CD141 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT0725
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Rat;Mouse;
- Target:
- CD141
- Fields:
- >>Complement and coagulation cascades;>>AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications;>>Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis
- Gene Name:
- THBD
- Protein Name:
- Thrombomodulin
- Human Gene Id:
- 7056
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P07204
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P15306
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human THBD. AA range:526-575
- Specificity:
- CD141 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of CD141 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:5000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- THBD;THRM;Thrombomodulin;TM;Fetomodulin;CD antigen CD141
- Observed Band(KD):
- 100kD
- Background:
- The protein encoded by this intronless gene is an endothelial-specific type I membrane receptor that binds thrombin. This binding results in the activation of protein C, which degrades clotting factors Va and VIIIa and reduces the amount of thrombin generated. Mutations in this gene are a cause of thromboembolic disease, also known as inherited thrombophilia. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in THBD are the cause of thrombophilia due to thrombomodulin defect (THR-THBDD) [MIM:188040]. THR-THBDD is a hemostatic disorder characterized by a tendency to thrombosis.,function:Thrombomodulin is a specific endothelial cell receptor that forms a 1:1 stoichiometric complex with thrombin. This complex is responsible for the conversion of protein C to the activated protein C (protein Ca). Once evolved, protein Ca scissions the activated cofactors of the coagulation mechanism, factor Va and factor VIIIa, and thereby reduces the amount of thrombin generated.,online information:Thrombomodulin,online information:Thrombomodulin entry,PTM:N-glycosylated.,PTM:The iron and 2-oxoglutarate dependent 3-hydroxylation of aspartate and asparagine is (R) stereospecific within EGF domains.,similarity:Contains 1 C-type lectin domain.,similarity:Contains 6 EGF-like domains.,tissue specific
- Subcellular Location:
- Membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.
- Expression:
- Endothelial cells are unique in synthesizing thrombomodulin.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
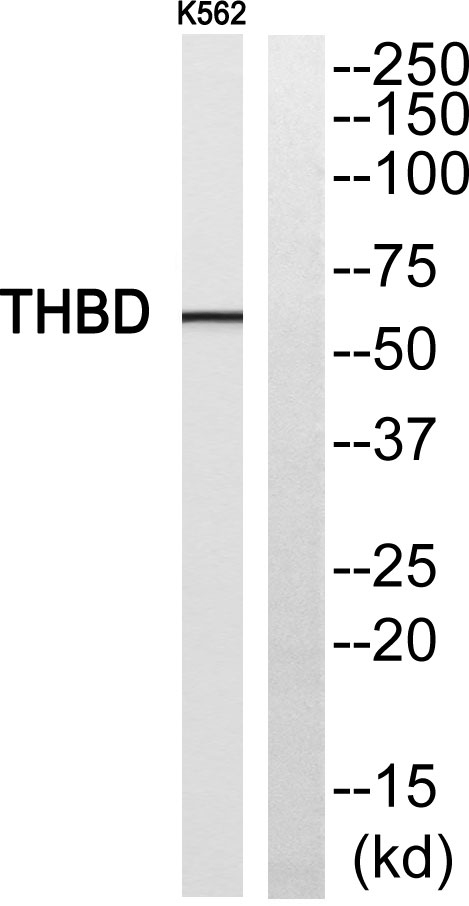
- Western blot analysis of THBD Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the THBD peptide.
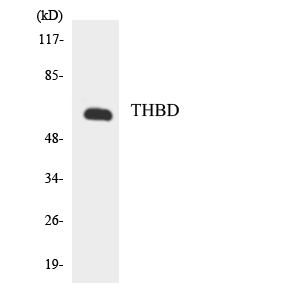
- Western blot analysis of the lysates from HeLa cells using THBD antibody.



