Catalog: KA1469C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$470.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Target
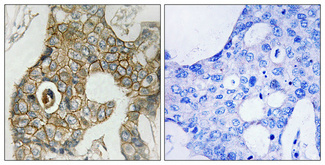
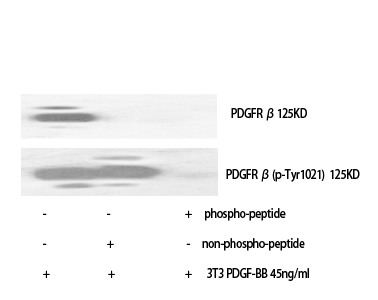
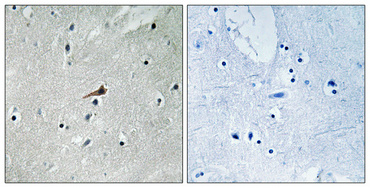
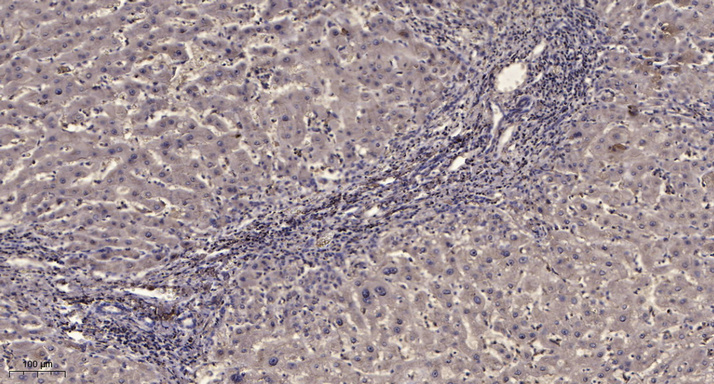
PDGFR-β Phospho Tyr740
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Phospho
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Phospho
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
PDGFRB PDGFR PDGFR1
show all
Other Name:
PDGFRB ;
PDGFR ;
PDGFR1 ;
Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta ;
PDGF-R-beta ;
PDGFR-beta ;
Beta platelet-derived growth factor receptor ;
Beta-type platelet-derived growth factor receptor ;
CD140 antigen-like family member B ;
Platelet-deri
PDGFR ;
PDGFR1 ;
Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta ;
PDGF-R-beta ;
PDGFR-beta ;
Beta platelet-derived growth factor receptor ;
Beta-type platelet-derived growth factor receptor ;
CD140 antigen-like family member B ;
Platelet-deri
show all
Database Link:
Background:
catalytic activity:ATP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine = ADP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine phosphate.,disease:A chromosomal aberration involving PDGFRB is a cause in many instances of chronic myeloproliferative disorder with eosinophilia (MPE) [MIM:131440]. Translocation t(5;12) with ETV6 on chromosome 12 creating an PDGFRB-ETV6 fusion protein.,disease:A chromosomal aberration involving PDGFRB is found in a form of chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML). Translocation t(5;12)(q33;p13) with EVT6/TEL. It is characterized by abnormal clonal myeloid proliferation and by progression to acute myelogenous leukemia (AML).,disease:A chromosomal aberration involving PDGFRB may be a cause of acute myelogenous leukemia. Translocation t(5;14)(q33;q32) with TRIP11. The fusion protein may be involved in clonal evolution of leukemia and eosinophilia.,disease:A chromosomal aberration involving PDGFRB may be a cause of juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia. Translocation t(5;17)(q33;p11.2) with SPECC1.,disease:A chromosomal aberration involving PDGFRB may be the cause of a myeloproliferative disorder (MBD) associated with eosinophilia. Translocation t(1;5)(q23;q33) that forms a PDE4DIP-PDGFRB fusion protein.,function:Receptor that binds specifically to PDGFB and PDGFD and has a tyrosine-protein kinase activity. Phosphorylates Tyr residues at the C-terminus of PTPN11 creating a binding site for the SH2 domain of GRB2.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. CSF-1/PDGF receptor subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 protein kinase domain.,similarity:Contains 5 Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains.,subunit:Homodimer, and heterodimer with PDGFRA. Interacts with APS. The autophosphorylated form interacts directly with SHB and with PIK3C2B, maybe indirectly.,
show all
Function:
skeletal system development, urogenital system development, in utero embryonic development, kidney development,tissue homeostasis, regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation, protein amino acid phosphorylation,phosphorus metabolic process, phosphate metabolic process, cell motion, chemotaxis, cell surface receptor linked signal transduction, enzyme linked receptor protein signaling pathway, transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway, muscle organ development, behavior, locomotory behavior, positive regulation of cell proliferation, embryonic development ending in birth or egg hatching, phosphorylation, cell migration, peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation, peptidyl-tyrosine modification, regulation of phosphate metabolic process, regulation of cell migration, positive regulation of cell migration, regulation of protein modification process, regulation of cellular protein metabolic process, regulation of locomotion, positive regulation of locomotion, regulation of cell proliferation,regulation of phosphorylation, taxis, homeostatic process, chordate embryonic development, protein amino acid autophosphorylation, platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway, skeletal system morphogenesis, smooth muscle tissue development, cell motility,multicellular organismal homeostasis, regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation, regulation of phosphorus metabolic process, regulation of cell motion, positive regulation of cell motion, localization of cell, anatomical structure homeostasis, cell chemotaxis, muscle tissue development,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cytoplasmic vesicle. Lysosome lumen. After ligand binding, the autophosphorylated receptor is ubiquitinated and internalized, leading to its degradation.
show all
Signaling Pathway
Cellular Processes >> Cellular community - eukaryotes >> Focal adhesion
Cellular Processes >> Cellular community - eukaryotes >> Gap junction
Cellular Processes >> Cell motility >> Regulation of actin cytoskeleton
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> Pathways in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> MicroRNAs in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> Central carbon metabolism in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Glioma
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Melanoma
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Prostate cancer
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> MAPK signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Ras signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Rap1 signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> JAK-STAT signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Calcium signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Phospholipase D signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> PI3K-Akt signaling pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA1469C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$470.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}