Arrestin-β-1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT0343
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Monkey
- Target:
- Arrestin 1
- Fields:
- >>MAPK signaling pathway;>>Chemokine signaling pathway;>>Endocytosis;>>Hedgehog signaling pathway;>>Dopaminergic synapse;>>Olfactory transduction;>>Relaxin signaling pathway;>>Parathyroid hormone synthesis, secretion and action;>>GnRH secretion;>>Morphine addiction;>>Chemical carcinogenesis - receptor activation
- Gene Name:
- ARRB1
- Protein Name:
- Beta-arrestin-1
- Human Gene Id:
- 408
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P49407
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q8BWG8
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Arrestin 1. AA range:369-418
- Specificity:
- Arrestin-β-1 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Arrestin-β-1 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- ARRB1;ARR1;Beta-arrestin-1;Arrestin beta-1
- Observed Band(KD):
- 47kD
- Background:
- Members of arrestin/beta-arrestin protein family are thought to participate in agonist-mediated desensitization of G-protein-coupled receptors and cause specific dampening of cellular responses to stimuli such as hormones, neurotransmitters, or sensory signals. Arrestin beta 1 is a cytosolic protein and acts as a cofactor in the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase (BARK) mediated desensitization of beta-adrenergic receptors. Besides the central nervous system, it is expressed at high levels in peripheral blood leukocytes, and thus the BARK/beta-arrestin system is believed to play a major role in regulating receptor-mediated immune functions. Alternatively spliced transcripts encoding different isoforms of arrestin beta 1 have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2011],
