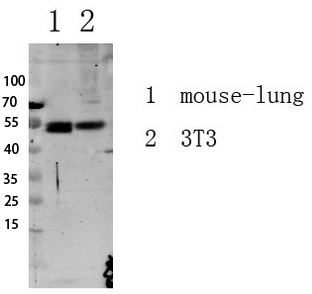
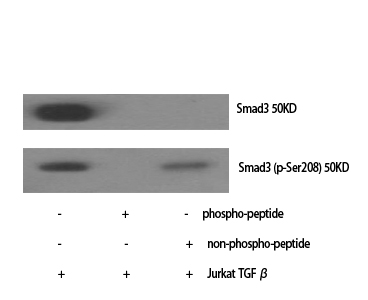
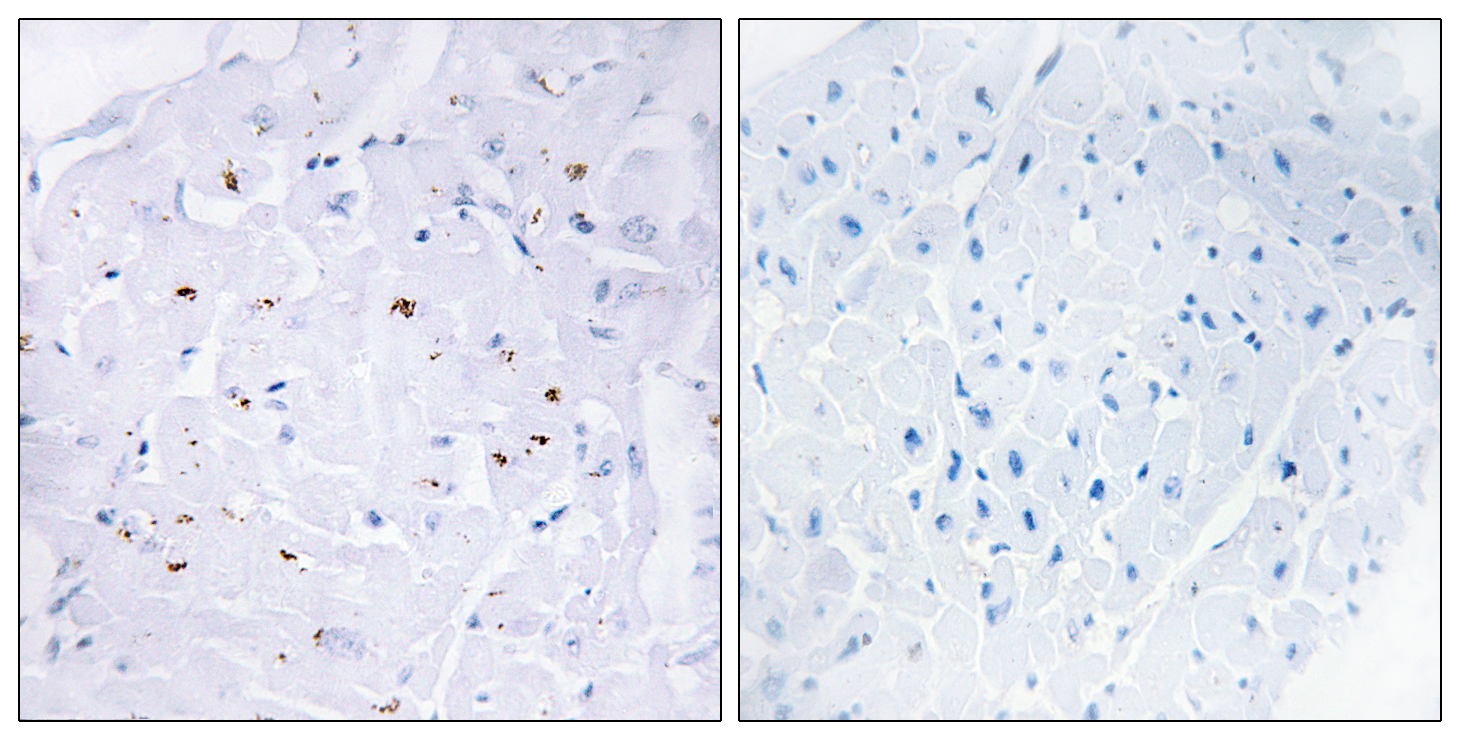
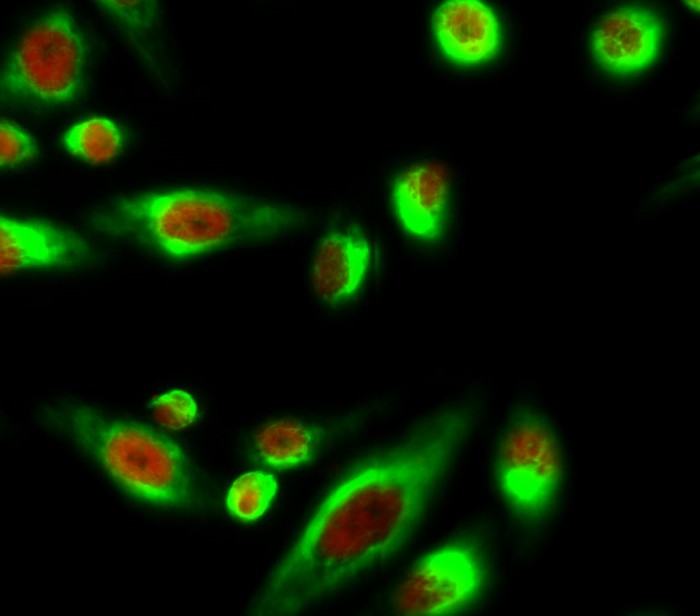
Catalog: KA1475C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$470.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
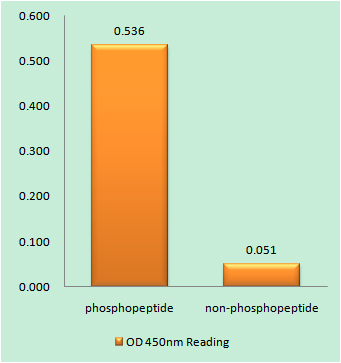
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Phospho
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Phospho
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
SMAD3 MADH3
show all
Other Name:
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 ;
MAD homolog 3 ;
Mad3 ;
Mothers against DPP homolog 3 ;
hMAD-3 ;
JV15-2 ;
SMAD family member 3 ;
SMAD 3 ;
Smad3 ;
hSMAD3 ;
MAD homolog 3 ;
Mad3 ;
Mothers against DPP homolog 3 ;
hMAD-3 ;
JV15-2 ;
SMAD family member 3 ;
SMAD 3 ;
Smad3 ;
hSMAD3 ;
show all
Database Link:
Background:
disease:Defects in SMAD3 may be a cause of colorectal cancer (CRC) [MIM:114500].,domain:The MH2 domain is sufficient to carry protein nuclear export.,function:Transcriptional modulator activated by TGF-beta (transforming growth factor) and activin type 1 receptor kinase. SMAD3 is a receptor-regulated SMAD (R-SMAD).,PTM:Phosphorylated on serine by TGF-beta and activin type 1 receptor kinases.,similarity:Belongs to the dwarfin/SMAD family.,similarity:Contains 1 MH1 (MAD homology 1) domain.,similarity:Contains 1 MH2 (MAD homology 2) domain.,subcellular location:In the cytoplasm in the absence of ligand. Migration to the nucleus when complexed with Smad4.,subunit:Interacts with HGS. Interacts with NEDD4L in response to TGF-beta. Interacts with TTRAP (By similarity). Interacts with SARA (SMAD anchor for receptor activation); form trimers with another SMAD3 and the co-SMAD SMAD4. Interacts with JUN/FOS, vitamin D receptor, homeobox protein TGIF and TGIF2, PEBP2-alpha C subunit, CREB-binding protein (CBP), p300, SKI, SNON, ATF2, SMURF2, AIP1, DACH1 and TGFB1I1. Part of a complex consisting of AIP1, ACVR2A, ACVR1B and SMAD3. Found in a complex with SMAD2 and TRIM33 upon addition of TGF-beta. Interacts with SMAD2 and TRIM33. Found in a complex with SMAD3, Ran and XPO4. Interacts with XPO4. Interacts with LBXCOR1 and CORL2.,
show all
Function:
negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, skeletal system development, ossification,regulation of cell growth, osteoblast differentiation, response to hypoxia, formation of primary germ layer, mesoderm formation, cell activation, regulation of cytokine production, positive regulation of cytokine production, release of cytochrome c from mitochondria, regulation of cell-matrix adhesion, positive regulation of cell-matrix adhesion,osteoblast development, transcription, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, RNA processing, protein complex assembly, apoptosis, induction of apoptosis, activation of caspase activity, immune response, mitochondrion organization, cell cycle, cell cycle arrest, cell surface receptor linked signal transduction, enzyme linked receptor protein signaling pathway, transmembrane receptor protein serine/threonine kinase signaling pathway, transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway, SMAD protein complex assembly, regulation of mitotic cell cycle, gastrulation, mesoderm development, cell death, negative regulation of cell