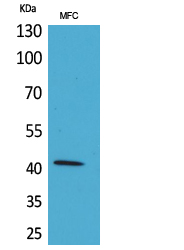
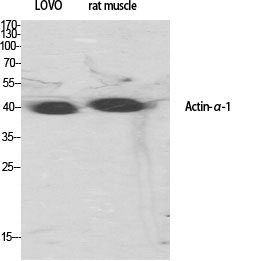
Total Actin α1 Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA3199C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Gene Name:
- ACTA1
- Human Gene Id:
- 58
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P68133
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P68134
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P68136
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- Actin, alpha skeletal muscle (Alpha-actin-1)
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- disease:Defects in ACTA1 are a cause of congenital myopathy with excess of thin myofilaments (CM) [MIM:102610].,disease:Defects in ACTA1 are a cause of congenital myopathy with fiber-type disproportion (CFTD) [MIM:255310]; also known as congenital fiber-type disproportion myopathy (CFTDM). CFTD is a genetically heterogeneous disorder in which there is relative hypotrophy of type 1 muscle fibers compared to type 2 fibers on skeletal muscle biopsy. However, these findings are not specific and can be found in many different myopathic and neuropathic conditions.,disease:Defects in ACTA1 are the cause of nemaline myopathy type 3 (NEM3) [MIM:161800]. Nemaline myopathy (NEM) is a form of congenital myopathy characterized by abnormal thread- or rod-like structures in muscle fibers on histologic examination. The clinical phenotype is highly variable, with differing age at onset and severity.,function:Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in various types of cell motility and are ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic cells.,miscellaneous:In vertebrates 3 main groups of actin isoforms, alpha, beta and gamma have been identified. The alpha actins are found in muscle tissues and are a major constituent of the contractile apparatus. The beta and gamma actins coexist in most cell types as components of the cytoskeleton and as mediators of internal cell motility.,similarity:Belongs to the actin family.,subunit:Polymerization of globular actin (G-actin) leads to a structural filament (F-actin) in the form of a two-stranded helix. Each actin can bind to 4 others. Interacts with TTID.,
- Function:
- muscle system process, muscle contraction, cytoskeleton organization, actin filament organization, muscle organ development, skeletal muscle tissue development, regulation of cell size, response to mechanical stimulus, response to abiotic stimulus, response to endogenous stimulus, response to hormone stimulus, response to extracellular stimulus, response to organic substance, cellular component assembly involved in morphogenesis, striated muscle tissue development, skeletal myofibril assembly, striated muscle adaptation, cell growth, actin filament-based process,actin cytoskeleton organization, myofibril assembly, muscle thin filament assembly, actomyosin structure organization,regulation of cellular component size, cellular component morphogenesis, growth, muscle cell differentiation, response to long exposure to lithium ion, muscle adaptation, skeletal muscle adaptation, skeletal muscl
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs