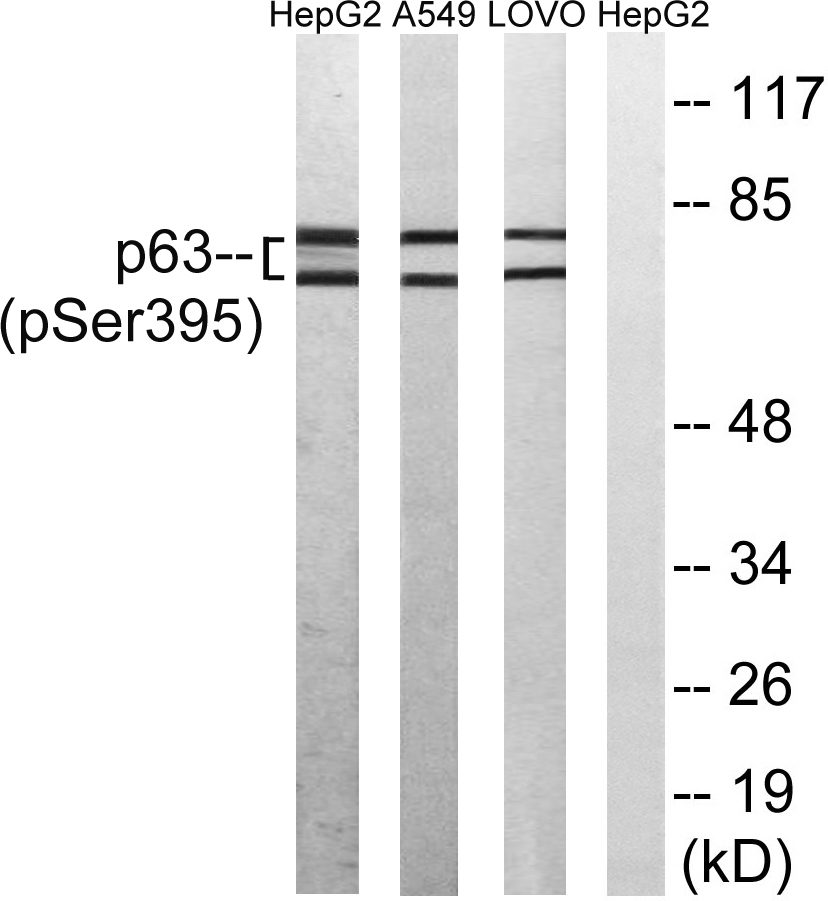
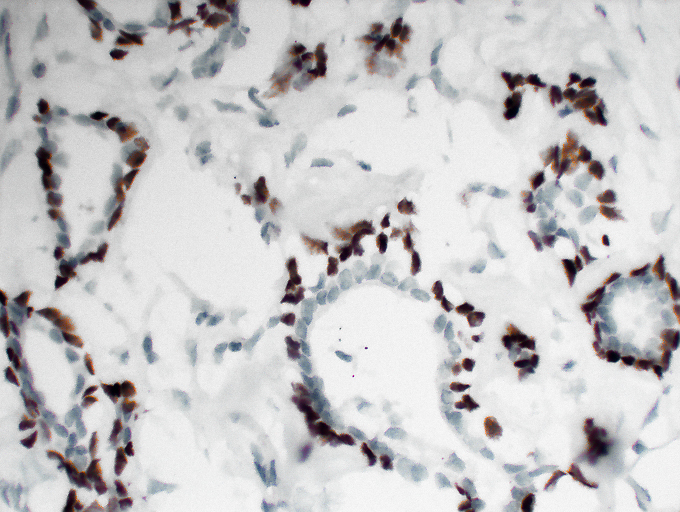
Catalog: KA1380C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$470.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Reactivity
Human
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Phospho
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Phospho
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
TP63
show all
Other Name:
Tumor protein 63 ;
p63 ;
Chronic ulcerative stomatitis protein ;
CUSP ;
Keratinocyte transcription factor KET ;
Transformation-related protein 63 ;
TP63 ;
Tumor protein p73-like ;
p73L ;
p40 ;
p51 ;
p63 ;
Chronic ulcerative stomatitis protein ;
CUSP ;
Keratinocyte transcription factor KET ;
Transformation-related protein 63 ;
TP63 ;
Tumor protein p73-like ;
p73L ;
p40 ;
p51 ;
show all
Background:
cofactor:Binds 1 zinc ion per subunit.,disease:Defects in TP63 are a cause of cervical, colon, head and neck, lung and ovarian cancers.,disease:Defects in TP63 are a cause of ectodermal dysplasia Rapp-Hodgkin type (EDRH) [MIM:129400]; also called Rapp-Hodgkin syndrome or anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia with cleft lip/palate. Ectodermal dysplasia defines a heterogeneous group of disorders due to abnormal development of two or more ectodermal structures. EDRH is characterized by the combination of anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia, cleft lip, and cleft palate. The clinical syndrome is comprised of a characteristic facies (narrow nose and small mouth), wiry, slow-growing, and uncombable hair, sparse eyelashes and eyebrows, obstructed lacrimal puncta/epiphora, bilateral stenosis of external auditory canals, microsomia, hypodontia, cone-shaped incisors, enamel hypoplasia, dystrophic nails, and cleft lip/cleft palate.,disease:Defects in TP63 are the cause of acro-dermato-ungual-lacrimal-tooth syndrome (ADULT syndrome) [MIM:103285]; a form of ectodermal dysplasia. Ectodermal dysplasias (EDs) constitute a heterogeneous group of developmental disorders affecting tissues of ectodermal origin. EDs are characterized by abnormal development of two or more ectodermal structures such as hair, teeth, nails and sweat glands, with or without any additional clinical sign. Each combination of clinical features represents a different type of ectodermal dysplasia. ADULT syndrome involves ectrodactyly, syndactyly, finger- and toenail dysplasia, hypoplastic breasts and nipples, intensive freckling, lacrimal duct atresia, frontal alopecia, primary hypodontia, and loss of permanent teeth. ADULT differs significantly from EEC3 syndrome by the absence of facial clefting.,disease:Defects in TP63 are the cause of ankyloblepharon-ectodermal defects-cleft lip/palate (AEC) [MIM:106260]. AEC is an autosomal dominant condition characterized by congenital ectodermal dysplasia with coarse, wiry, sparse hair, dystrophic nails, slight hypohidrosis, scalp infections, ankyloblepharon filiforme adnatum, maxillary hypoplasia, hypodontia and cleft lip/palate.,disease:Defects in TP63 are the cause of ectrodactyly-ectodermal dysplasia-cleft lip/palate syndrome type 3 (EEC3) [MIM:604292]. EEC3 is an autosomal dominant syndrome characterized by ectrodactyly of hands and feet, ectodermal dysplasia and facial clefting.,disease:Defects in TP63 are the cause of limb-mammary syndrome (LMS) [MIM:603543]. LMS is characterized by ectrodactyly, cleft palate and mammary-gland abnormalities.,disease:Defects in TP63 are the cause of non-syndromic orofacial cleft type 8 (OFC8) [MIM:129400]. Non-syndromic orofacial cleft is a common birth defect consisting of cleft lips with or without cleft palate. Cleft lips are associated with cleft palate in two-third of cases. A cleft lip can occur on one or both sides and range in severity from a simple notch in the upper lip to a