MuSK Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0457
- Applications:IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- MuSK
- Gene Name:
- MUSK
- Protein Name:
- Muscle, skeletal receptor tyrosine-protein kinase
- Human Gene Id:
- 4593
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- O15146
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q61006
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant extracellular fragment of human MuSK (aa24-209) fused with hIgGFc tag expressed in HEK293 cell line.
- Specificity:
- MuSK Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of MuSK protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:200 - 1:1000. IF 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- MUSK;Muscle; skeletal receptor tyrosine-protein kinase;Muscle-specific tyrosine-protein kinase receptor;MuSK;Muscle-specific kinase receptor
- References:
- 1. J Neuroimmunol. 2006 Aug;177(1-2):119-31.
2. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1132:76-83.
- Background:
- This gene encodes a muscle-specific tyrosine kinase receptor. The encoded protein may play a role in clustering of the acetylcholine receptor in the postsynaptic neuromuscular junction. Mutations in this gene have been associated with congenital myasthenic syndrome. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:ATP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine = ADP + a [protein]-L-tyrosine phosphate.,disease:Defects in MUSK is a cause of autosomal recessive congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) [MIM:608931]. Congenital myasthenic syndromes are inherited disorders of neuromuscular transmission that stem from mutations in presynaptic, synaptic, or postsynaptic proteins. MUSK mutations lead to decreased agrin-dependent AChR aggregation, a critical step in the formation of the neuromuscular junction.,function:Receptor tyrosine kinase that is a key mediator of agrin's action and is involved in neuromuscular junction (NMJ) organization.,online information:MuSK entry,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family.,similarity:Contains 1 FZ (frizzled) domain.,similarity:Contains 1 protein kinase domain.,similarity:Contains 3 Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains.,s
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell junction, synapse, postsynaptic cell membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein . Colocalizes with acetylcholine receptors (AChR) to the postsynaptic cell membrane of the neuromuscular junction. .
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
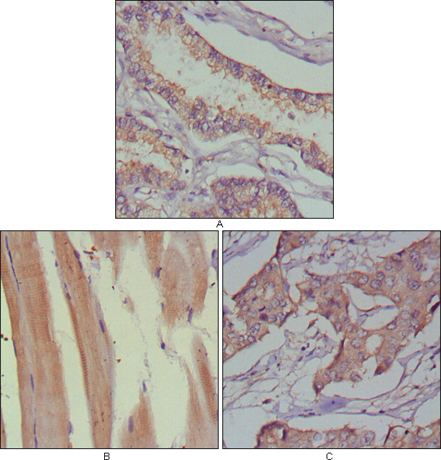
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human lung cancer (A), muscles (B) and breast cancer (C) with DAB staining using MuSK Monoclonal Antibody.
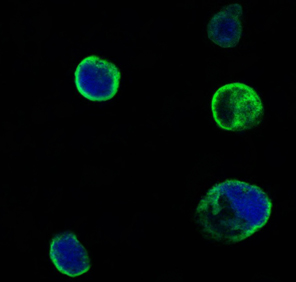
- Confocal immunofluorescence analysis of HEK293 cells trasfected with extracellular MUSK (aa24-209)-hIgGFc using MuSK Monoclonal Antibody (green). Blue: DRAQ5 fluorescent DNA dye.



