EpoR (phospho Tyr426) Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YP1205
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- EpoR
- Fields:
- >>Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction;>>PI3K-Akt signaling pathway;>>JAK-STAT signaling pathway;>>Hematopoietic cell lineage;>>Pathways in cancer
- Gene Name:
- EPOR
- Protein Name:
- Erythropoietin receptor
- Human Gene Id:
- 2057
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P19235
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 13857
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P14753
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q07303
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized phospho-peptide around the phosphorylation site of human EpoR (phospho Tyr426)
- Specificity:
- Phospho-EpoR (Y426) Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of EpoR protein only when phosphorylated at Y426.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:20000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- EPOR;Erythropoietin receptor;EPO-R
- Observed Band(KD):
- 55kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes the erythropoietin receptor which is a member of the cytokine receptor family. Upon erythropoietin binding, this receptor activates Jak2 tyrosine kinase which activates different intracellular pathways including: Ras/MAP kinase, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and STAT transcription factors. The stimulated erythropoietin receptor appears to have a role in erythroid cell survival. Defects in the erythropoietin receptor may produce erythroleukemia and familial erythrocytosis. Dysregulation of this gene may affect the growth of certain tumors. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, May 2010],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in EPOR are the cause of erythrocytosis familial type 1 (ECYT1) [MIM:133100]. ECYT1 is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by increased serum red blood cell mass, elevated hemoglobin and hematocrit, hypersensitivity of erythroid progenitors to erythropoietin, erythropoietin low serum levels, and no increase in platelets nor leukocytes. It has a relatively benign course and does not progress to leukemia.,domain:Contains 1 copy of a cytoplasmic motif that is referred to as the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitor motif (ITIM). This motif is involved in modulation of cellular responses. The phosphorylated ITIM motif can bind the SH2 domain of several SH2-containing phosphatases.,domain:The box 1 motif is required for JAK interaction and/or activation.,domain:The WSXWS motif appears to be necessary for proper protein folding and thereby efficient intracellular tra
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.; [Isoform EPOR-S]: Secreted . Secreted and located to the cell surface.
- Expression:
- Erythroid cells and erythroid progenitor cells. Isoform EPOR-F is the most abundant form in EPO-dependent erythroleukemia cells and in late-stage erythroid progenitors. Isoform EPOR-S and isoform EPOR-T are the predominant forms in bone marrow. Isoform EPOR-T is the most abundant from in early-stage erythroid progenitor cells.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
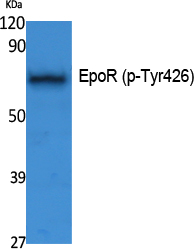
- Western Blot analysis of extracts from K562 cells, using Phospho-EpoR (Y426) Polyclonal Antibody.