proliferation, regulation of cell size, activation of pro-apoptotic gene products, apoptotic mitochondrial changes, response to wounding, negative regulation of biosynthetic process, positive regulation of biosynthetic process, response to organic substance, regulation of specific transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, positive regulation of specific transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, negative regulation of specific transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression, positive regulation of gene expression, negative regulation of gene expression, positive regulation of organelle organization, regulation of alkaline phosphatase activity, positive regulation of alkaline phosphatase activity, regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition, positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition, positive regulation of cell development, regulation of cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation, positive regulation of cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation, regulation of cell-substrate adhesion, positive regulation of cell-substrate adhesion,regulation of phosphatase activity, positive regulation of phosphatase activity, regulation of cell death, positive regulation of cell death, positive regulation of peptidase activity, programmed cell death, induction of programmed cell death, viral reproduction, regulation of striated muscle tissue development, death, posttranscriptional gene silencing,gene silencing, negative regulation of transcription, regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway, virus-host interaction, evasion of host defenses by virus, regulation of phosphate metabolic process, cell cycle process, viral reproductive process, regulation of cell morphogenesis, regulation of cell adhesion, regulation of ossification, negative regulation of cell growth, regulation of cell migration, positive regulation of cell migration,regulation of bone mineralization, positive regulation of bone mineralization, gene silencing by RNA, dsRNA fragmentation, primary microRNA processing, negative regulation of cellular biosynthetic process, positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process, regulation of response to external stimulus, positive regulation of response to external stimulus, regulation of actin filament bundle formation, positive regulation of actin filament bundle formation,regulation of intracellular transport, positive regulation of intracellular transport, regulation of cellular component size,negative regulation of gene-specific transcription, regulation of gene-specific transcription, regulation of interleukin-1 beta production, regulation of interleukin-1 production, positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production, positive regulation of interleukin-1 production, regulation of protein localization, regulation of transforming growth factor-beta2 production, regulation of transforming growth factor-beta3 production, positive regulation of transforming growth factor-beta3 production, regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization, regulation of actin filament-based process,regulation of organelle organization, regulation of intracellular protein transport, cell junction organization, ncRNA processing, cellular