GCK Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0302
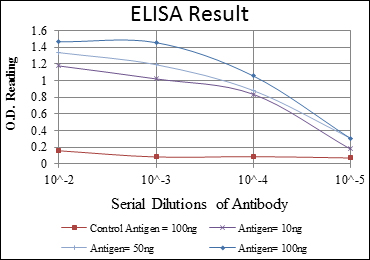
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- GCK
- Fields:
- >>Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis;>>Galactose metabolism;>>Starch and sucrose metabolism;>>Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism;>>Neomycin, kanamycin and gentamicin biosynthesis;>>Metabolic pathways;>>Carbon metabolism;>>Biosynthesis of nucleotide sugars;>>Insulin signaling pathway;>>Insulin secretion;>>Prolactin signaling pathway;>>Glucagon signaling pathway;>>Type II diabetes mellitus;>>Maturity onset diabetes of the young;>>Central carbon metabolism in cancer
- Gene Name:
- GCK
- Protein Name:
- Glucokinase
- Human Gene Id:
- 2645
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P35557
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P52792
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant fragment of human GCK expressed in E. Coli.
- Specificity:
- GCK Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of GCK protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:10000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- GCK;Glucokinase;Hexokinase type IV;HK IV;Hexokinase-4;HK4;Hexokinase-D
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 52kD
- References:
- 1. Mol Endocrinol. 2009 Dec;23(12):1983-9.
2. Int J Mol Med. 2009 Aug;24(2):233-46.
- Background:
- Hexokinases phosphorylate glucose to produce glucose-6-phosphate, the first step in most glucose metabolism pathways. Alternative splicing of this gene results in three tissue-specific forms of glucokinase, one found in pancreatic islet beta cells and two found in liver. The protein localizes to the outer membrane of mitochondria. In contrast to other forms of hexokinase, this enzyme is not inhibited by its product glucose-6-phosphate but remains active while glucose is abundant. Mutations in this gene have been associated with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM), maturity onset diabetes of the young, type 2 (MODY2) and persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy (PHHI). [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2009],
- Function:
- catalytic activity:ATP + D-glucose = ADP + D-glucose 6-phosphate.,disease:Defects in GCK are the cause of familial hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia type 3 (HHF3) [MIM:602485]. HHF is the most common cause of persistent hypoglycemia in infancy. Unless early and aggressive intervention is undertaken, brain damage from recurrent episodes of hypoglycemia may occur.,disease:Defects in GCK are the cause of maturity onset diabetes of the young type 2 (MODY2) [MIM:125851]; also shortened MODY-2. MODY [MIM:606391] is a form of diabetes mellitus characterized by autosomal dominant transmission and early age of onset. Mutations in GCK result in mild chronic hyperglycemia due to reduced pancreatic beta cell responsiveness to glucose, decreased net accumulation of hepatic glycogen and increased hepatic gluconeogenesis following meals.,enzyme regulation:The use of alternative promoters apparently enables
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm . Nucleus . Mitochondrion . Under low glucose concentrations, GCK associates with GCKR and the inactive complex is recruited to the hepatocyte nucleus. .
- Expression:
- Lung,Pancreas,Placenta,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Western Blot analysis using GCK Monoclonal Antibody against HEK293 (1) and GCK-hIgGFc transfected HEK293 (2) cell lysate.