendage morphogenesis, limb morphogenesis, embryonic appendage morphogenesis, tube morphogenesis, segmentation, tube development, growth, regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway, T cell activation, molting cycle, regulation of phosphorylation, negative regulation of phosphorylation, positive regulation of phosphorylation, regulation of membrane potential, homeostatic process, response to starvation, hair cycle, anagen, regulation of apoptosis, amyloid precursor protein metabolic process, amyloid precursor protein catabolic process, chordate embryonic development, positive regulation of apoptosis, negative regulation of apoptosis, regulation of programmed cell death, positive regulation of programmed cell death, negative regulation of programmed cell death, positive regulation of catalytic activity, negative regulation of catalytic activity, regulation of protein binding, regulation of MAP kinase activity, positive regulation of MAP kinase activity, biopolymer glycosylation, regulation of neuron apoptosis, negative regulation of neuron apoptosis, regulation of kinase activity, regulation of system process, negative regulation of molecular function, positive regulation of molecular function, cellular protein catabolic process, cellular macromolecule catabolic process, cell fate commitment,establishment of protein localization, leukocyte activation, negative regulation of cell differentiation, regulation of neuron differentiation, regulation of protein kinase activity, positive regulation of protein kinase activity, negative regulation of phosphate metabolic process, positive regulation of phosphate metabolic process, lymphocyte activation,secretion, intracellular transport, carboxylic acid transport, regulation of synaptic plasticity, synaptic vesicle transport,hemopoietic or lymphoid organ development, thymus development, positive regulation of response to stimulus,developmental growth, embryonic morphogenesis, neuron development, skeletal system morphogenesis, appendage development, hair follicle maturation, brain morphogenesis, cell motility, chemical homeostasis, beta-amyloid metabolic process, epithelial cell proliferation, regulation of neurogenesis, negative regulation of neurogenesis, regulation of axonogenesis, negative regulation of axonogenesis, positive regulation of immune response, ion homeostasis,regulation of synaptic transmission, regulation of coagulation, positive regulation of coagulation, antigen receptor-mediated signaling pathway, T cell receptor signaling pathway, neurological system process, cognition, regulation of binding, negative regulation of cellular component organization, regulation of phosphorus metabolic process, positive regulation of multicellular organismal process, positive regulation of protein metabolic process, negative regulation of protein metabolic process, regulation of transferase activity, positive regulation of transferase activity, negative regulation of transferase activity, neuron apoptosis, smooth endoplasmic reticulum calcium ion homeostasis,proteolysis involved in cellular protein catabolic process, protein maturation, protein maturation by peptide bond cleavage, organelle localization, vesicle localization, establishment of vesicle localization, establishment of organelle localization, localization of cell, regulation of nervous system development, regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic, regulation of transmission of nerve impulse, metal ion homeostasis, di-, tri-valent inorganic cation homeostasis, calcium ion homeostasis, cation homeostasis, cellular chemical homeostasis, regulation of resting membrane potential, limb development, regulation of cell development, negative regulation of cell death,glycosylation,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Endoplasmic reticulum . Endoplasmic reticulum membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Golgi apparatus membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Cytoplasmic granule . Cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Cell projection, growth cone . Early endosome . Early endosome membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Cell projection, neuron projection . Cell projection, axon . Cell junction, synapse . Translocates with bound NOTCH1 from the endoplasmic reticulum and/or Golgi to the cell surface (PubMed:10593990). Colocalizes with CDH1/2 at sites of cell-cell contact. Colocalizes with CTNNB1 in the endoplasmic reticulum and the proximity of the plasma membrane (PubMed:9738936). Also present in azurophil granules of neutrophils (PubMed:11987239). Colocalizes with UBQLN1 in the cell membrane and in cytoplasmic juxtanuclear structures called aggresomes (PubMed:21143716). .
show all
Signaling Pathway
Organismal Systems >> Nervous system >> Neurotrophin signaling pathway
Human Diseases >> Neurodegenerative disease >> Alzheimer disease
Human Diseases >> Neurodegenerative disease >> Pathways of neurodegeneration - multiple diseases
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Wnt signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Notch signaling pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA1757C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$470.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}