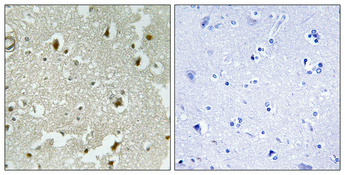
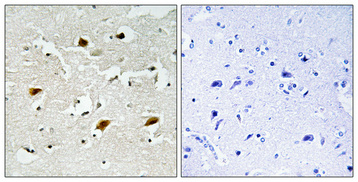
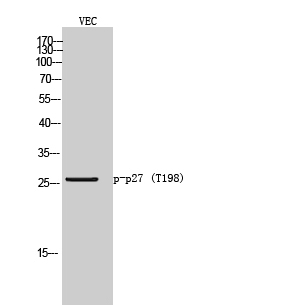
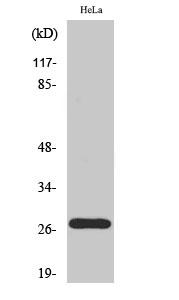
Catalog: KA1626C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$470.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Phospho
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Phospho
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
CDKN1B KIP1
show all
Other Name:
CDKN1B ;
KIP1 ;
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B ;
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 ;
p27Kip1
KIP1 ;
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B ;
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 ;
p27Kip1
show all
Background:
disease:Defects in CDKN1B are the cause of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 4 (MEN4) [MIM:610755]. Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) syndromes are inherited cancer syndromes of the thyroid. MEN4 is a MEN-like syndrome with a phenotypic overlap of both MEN1 and MEN2.,domain:A peptide sequence containing only AA 28-79 retains substantial Kip1 cyclin A/CDK2 inhibitory activity.,function:Important regulator of cell cycle progrssion. Involved in G1 arrest. Potent inhibitor of cyclin E- and cyclin A-CDK2 complexes. Positive regulator of cyclin D-dependent kinases such as CDK4. Regulated by phosphorylation and degradation events.,induction:Maximal levels in quiescence cells and early G(1). Levels decrease after mitogen stimulation as cells progress toward S-phase.,miscellaneous:Decreased levels of p27Kip1, mainly due to proteosomal degradation, are found in various epithelial tumors originating from lung, breast, colon, ovary, esophagus, thyroid and prostate.,PTM:Phosphorylated; phosphorylation occurs on serine, threonine and tyrosine residues. Phosphorylation on Ser-10 is the major site of phosphorylation in resting cells, takes place at the G(0)-G(1) phase and leads to protein stability. Phosphorylation on other sites is greatly enhanced by mitogens, growth factors, cMYC and in certain cancer cell lines. The phosphorylated form found in the cytoplasm is inactivate. Phosphorylation on Thr-198 is required for interaction with 14-3-3 proteins. Phosphorylation on Thr-187, by CDK2 leads to protein ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Tyrosine phosphorylation promotes this process. Phosphorylation by PKB/AKT1 can be suppressed by LY294002, an inhibitor of the catalytic subunit of PI3K. Phosphorylation on Tyr-88 and Tyr-89 has no effect on binding CDK2, but is required for binding CDK4. Dephosphorylated on tyrosine residues by G-CSF.,PTM:Ubiquitinated; in the cytoplasm by the KPC1/KPC2 complex and, in the nucleus, by SCF/SKP2. The latter requires prior phosphorylation on Thr-187.,similarity:Belongs to the CDI family.,subcellular location:Nuclear and cytoplasmic in quiescent cells. AKT- or RSK-mediated phosphorylation on Thr-198, binds 14-3-3, translocates to the cytoplasm and promotes cell cycle progression. Mitogen-activated UHMK1 phosphorylation on Ser-10 also results in translocation to the cytoplasm and cell cycle progression. Phosphorylation on Ser-10 facilitates nuclear export. Translocates to the nucleus on phosphorylation of Tyr-88 and Tyr-89.,subunit:Interacts with NUP50; the interaction leads to nuclear import and degradation of phosphorylated p27kip1. Interacts with COPS5, subunit of the COP9 signalosome complex; the interaction leads to p27KIP degradation. Interacts with SPDYA in the SPDYA/CDK2/p27kip1 complex. Interacts (Thr-198 phosphorylated-form) with 14-3-3 proteins, binds strongly YWHAQ, weakly YWHAE and YWHAH, but not YWHAB nor YWHAZ; the interaction with YWHAQ results in translocation to the cytoplasm. Interacts with AKT1, LYN and UHMK1; the interactions lead to cytoplasmic mislocation, phosphorylation of p27kip1 and inhibition of cell cycle arrest. Interacts (unphosphorylated form) with CDK2. Interacts (phosphorylated on Tyr-88 and Tyr-89) with CDK4; the interaction induces nuclear translocation. Interacts with GRB2.,tissue specificity:Expressed in all tissues tested. Highest levels in skeletal muscle, lowest in liver and kidney.,
show all
Function:
regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity, G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle, mitotic cell cycle, regulation of cell growth, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, negative regulation of protein kinase activity, ion transport,cation transport, potassium ion transport, induction of apoptosis, cell cycle, cell cycle arrest, sensory organ development, sensory perception, sensory perception of sound, cell death, positive regulation of cell proliferation,negative regulation of cell proliferation, regulation of cell size, negative regulation of biosynthetic process, negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, negative regulation of phosphorus metabolic process, negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, negative regulation of gene expression, positive regulation of organelle organization, regulation of cell death, positive regulation of cell death, programmed cell death, induction of programmed cell death, monovalent inorganic cation transport, death, negative regulation of transcription, regulation of phosphate metabolic process, cell cycle process, cell cycle phase, metal ion transport, negative regulation of cell growth, regulation of microtubule polymerization or depolymerization, positive regulation of microtubule polymerization or depolymerization, regulation of microtubule polymerization, positive regulation of microtubule polymerization, negative regulation of cellular biosynthetic process, positive regulation of protein complex assembly,regulation of protein polymerization, positive regulation of protein polymerization, regulation of cellular component size, negative regulation of gene-specific transcription, regulation of gene-specific transcription, regulation of microtubule-based process, regulation of organelle organization, negative regulation of kinase activity, regulation of growth, regulation of cell proliferation, regulation of phosphorylation, negative regulation of phosphorylation,regulation of apoptosis, positive regulation of apoptosis, regulation of programmed cell death, positive regulation of programmed cell death, negative regulation of catalytic activity, regulation of protein complex assembly, regulation of kinase activity, ear development, regulation of cellular component biogenesis, negative regulation of molecular function, regulation of transcription, negative regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity, negative regulation of cell cycle, negative regulation of cell size, regulation of protein kinase activity, negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, negative regulation of growth, negative regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process, negative regulation of phosphate metabolic process, autophagic cell death, inner ear development, regulation of epithelial cell proliferation, negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation, neurological system process, cognition, sensory perception of mechanical stimulus, positive regulation of cellular component organization, negative regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process, regulation of phosphorus metabolic process, regulation of RNA metabolic process, negative regulation of RNA metabolic process,regulation of cell motion, negative regulation of cell motion, interphase, interphase of mitotic cell cycle, regulation of transferase activity, negative regulation of transferase activity, regulation of cytoskeleton organization, positive regulation of cytoskeleton organization, regulation of cell cycle, regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Endosome . Nuclear and cytoplasmic in quiescent cells. AKT- or RSK-mediated phosphorylation on Thr-198, binds 14-3-3, translocates to the cytoplasm and promotes cell cycle progression. Mitogen-activated UHMK1 phosphorylation on Ser-10 also results in translocation to the cytoplasm and cell cycle progression. Phosphorylation on Ser-10 facilitates nuclear export. Translocates to the nucleus on phosphorylation of Tyr-88 and Tyr-89. Colocalizes at the endosome with SNX6; this leads to lysosomal degradation (By similarity). .
show all
Signaling Pathway
Cellular Processes >> Cell growth and death >> Cell cycle
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> Pathways in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> Transcriptional misregulation in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> MicroRNAs in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Gastric cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Chronic myeloid leukemia
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Prostate cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Small cell lung cancer
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> ErbB signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> HIF-1 signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> FoxO signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> PI3K-Akt signaling pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA1626C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$470.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}