macromolecular complex subunit organization, cellular macromolecular complex assembly,posttranscriptional gene silencing by RNA, gene silencing by miRNA, gene silencing by miRNA, production of miRNAs,regulation of dephosphorylation, regulation of growth, regulation of locomotion, positive regulation of locomotion,regulation of gene expression, epigenetic, wound healing, T cell activation, regulation of cell proliferation, regulation of protein import into nucleus, positive regulation of protein import into nucleus, regulation of apoptosis, regulation of transcription factor import into nucleus, positive regulation of transcription factor import into nucleus, positive regulation of apoptosis, negative regulation of apoptosis, regulation of programmed cell death, positive regulation of programmed cell death, negative regulation of programmed cell death, positive regulation of catalytic activity, positive regulation of gene-specific transcription, positive regulation of caspase activity, regulation of caspase activity,response to dsRNA, cellular protein complex assembly, macromolecular complex subunit organization, regulation of cellular component biogenesis, positive regulation of molecular function, avoidance of host defenses, evasion or tolerance of host defenses, cell-cell junction organization, leukocyte activation, regulation of transcription, negative regulation of cell differentiation, positive regulation of cell differentiation, regulation of osteoblast differentiation,negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation, positive regulation of ossification, positive regulation of cell adhesion,negative regulation of cell cycle, negative regulation of cell size, negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent,positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, negative regulation of growth, negative regulation of mitotic cell cycle, negative regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process, positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process, positive regulation of transcription, positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, lymphocyte activation, regulation of nucleocytoplasmic transport, positive regulation of nucleocytoplasmic transport, mesoderm morphogenesis, paraxial mesoderm development, paraxial mesoderm morphogenesis, positive regulation of behavior, positive regulation of response to stimulus, embryonic morphogenesis, regulation of muscle development, tissue morphogenesis, regulation of epithelial cell proliferation, regulation of behavior, regulation of chemotaxis, positive regulation of chemotaxis, regulation of positive chemotaxis, positive regulation of positive chemotaxis, positive regulation of transport, positive regulation of developmental process, regulation of binding, positive regulation of cellular component organization, negative regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process, positive regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process,regulation of phosphorus metabolic process, positive regulation of protein transport, regulation of protein transport,positive regulation of multicellular organismal process, regulation of RNA metabolic process, negative regulation of RNA metabolic process, positive regulation of RNA metabolic process, regulation of cell