MTDH Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0454
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;FCM;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- MTDH
- Gene Name:
- MTDH
- Protein Name:
- Protein LYRIC
- Human Gene Id:
- 92140
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q86UE4
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q80WJ7
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant fragment of human MTDH expressed in E. Coli.
- Specificity:
- MTDH Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of MTDH protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:200 - 1:1000. Flow cytometry: 1:200 - 1:400. ELISA: 1:10000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- MTDH;AEG1;LYRIC;Protein LYRIC;3D3/LYRIC;Astrocyte elevated gene-1 protein;AEG-1;Lysine-rich CEACAM1 co-isolated protein;Metadherin;Metastasis adhesion protein
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 64kD
- References:
- 1. Cancer Cell. 2004 Apr;5(4):365-74.
2. Exp Cell Res. 2004 Oct 15;300(1):134-48.
3. Cancer Cell. 2009 Jan 6;15(1):9-20.
- Background:
- caution:Was originally (PubMed:15093543) thought to be a type II membrane protein but this is inconsistent with the results of multiple phosphorylation studies because this topology would locate the phosphorylation sites in the lumen or extracellularly rather than in the cytoplasm.,function:Downregulates SLC1A2/EAAT2 promoter activity when expressed ectopically. Activates the nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-kappa-B) transcription factor. Promotes anchorage-independent growth of immortalized melanocytes and astrocytes which is a key component in tumor cell expansion. Promotes lung metastasis and also has an effect on bone and brain metastasis, possibly by enhancing the seeding of tumor cells to the target organ endothelium. Induces chemoresistance.,induction:By TNF-alpha (at protein level). By HIV-1 infection of primary fetal astrocytes.,miscellaneous:Knockdown significantly reduces the adhesion of cancer cells to lung microvascular endothelial cells and the reciprocal effect is observed following overexpression.,subcellular location:In epithelial cells, recruited to tight junctions (TJ) during the maturation of the TJ complexes. A nucleolar staining may be due to nuclear targeting of an isoform lacking the transmembrane domain (By similarity). TNF-alpha causes translocation from the cytoplasm to the nucleus.,subunit:Interacts with BCIPP, CREBBP/CBP and RELA/p65.,tissue specificity:Widely expressed with highest levels in muscle-dominating organs such as skeletal muscle, heart, tongue and small intestine and in endocrine glands such as thyroid and adrenal gland. Overexpressed in various cancers including breast, brain, prostate, melanoma and glioblastoma multiforme.,
- Function:
- caution:Was originally (PubMed:15093543) thought to be a type II membrane protein but this is inconsistent with the results of multiple phosphorylation studies because this topology would locate the phosphorylation sites in the lumen or extracellularly rather than in the cytoplasm.,function:Downregulates SLC1A2/EAAT2 promoter activity when expressed ectopically. Activates the nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-kappa-B) transcription factor. Promotes anchorage-independent growth of immortalized melanocytes and astrocytes which is a key component in tumor cell expansion. Promotes lung metastasis and also has an effect on bone and brain metastasis, possibly by enhancing the seeding of tumor cells to the target organ endothelium. Induces chemoresistance.,induction:By TNF-alpha (at protein level). By HIV-1 infection of primary fetal astrocytes.,miscellaneous:Knockdown significantly reduces the adhesi
- Subcellular Location:
- Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Single-pass membrane protein. Nucleus membrane ; Single-pass membrane protein . Cell junction, tight junction . Nucleus, nucleolus . Cytoplasm, perinuclear region. In epithelial cells, recruited to tight junctions (TJ) during the maturation of the TJ complexes. A nucleolar staining may be due to nuclear targeting of an isoform lacking the transmembrane domain (By similarity). TNF-alpha causes translocation from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. .
- Expression:
- Widely expressed with highest levels in muscle-dominating organs such as skeletal muscle, heart, tongue and small intestine and in endocrine glands such as thyroid and adrenal gland. Overexpressed in various cancers including breast, brain, prostate, melanoma and glioblastoma multiforme.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Western Blot analysis using MTDH Monoclonal Antibody against K562 (1), SKBR-3 (2), T47D (3), HeLa (4) and MCF-7 (5) cell lysate.
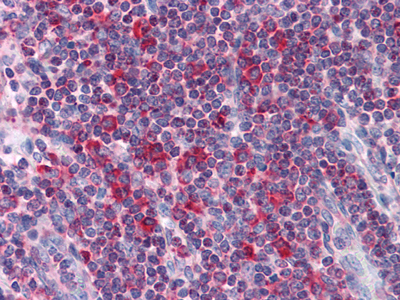
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human Liver tissues with AEC staining using MTDH Monoclonal Antibody.
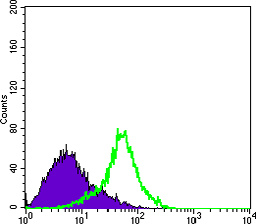
- Flow cytometric analysis of Hela cells using MTDH Monoclonal Antibody (green) and negative control (purple).