complete opening in the lip extending into the floor of the nostril and involving the upper gum.,disease:Defects in TP63 are the cause of split-hand/foot malformation 4 (SHFM4) [MIM:605289]. Split-hand/split-foot malformation is a limb malformation involving the central rays of the autopod and presenting with syndactyly, median clefts of the hands and feet, and aplasia and/or hypoplasia of the phalanges, metacarpals, and metatarsals. There is restricted overlap between the mutational spectra of EEC3 and SHFM4.,domain:The transactivation inhibitory domain (TID) can interact with, and inhibit the activity of the N-terminal transcriptional activation domain of TA*-type isoforms.,function:Acts as a sequence specific DNA binding transcriptional activator or repressor. The isoforms contain a varying set of transactivation and auto-regulating transactivation inhibiting domains thus showing an isoform specific activity. May be required in conjunction with TP73/p73 for initiation of TP53/p53 dependent apoptosis in response to genotoxic insults and the presence of activated oncogenes. Involved in Notch signaling by probably inducing JAG1 and JAG2. Plays a role in the regulation of epithelial morphogenesis. The ratio of DeltaN-type and TA*-type isoforms may govern the maintenance of epithelial stem cell compartments and regulate the initiation of epithelial stratification from the undifferentiated embryonal ectoderm. Required for limb formation from the apical ectodermal ridge.,PTM:May be sumoylated.,similarity:Belongs to the p53 family.,similarity:Contains 1 SAM (sterile alpha motif) domain.,subunit:Binds DNA as a homotetramer. Isoform composition of the tetramer may determine transactivation activity. Isoforms Alpha and Gamma interact with HIPK2. Interacts with SSRP1, leading to stimulate coactivator activity.,tissue specificity:Widely expressed, notably in heart, kidney, placenta, prostate, skeletal muscle, testis and thymus, although the precise isoform varies according to tissue type. Progenitor cell layers of skin, breast, eye and prostate express high levels of DeltaN-type isoforms. Isoform 10 is predominantly expressed in skin squamous cell carcinomas, but not in normal skin tissues.,
show all
Function:
negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, replicative cell aging, skeletal system development, regulation of cell growth, urogenital system development, establishment of planar polarity,morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium, hair follicle development, morphogenesis of an epithelium, positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation, epithelial cell development, response to tumor cell, regionalization,reproductive developmental process, transcription, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, protein complex assembly, apoptosis, anti-apoptosis, induction of apoptosis, response to DNA damage stimulus, establishment of tissue polarity, cell surface receptor linked signal transduction, Notch signaling pathway, intracellular signaling cascade, cell-cell signaling, pattern specification process,ectoderm development, mesoderm development, ectoderm and mesoderm interaction, muscle organ development,sex differentiation, aging, cell aging, cell death, cell proliferation, positive regulation of cell proliferation, regulation of cell size, epidermis development, regulation of Notch signaling pathway, induction of apoptosis by intracellular signals,DNA damage response, signal transduction resulting in induction of apoptosis, negative regulation of biosynthetic process, positive regulation of biosynthetic process, proximal/distal pattern formation, positive regulation of signal transduction, multicellular organismal aging, regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation, positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, positive regulation of gene expression, negative regulation of gene expression, positive regulation of cell communication, regulation of cell death,positive regulation of cell death, programmed cell death, induction of programmed cell death, death, negative regulation of transcription, molting cycle process, hair cycle process, negative regulation of cell growth, embryonic limb morphogenesis, DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator, female genitalia development,prostate gland development, epithelial cell differentiation, regulation of epithelial cell differentiation, negative regulation of epithelial cell differentiation, polarized epithelial cell differentiation, hair follicle morphogenesis, negative regulation of cellular biosynthetic process, positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process, regulation of cellular component size, cellular response to stress, appendage morphogenesis, limb morphogenesis, genitalia morphogenesis, embryonic appendage morphogenesis, tail morphogenesis, tube morphogenesis, tube development,regulation of growth, regulation of cell proliferation, molting cycle, odontogenesis of dentine-containing tooth,odontogenesis, hair cycle, DNA damage response, signal transduction, DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in induction of apoptosis, regulation of apoptosis, positive regulation of apoptosis,negative regulation of apoptosis, regulation of programmed cell death, positive regulation of programmed cell death,negative regulation of programmed cell death, skin development, skin morphogenesis, keratinocyte proliferation,macromolecular complex subunit organization, development of primary sexual characteristics, regulation of transcription, negative regulation of cell differentiation, regulation of epidermal cell differentiation, negative regulation of epidermal cell differentiation, regulation of keratinocyte differentiation, negative regulation of keratinocyte differentiation, regulation of epidermis development, negative regulation of epidermis development, positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway, negative regulation of cell size, negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, negative regulation of growth, negative regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process, positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process, positive regulation of transcription, positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, development of primary female sexual characteristics, female sex differentiation,autonomic nervous system development, sympathetic nervous system development, digestive tract morphogenesis,embryonic morphogenesis, reproductive structure development, tissue morphogenesis, epidermis morphogenesis,gland development, appendage development, smooth muscle tissue development, genitalia development, female genitalia morphogenesis, negative regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process, positive regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process, regulation of RNA metabolic process, negative regulation of RNA metabolic process,positive regulation of RNA metabolic process, protein oligomerization, protein homooligomerization, protein tetramerization, protein homotetramerization, neuron apoptosis, digestive system development, urinary bladder development, limb development, cloacal septation, epithelium development, muscle tissue development, negative regulation of cell death, macromolecular complex assembly, protein complex biogenesis,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Nucleus .
show all
Signaling Pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA1380C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$470.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}









.jpg)