- Function:
- function:Regulates beta-adrenergic receptor function. Beta-arrestins seem to bind phosphorylated beta-adrenergic receptors, thereby causing a significant impairment of their capacity to activate G(S) proteins.,online information:Arrestin entry,similarity:Belongs to the arrestin family.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cell membrane. Membrane, clathrin-coated pit . Cell projection, pseudopodium . Cytoplasmic vesicle. Translocates to the plasma membrane and colocalizes with antagonist-stimulated GPCRs. The monomeric form is predominantly located in the nucleus. The oligomeric form is located in the cytoplasm. Translocates to the nucleus upon stimulation of OPRD1 (By similarity). .
- Expression:
- Brain,Peripheral blood,Uterus,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
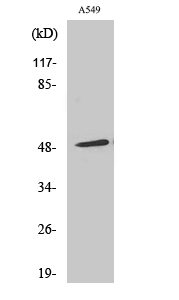
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using Arrestin-β-1 Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:500

- Western Blot analysis of various cells using Antibody diluted at 1:1000. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS0002) was diluted at 1:20000

- Immunofluorescence analysis of A549 cells, using Arrestin 1 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
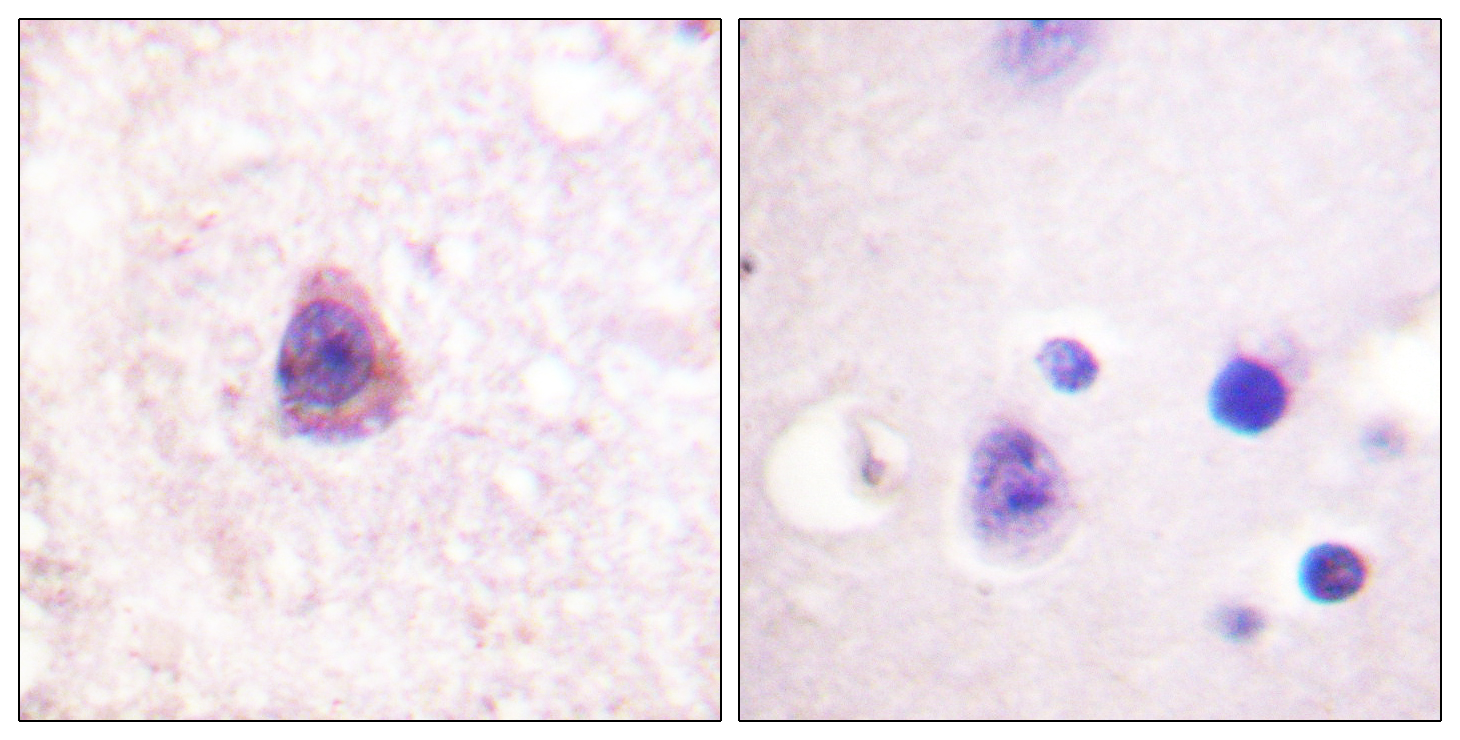
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human brain tissue, using Arrestin 1 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
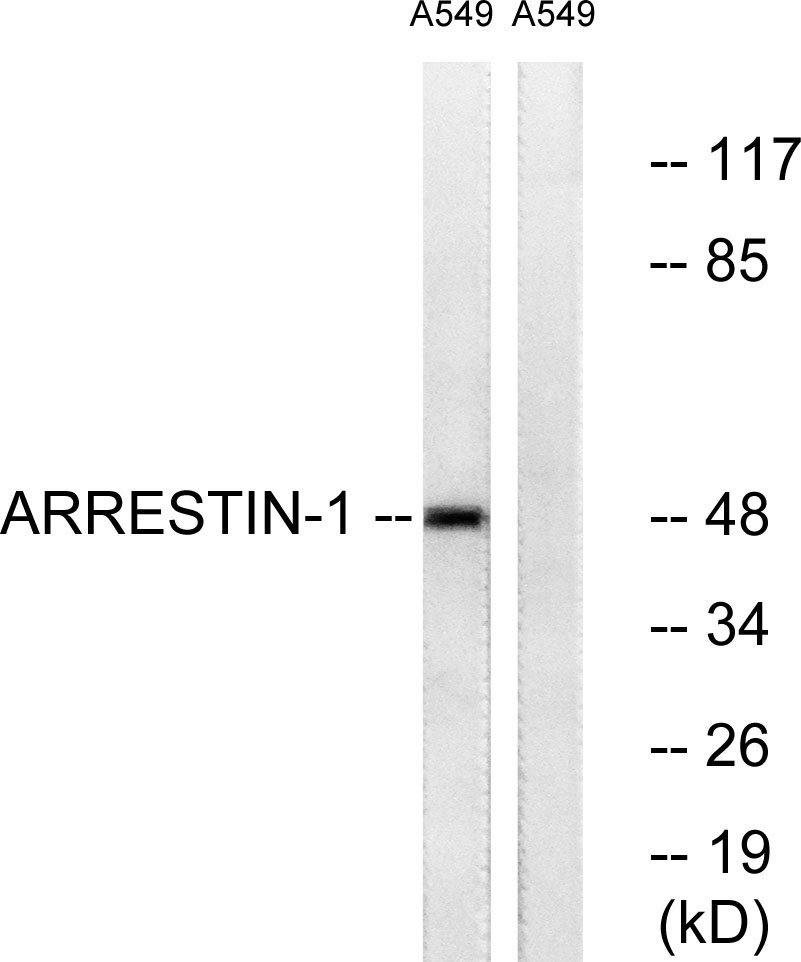
- Western blot analysis of lysates from A549 cells, treated with Etoposide 25uM 60', using Arrestin 1 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.



