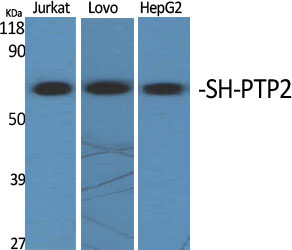
Catalog: KA1181C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$470.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Main Information
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Phospho
Detailed Information
Storage
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
Modification
Phospho
Detection Method
Colorimetric
Related Products
Antigen&Target Information
Gene Name:
PTPN11
show all
Other Name:
Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 11 ;
Protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1D ;
PTP-1D ;
Protein-tyrosine phosphatase 2C ;
PTP-2C ;
SH-PTP2 ;
SHP-2 ;
Shp2 ;
SH-PTP3 ;
Protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1D ;
PTP-1D ;
Protein-tyrosine phosphatase 2C ;
PTP-2C ;
SH-PTP2 ;
SHP-2 ;
Shp2 ;
SH-PTP3 ;
show all
Background:
catalytic activity:Protein tyrosine phosphate + H(2)O = protein tyrosine + phosphate.,disease:Defects in PTPN11 are a cause of juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML) [MIM:607785]. JMML is a pediatric myelodysplastic syndrome that constitutes approximately 30% of childhood cases of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and 2% of leukemia. It is characterized by leukocytosis with tissue infiltration and in vitro hypersensitivity of myeloid progenitors to granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor.,disease:Defects in PTPN11 are a cause of Noonan-like syndrome [MIM:163955]; also known as Noonan-like/multiple giant cell lesion syndrome. It is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by Noonan features associates with giant cell lesions of bone and soft tissue.,disease:Defects in PTPN11 are the cause of LEOPARD syndrome [MIM:151100]. It is an autosomal dominant disorder allelic with Noonan syndrome. The acronym LEOPARD stands for lentigines, electrocardiographic conduction abnormalities, ocular hypertelorism, pulmonic stenosis, abnormalities of genitalia, retardation of growth, and deafness.,disease:Defects in PTPN11 are the cause of Noonan syndrome 1 (NS1) [MIM:163950]. Noonan syndrome (NS) is a disorder characterized by dysmorphic facial features, short stature, hypertelorism, cardiac anomalies, deafness, motor delay, and a bleeding diathesis. It is a genetically heterogeneous and relatively common syndrome, with an estimated incidence of 1 in 1000-2500 live births. Mutations in PTPN11 account for more than 50% of the cases. Rarely, NS is associated with juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML). NS1 inheritance is autosomal dominant.,domain:The SH2 domains repress phosphatase activity. Binding of these domains to phosphotyrosine-containing proteins relieves this auto-inhibition, possibly by inducing a conformational change in the enzyme.,function:Acts downstream of various receptor and cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinases to participate in the signal transduction from the cell surface to the nucleus.,PTM:Phosphorylated on Tyr-546 and Tyr-584 upon receptor protein tyrosine kinase activation; which creates a binding site for GRB2 and other SH2-containing proteins.,similarity:Belongs to the protein-tyrosine phosphatase family. Non-receptor class 2 subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 tyrosine-protein phosphatase domain.,similarity:Contains 2 SH2 domains.,subunit:Interacts with phosphorylated LIME1 and BCAR3. Interacts with SHB and INPP5D/SHIP1 (By similarity). Interacts with PTPNS1 and CD84. Interacts with phosphorylated SIT1 and MPZL1. Interacts with FCRL3, FCRL4, FCRL6 and ANKHD1.,tissue specificity:Widely expressed, with highest levels in heart, brain, and skeletal muscle.,
show all
Function:
cell cycle checkpoint, DNA damage checkpoint, MAPKKK cascade, activation of MAPK activity, cell morphogenesis, cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation, regulation of peptide secretion, negative regulation of peptide secretion,protein amino acid phosphorylation, protein amino acid dephosphorylation, neutral lipid metabolic process, acylglycerol metabolic process, triglyceride metabolic process, glycerol ether metabolic process, phosphorus metabolic process,phosphate metabolic process, response to DNA damage stimulus, cell surface receptor linked signal transduction,enzyme linked receptor protein signaling pathway, transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway, intracellular signaling cascade, protein kinase cascade, axonogenesis, response to endogenous stimulus,response to hormone stimulus, hormone-mediated signaling, positive regulation of signal transduction, response to organic substance, positive regulation of cell communication, regulation of hormone levels, phosphorylation,dephosphorylation, organic ether metabolic process, regulation of phosphate metabolic process, cell projection organization, neuron differentiation, neuron projection development, DNA integrity checkpoint, regulation of intracellular transport, multicellular organism reproduction, cellular response to hormone stimulus, regulation of protein localization, cellular component morphogenesis, cell part morphogenesis, regulation of intracellular protein transport, carbohydrate homeostasis, cellular response to stress, positive regulation of kinase activity, organ growth,growth, regulation of growth, regulation of multicellular organism growth, regulation of phosphorylation, hormone metabolic process, homeostatic process, glucose homeostasis, DNA damage response, signal transduction, positive regulation of catalytic activity, regulation of MAP kinase activity, positive regulation of MAP kinase activity, regulation of kinase activity, regulation of system process, positive regulation of molecular function, regulation of protein kinase activity, positive regulation of protein kinase activity, glycerolipid metabolic process, negative regulation of insulin secretion, regulation of nucleocytoplasmic transport, regulation of protein export from nucleus, regulation of hormone secretion, positive regulation of hormone secretion, negative regulation of hormone secretion, nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway, reproductive process in a multicellular organism, neuron development, cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation, neuron projection morphogenesis, cell projection morphogenesis, chemical homeostasis, regulation of insulin secretion, regulation of secretion, positive regulation of secretion, negative regulation of secretion, positive regulation of transport, negative regulation of transport, regulation of phosphorus metabolic process, regulation of protein transport, regulation of transferase activity, positive regulation of transferase activity, regulation of cortisol secretion, negative regulation of cortisol secretion, regulation of cell cycle, regulation of growth hormone secretion, negative regulation of growth hormone secretion, regulation of cellular localization,regulation of establishment of protein localization,
show all
Cellular Localization:
Cytoplasm . Nucleus .
show all
Tissue Expression:
Signaling Pathway
Organismal Systems >> Immune system >> Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity
Organismal Systems >> Immune system >> T cell receptor signaling pathway
Organismal Systems >> Immune system >> Leukocyte transendothelial migration
Organismal Systems >> Endocrine system >> Adipocytokine signaling pathway
Organismal Systems >> Nervous system >> Neurotrophin signaling pathway
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Chronic myeloid leukemia
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Renal cell carcinoma
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Ras signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> JAK-STAT signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Phospholipase D signaling pathway
Reference Citation({{totalcount}})
Catalog: KA1181C
Size
Price
Status
Qty.
96well
$470.00
In stock
0
Add to cart


Collected


Collect
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allPRODUCTS
CUSTOMIZED
ABOUT US
Toggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
Main Information
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
Product {{index}}/{{pcount}}
Prev
Next
{{pvTitle}}
Scroll wheel zooms the picture
{{pvDescr}}