motion, positive regulation of cell motion, regulation of hydrolase activity, positive regulation of hydrolase activity, regulation of stress fiber formation,regulation of cytoskeleton organization, positive regulation of cytoskeleton organization, positive regulation of stress fiber formation, regulation of cell cycle, avoidance of defenses of other organism during symbiotic interaction, evasion or tolerance of defenses of other organism during symbiotic interaction, regulation of focal adhesion formation,positive regulation of focal adhesion formation, response to defenses of other organism during symbiotic interaction,response to host defenses, regulation of peptidase activity, regulation of endopeptidase activity, regulation of cell development, transdifferentiation, regulation of cellular localization, bone development, negative regulation of cell death, macromolecular complex assembly, regulation of biomineral formation, positive regulation of biomineral formation, regulation of establishment of protein localization, protein complex biogenesis, response to oxygen levels,response to host,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Cytoplasm . Nucleus . Cytoplasmic and nuclear in the absence of TGF-beta. On TGF-beta stimulation, migrates to the nucleus when complexed with SMAD4 (PubMed:15799969, PubMed:21145499). Through the action of the phosphatase PPM1A, released from the SMAD2/SMAD4 complex, and exported out of the nucleus by interaction with RANBP1 (PubMed:16751101, PubMed:19289081). Co-localizes with LEMD3 at the nucleus inner membrane (PubMed:15601644). MAPK-mediated phosphorylation appears to have no effect on nuclear import (PubMed:19218245). PDPK1 prevents its nuclear translocation in response to TGF-beta (PubMed:17327236). Localized mainly to the nucleus in the early stages of embryo development with expression becoming evident in the cytoplasm of the inner cell mass at the blastocyst stage (By similarity). .
show all
Signaling Pathway
Cellular Processes >> Cell growth and death >> Cell cycle
Cellular Processes >> Cell growth and death >> Cellular senescence
Cellular Processes >> Cellular community - eukaryotes >> Adherens junction
Cellular Processes >> Cellular community - eukaryotes >> Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells
Organismal Systems >> Immune system >> Th17 cell differentiation
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> Pathways in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Colorectal cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Pancreatic cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Hepatocellular carcinoma
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Gastric cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Chronic myeloid leukemia
Human Diseases >> Immune disease >> Inflammatory bowel disease
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Wnt signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> TGF-beta signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Hippo signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Apelin signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> FoxO signaling pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA1475C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$470.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}