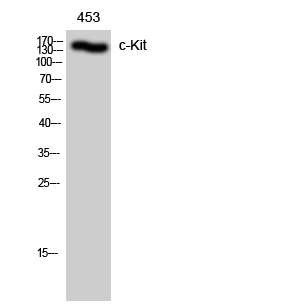
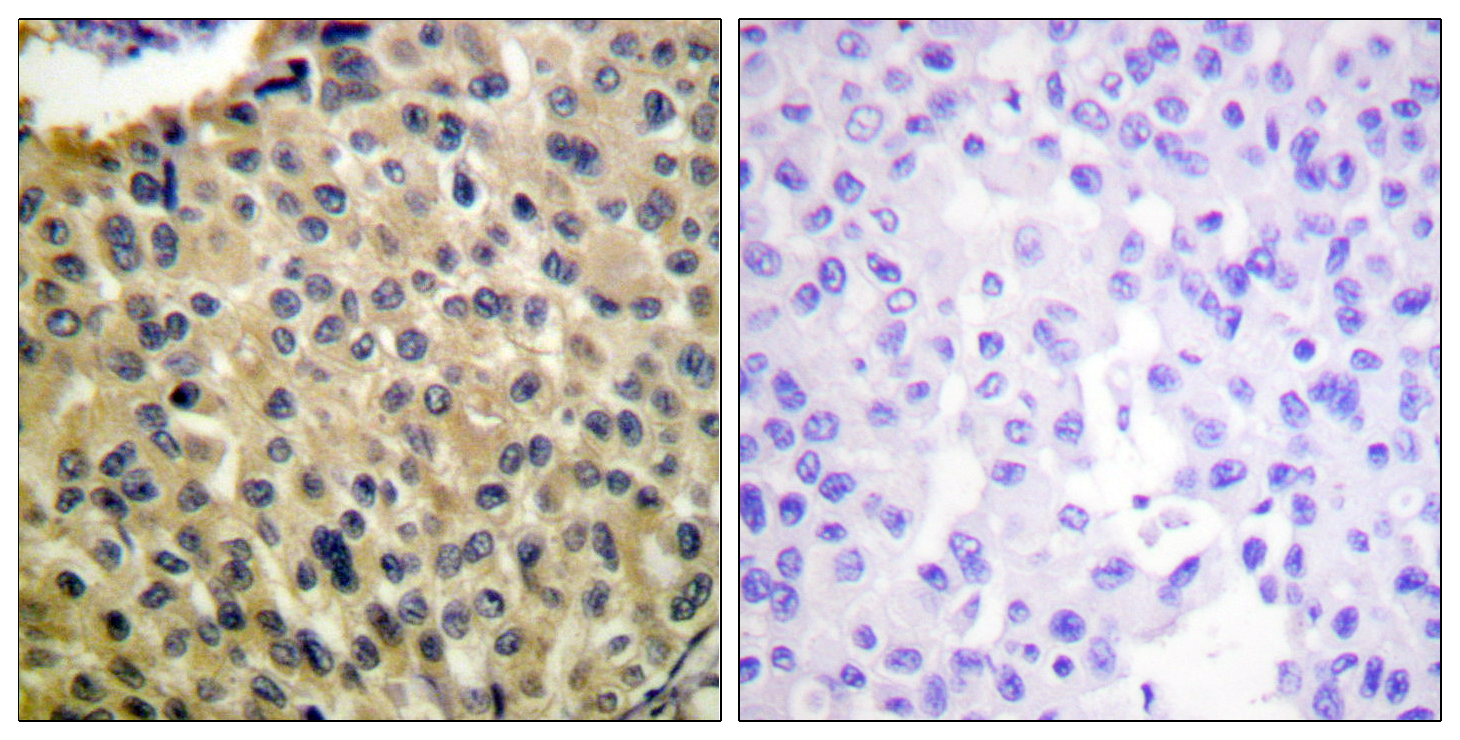
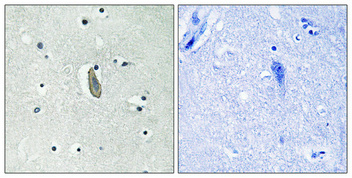
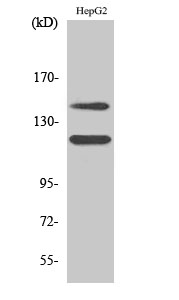
Catalog: KA1600C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$470.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Phospho
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Phospho
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
KIT SCFR
show all
Other Name:
Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit ;
SCFR ;
Piebald trait protein ;
PBT ;
Proto-oncogene c-Kit ;
Tyrosine-protein kinase Kit ;
p145 c-kit ;
v-kit Hardy-Zuckerman 4 feline sarcoma viral oncogene homolog ;
CD antigen CD117 ;
SCFR ;
Piebald trait protein ;
PBT ;
Proto-oncogene c-Kit ;
Tyrosine-protein kinase Kit ;
p145 c-kit ;
v-kit Hardy-Zuckerman 4 feline sarcoma viral oncogene homolog ;
CD antigen CD117 ;
show all
Background:
catalytic activity:ATP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine = ADP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine phosphate.,disease:Defects in KIT are a cause of gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) [MIM:606764].,disease:Defects in KIT are a cause of piebaldism [MIM:172800]. Piebaldism is an autosomal dominant genetic developmental abnormality of pigmentation characterized by congenital patches of white skin and hair that lack melanocytes.,disease:Defects in KIT have been associated with testicular tumors [MIM:273300]. It includes germ cell tumor (GCT) or testicular germ cell tumor (TGCT).,function:This is the receptor for stem cell factor (mast cell growth factor). It has a tyrosine-protein kinase activity. Binding of the ligands leads to the autophosphorylation of KIT and its association with substrates such as phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (Pi3K).,online information:CD117 entry,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. CSF-1/PDGF receptor subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 protein kinase domain.,similarity:Contains 5 Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains.,subunit:Interacts with APS. Interacts with MPDZ (via the tenth PDZ domain). Interacts with PTPRU.,
show all
Function:
hemopoietic progenitor cell differentiation, myeloid progenitor cell differentiation, lymphoid progenitor cell differentiation, immune system development, leukocyte differentiation, myeloid leukocyte differentiation, reproductive developmental process, protein amino acid phosphorylation, membrane lipid metabolic process, glycolipid metabolic process, sphingolipid metabolic process, glycosphingolipid metabolic process, phosphorus metabolic process,phosphate metabolic process, cell motion, cell surface receptor linked signal transduction, enzyme linked receptor protein signaling pathway, transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway, intracellular signaling cascade, protein kinase cascade, gamete generation, germ cell development, spermatogenesis, spermatid development, behavior, learning or memory, learning, visual behavior, cell death, cell proliferation, positive regulation of cell proliferation, germ cell migration, visual learning, regulation of Notch signaling pathway, response to radiation,response to light stimulus, response to abiotic stimulus, positive regulation of signal transduction, positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, developmental programmed cell death, positive regulation of gene expression,positive regulation of cell communication, positive regulation of cell development, regulation of cell death, programmed cell death, death, phosphorylation, cell migration, stem cell division, peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation, peptidyl-tyrosine modification, regulation of phosphate metabolic