Dynactin 1 Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM1031
- Applications:WB;IF
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Bovine;Pig
- Target:
- Dynactin 1
- Fields:
- >>Vasopressin-regulated water reabsorption;>>Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis;>>Huntington disease;>>Pathways of neurodegeneration - multiple diseases;>>Salmonella infection
- Gene Name:
- DCTN1
- Protein Name:
- Dynactin subunit 1
- Human Gene Id:
- 1639
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q14203
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 13191
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- O08788
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant human Dynactin 1 protein fragments expressed in E.coli.
- Specificity:
- Dynactin 1 Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Dynactin 1 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:1000 - 1:2000. IF 1:100 - 1:500. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- DCTN1;Dynactin subunit 1;150 kDa dynein-associated polypeptide;DAP-150;DP-150;p135;p150-glued
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 142kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes the largest subunit of dynactin, a macromolecular complex consisting of 10 subunits ranging in size from 22 to 150 kD. Dynactin binds to both microtubules and cytoplasmic dynein. Dynactin is involved in a diverse array of cellular functions, including ER-to-Golgi transport, the centripetal movement of lysosomes and endosomes, spindle formation, chromosome movement, nuclear positioning, and axonogenesis. This subunit interacts with dynein intermediate chain by its domains directly binding to dynein and binds to microtubules via a highly conserved glycine-rich cytoskeleton-associated protein (CAP-Gly) domain in its N-terminus. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. Mutations in this gene cause distal hereditary motor neuronopathy type VIIB (HMN7B) which is also known as distal spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy (dSBMA). [
- Function:
- disease:Defects in DCTN1 are the cause of progressive lower motor neuron disease (PLMND) [MIM:607641]. PLMND is a progressive dominant disease that has no sensory symptoms.,function:Required for the cytoplasmic dynein-driven retrograde movement of vesicles and organelles along microtubules. Dynein-dynactin interaction is a key component of the mechanism of axonal transport of vesicles and organelles.,PTM:Phosphorylated.,similarity:Belongs to the dynactin 150 kDa subunit family.,similarity:Contains 1 CAP-Gly domain.,subunit:Large macromolecular complex of at least 10 components; p150(glued) binds directly to microtubules and to cytoplasmic dynein. Interacts with the C-terminus of MAPRE1, MAPRE2 and MAPRE3.,tissue specificity:Brain.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome, centriole . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle . Nucleus envelope . Cytoplasm, cell cortex . Localizes to microtubule plus ends (PubMed:17828277, PubMed:22777741, PubMed:25774020). Localizes preferentially to the ends of tyrosinated microtubules (PubMed:26972003). Localization at centrosome is regulated by SLK-dependent phosphorylation (PubMed:23985322). Localizes to centrosome in a PARKDA-dependent manner (PubMed:20719959). Localizes to the subdistal appendage region of the centriole in a KIF3A-dependent manner (PubMed:23386061). PLK1-mediated phosphorylation at Ser-179 is essential for its localization in the nuclear
- Expression:
- Brain.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
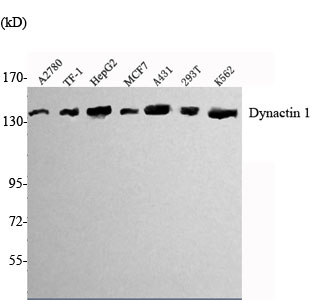
- Western Blot analysis using Dynactin 1 Monoclonal Antibody against A2780, TF-1, HepG2, MCF7, A431, K562 cell lysate.



