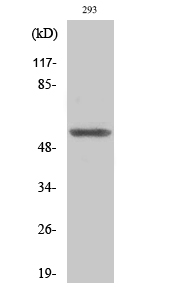
Sox-9 (phospho Ser181) Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YP0895
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Target:
- Sox-9
- Fields:
- >>cAMP signaling pathway
- Gene Name:
- SOX9
- Protein Name:
- Transcription factor SOX-9
- Human Gene Id:
- 6662
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P48436
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 20682
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q04887
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human SOX-9 around the phosphorylation site of Ser181. AA range:147-196
- Specificity:
- Phospho-Sox-9 (S181) Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Sox-9 protein only when phosphorylated at S181.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:5000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- SOX9;Transcription factor SOX-9
- Observed Band(KD):
- 65kD
- Background:
- SRY-box 9(SOX9) Homo sapiens The protein encoded by this gene recognizes the sequence CCTTGAG along with other members of the HMG-box class DNA-binding proteins. It acts during chondrocyte differentiation and, with steroidogenic factor 1, regulates transcription of the anti-Muellerian hormone (AMH) gene. Deficiencies lead to the skeletal malformation syndrome campomelic dysplasia, frequently with sex reversal. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in SOX9 are the cause of campomelic dysplasia (CMD1) [MIM:114290]. CMD1 is a rare, often lethal, dominantly inherited, congenital osteochondrodysplasia, associated with male-to-female autosomal sex reversal in two-thirds of the affected karyotypic males. A disease of the newborn characterized by congenital bowing and angulation of long bones, unusually small scapulae, deformed pelvis and spine and a missing pair of ribs. Craniofacial defects such as cleft palate, micrognatia, flat face and hypertelorism are common. Various defects of the ear are often evident, affecting the cochlea, malleus incus, stapes and tympanum. Most patients die soon after birth due to respiratory distress which has been attributed to hypoplasia of the tracheobronchial cartilage and small thoracic cage.,function:Plays an important role in the normal skeletal development. May regulate the expression
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus .
- Expression:
- Eye,PNS,Testis,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
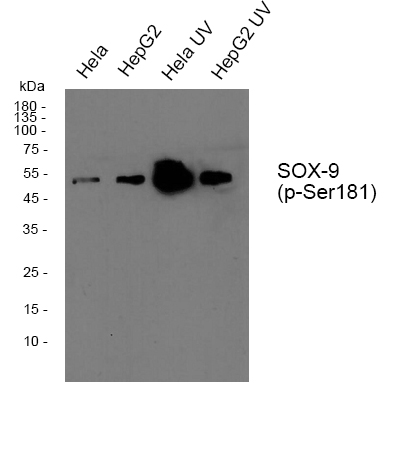
- Western blot analysis of Sox-9 (phospho Ser181) Polyclonal Antibody, using Hela, HepG2 cell treated or untreated with UV, 4° over night, secondary antibody(cat: RS0002 was diluted at 1:10000, 37° 1hour.

- Immunofluorescence analysis of A549 cells, using SOX-9 (Phospho-Ser181) Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.
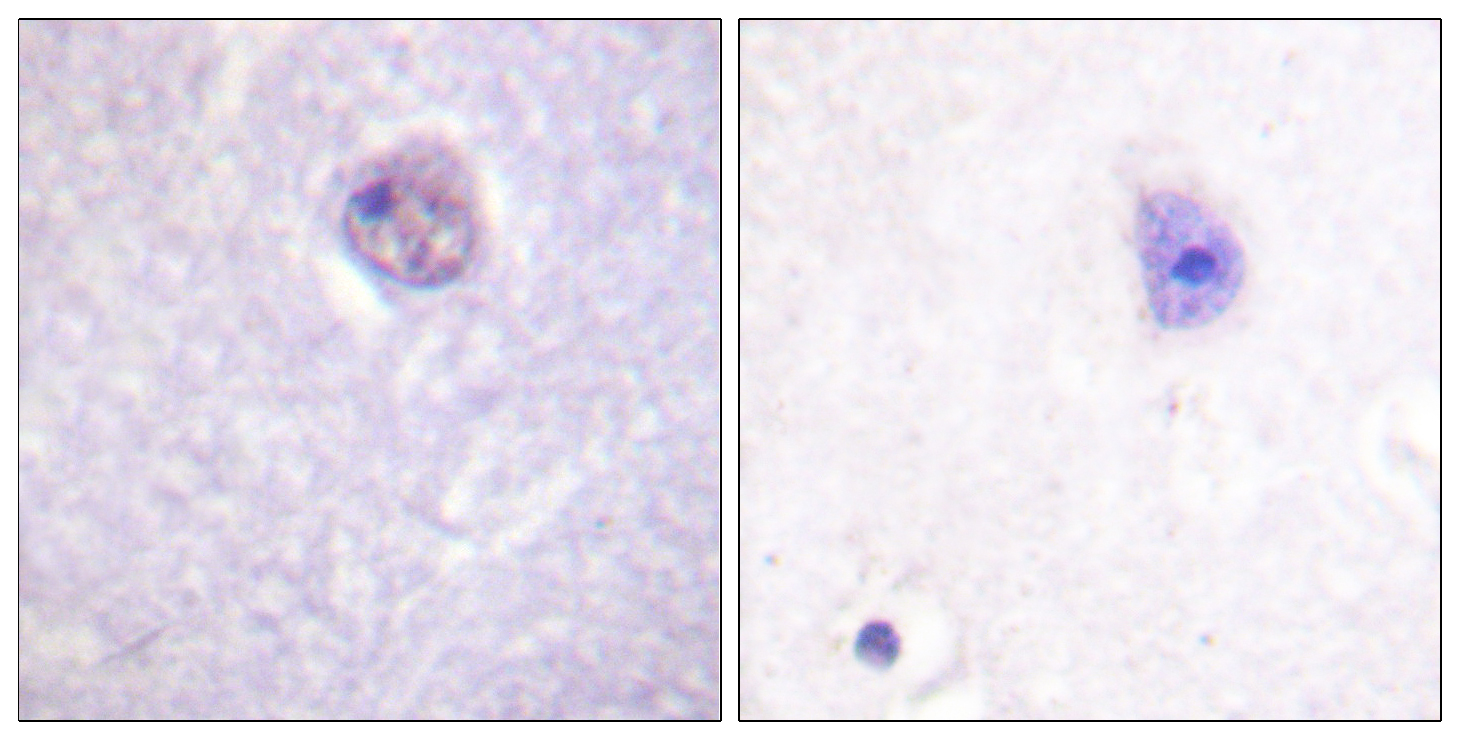
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human brain, using SOX-9 (Phospho-Ser181) Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.