Aldose Reductase Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM1008
- Applications:WB
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Dog;Rabbit
- Target:
- AKR1B1
- Fields:
- >>Pentose and glucuronate interconversions;>>Fructose and mannose metabolism;>>Galactose metabolism;>>Glycerolipid metabolism;>>Folate biosynthesis;>>Metabolic pathways
- Gene Name:
- AKR1B1
- Protein Name:
- Aldose reductase
- Human Gene Id:
- 231
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P15121
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 11677
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P45376
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P07943
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant human Aldose Reductase protein fragments expressed in E.coli.
- Specificity:
- Aldose Reductase Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Aldose Reductase protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:1000 - 1:2000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- AKR1B1;ALDR1;Aldose reductase;AR;Aldehyde reductase;Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B1
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 36kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a member of the aldo/keto reductase superfamily, which consists of more than 40 known enzymes and proteins. This member catalyzes the reduction of a number of aldehydes, including the aldehyde form of glucose, and is thereby implicated in the development of diabetic complications by catalyzing the reduction of glucose to sorbitol. Multiple pseudogenes have been identified for this gene. The nomenclature system used by the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee to define human aldo-keto reductase family members is known to differ from that used by the Mouse Genome Informatics database. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2009],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:Alditol + NAD(P)(+) = aldose + NAD(P)H.,disease:In diabetes and galactosemia, increased AR activity leads to high levels of sorbitol and galactitol, respectively, in the cells of many tissues. Accumulation of sugar alcohols has been shown to cause osmotic cataracts in the lens. AR is also thought to play a key role in diabetic complications of three other target tissues, namely, nerve, kidney and retina.,enzyme regulation:Cys-299 may regulate the kinetic and inhibition properties of the enzyme, but does not participate in catalysis.,function:Catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of a wide variety of carbonyl-containing compounds to their corresponding alcohols with a broad range of catalytic efficiencies.,similarity:Belongs to the aldo/keto reductase family.,subunit:Monomer.,tissue specificity:Highly expressed in embryonic epithelial cells (EUE) in response to osmoti
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm.
- Expression:
- Highly expressed in embryonic epithelial cells (EUE) in response to osmotic stress.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
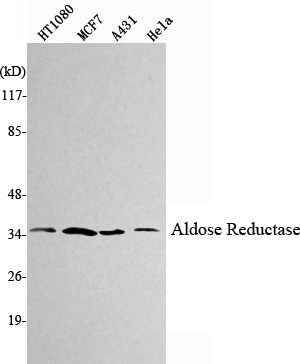
- Western Blot analysis using Aldose Reductase Monoclonal Antibody against HT1080, MCF7, A431, HeLa cell lysate.



