IkB-α(N-term) mouse mAb
- Catalog No.:YM1283
- Applications:WB
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Target:
- IκB-α
- Fields:
- >>cAMP signaling pathway;>>Chemokine signaling pathway;>>NF-kappa B signaling pathway;>>Apoptosis;>>Osteoclast differentiation;>>Toll-like receptor signaling pathway;>>NOD-like receptor signaling pathway;>>RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway;>>Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway;>>C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway;>>IL-17 signaling pathway;>>Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation;>>Th17 cell differentiation;>>T cell receptor signaling pathway;>>B cell receptor signaling pathway;>>TNF signaling pathway;>>Neurotrophin signaling pathway;>>Adipocytokine signaling pathway;>>Relaxin signaling pathway;>>Insulin resistance;>>Alcoholic liver disease;>>Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection;>>Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection;>>Shigellosis;>>Salmonella infection;>>Legionellosis;>>Yersinia infection;>>Leishmaniasis;>>Chagas disease;>>Toxoplasmosis;>>Hepatitis C;>>Hepatitis B;>>Measles;>>Human cytomegalovirus infection;>>Influenza A;>>Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection;>>
- Gene Name:
- NFKBIA IKBA MAD3 NFKBI
- Protein Name:
- NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha
- Human Gene Id:
- 4792
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P25963
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q9Z1E3
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant human IkB-alpha(N-terminus) protein fragments expressed in E.coli.
- Specificity:
- This antibody detects endogenous levels of IkB-alpha(N-terminus) and does not cross-react with related proteins.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- wb 1:1000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from mouse ascites by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- I kappa B alpha;I kappa B alpha;I(Kappa)B(alpha);I(Kappa)B(alpha);I-kappa-B-alpha;IkappaBalpha;IkB-alpha;IKBA;IKBA;IKBA_HUMAN;IKBalpha;MAD 3;MAD 3;MAD3;Major histocompatibility complex enhancer binding protein MAD3;Major histocompatibility complex enhancer binding protein MAD3;Major histocompatibility complex enhancer-binding protein MAD3;NF kappa B inhibitor alpha;NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha;NFKBI;NFKBI;NFKBIA;NFKBIA;Nuclear factor of kappa light chain gene enhancer in B cells;Nuclear factor of kappa light chain gene enhancer in B cells;Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells inhibitor alpha;Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells inhibitor alpha.
- Observed Band(KD):
- about 40kd
- Background:
- This gene encodes a member of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor family, which contain multiple ankrin repeat domains. The encoded protein interacts with REL dimers to inhibit NF-kappa-B/REL complexes which are involved in inflammatory responses. The encoded protein moves between the cytoplasm and the nucleus via a nuclear localization signal and CRM1-mediated nuclear export. Mutations in this gene have been found in ectodermal dysplasia anhidrotic with T-cell immunodeficiency autosomal dominant disease. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in NFKBIA are the cause of ectodermal dysplasia anhidrotic with T-cell immunodeficiency autosomal dominant (ADEDAID) [MIM:612132]. Ectodermal dysplasia defines a heterogeneous group of disorders due to abnormal development of two or more ectodermal structures. ADEDAID is an ectodermal dysplasia associated with decreased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and certain interferons, rendering patients susceptible to infection.,function:Inhibits the activity of dimeric NF-kappa-B/REL complexes by trapping REL dimers in the cytoplasm through masking of their nuclear localization signals. On cellular stimulation by immune and proinflammatory responses, becomes phosphorylated promoting ubiquitination and degradation, enabling the dimeric RELA to tranlocate to the nucleus and activate transcription.,induction:Induced in adherent monocytes.,online information:NFKBIA mutation
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm by a nuclear localization signal (NLS) and a CRM1-dependent nuclear export. .
- Expression:
- Brain,Kidney,Lymph node,Monocyte,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Western blot detection of IkB-alpha(N-terminus) in Jurkat and Hela cell lysates using IkB-alpha(N-terminus) mouse mAb (1:1000 diluted).Predicted band size: 36KDa.Observed band size: 36KDa.
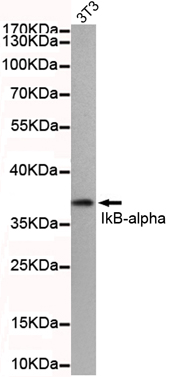
- Western blot detection of IkB-alpha(N-terminus) in 3T3 cell lysate using IkB-alpha(N-terminus) mouse mAb (1:500 diluted).Predicted band size: 36KDa.Observed band size: 36KDa.



