SFRP1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YN1999
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- SFRP1
- Fields:
- >>Wnt signaling pathway
- Gene Name:
- SFRP1 FRP FRP1 SARP2
- Protein Name:
- Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 (FRP-1) (sFRP-1) (Secreted apoptosis-related protein 2) (SARP-2)
- Human Gene Id:
- 6422
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q8N474
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q8C4U3
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q9R168
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from part region of human protein
- Specificity:
- SFRP1 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000 ELISA 1:5000-20000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Observed Band(KD):
- 34kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a member of the SFRP family that contains a cysteine-rich domain homologous to the putative Wnt-binding site of Frizzled proteins. Members of this family act as soluble modulators of Wnt signaling; epigenetic silencing of SFRP genes leads to deregulated activation of the Wnt-pathway which is associated with cancer. This gene may also be involved in determining the polarity of photoreceptor cells in the retina. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009],
- Function:
- domain:The FZ domain is involved in binding with Wnt ligands.,function:Soluble frizzled-related proteins (sFRPS) function as modulators of Wnt signaling through direct interaction with Wnts. They have a role in regulating cell growth and differentiation in specific cell types. SFRP1 decreases intracellular beta-catenin levels (By similarity). Has antiproliferative effects on vascular cells, in vitro and in vivo, and can induce, in vivo, an angiogenic response. In vascular cell cycle, delays the G1 phase and entry into the S phase (By similarity). In kidney development, inhibits tubule formation and bud growth in metanephroi (By similarity). Inhibits WNT1/WNT4-mediated TCF-dependent transcription.,induction:Down-regulated in colorectal and breast tumors. Up-regulated in uterine leiomyomas under high estrogenic conditions. Expression, in leiomyomal cells, also increased both under hypoxic
- Subcellular Location:
- Secreted. Cell membrane or extracellular matrix-associated. Released by heparin-binding.
- Expression:
- Widely expressed. Absent from lung, liver and peripheral blood leukocytes. Highest levels in heart and fetal kidney. Also expressed in testis, ovary, fetal brain and lung, leiomyomal cells, myometrial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells. Expressed in foreskin fibroblasts and in keratinocytes.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
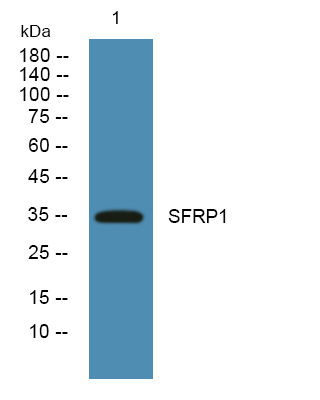
- Western blot analysis of lysates from K562 cells, primary antibody was diluted at 1:1000, 4°over night