process, cytokine-mediated signaling pathway, stem cell maintenance, sexual reproduction, hemopoiesis, myeloid cell differentiation, regulation of cell migration, positive regulation of cell migration, regulation of pseudopodium assembly, positive regulation of pseudopodium assembly,regulation of cell projection organization, positive regulation of cell projection organization, regulation of neurological system process, multicellular organism reproduction, positive regulation of kinase activity, somatic stem cell maintenance, germ cell programmed cell death, regulation of locomotion, positive regulation of locomotion, regulation of cell proliferation, regulation of phosphorylation, regulation of programmed cell death, negative regulation of programmed cell death, positive regulation of catalytic activity, regulation of MAP kinase activity, positive regulation of MAP kinase activity, pigmentation, regulation of kinase activity, regulation of system process, regulation of cellular component biogenesis, positive regulation of molecular function, negative regulation of cell differentiation, positive regulation of cell differentiation, positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway, regulation of protein kinase activity,positive regulation of protein kinase activity, protein amino acid autophosphorylation, pigmentation during development, regulation of pigmentation during development, somatic stem cell division, regulation of synaptic plasticity, regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity, regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity, positive regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity, male gamete generation, spermatid differentiation, hemopoietic or lymphoid organ development, reproductive process in a multicellular organism, reproductive cellular process, stem cell differentiation, stem cell development, cell motility, epithelial cell proliferation, regulation of neurogenesis, positive regulation of neurogenesis, regulation of synaptic transmission, neurological system process, cognition, positive regulation of developmental process, positive regulation of cellular component organization, regulation of phosphorus metabolic process, regulation of cell motion, positive regulation of cell motion, cell division, regulation of transferase activity, positive regulation of transferase activity, localization of cell, regulation of nervous system development,regulation of transmission of nerve impulse, regulation of cell development, regulation of cell projection assembly,negative regulation of cell death,
show all
Cellular Localization:
[Isoform 1]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.; [Isoform 2]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.; [Isoform 3]: Cytoplasm . Detected in the cytoplasm of spermatozoa, especially in the equatorial and subacrosomal region of the sperm head. .
show all
Signaling Pathway
Organismal Systems >> Immune system >> Hematopoietic cell lineage
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> Pathways in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> Central carbon metabolism in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Acute myeloid leukemia
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Breast cancer
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> MAPK signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Ras signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Rap1 signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Phospholipase D signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> PI3K-Akt signaling pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA1600C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$470.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}