Kir4.1 rabbit pAb
- Catalog No.:YT7795
- Applications:WB;IHC
- Reactivity:Human;Rat;Mouse
- Target:
- Kir4.1
- Fields:
- >>Gastric acid secretion;>>Huntington disease
- Gene Name:
- KCNJ10
- Protein Name:
- Kir4.1
- Human Gene Id:
- 3766
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P78508
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 16513
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q9JM63
- Rat Gene Id:
- 29718
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P49655
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human Kir4.1 AA range: 160-240
- Specificity:
- This antibody detects endogenous levels of Human,Rat,Mouse Kir4.1
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000;IHC 1:50-300
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 10 (ATP-dependent inwardly rectifying potassium channel Kir4.1;Inward rectifier K(+) channel Kir1.2;Potassium channel, inwardly rectifying subfamily J member 10)
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 42kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes a member of the inward rectifier-type potassium channel family, characterized by having a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into, rather than out of, a cell. The encoded protein may form a heterodimer with another potassium channel protein and may be responsible for the potassium buffering action of glial cells in the brain. Mutations in this gene have been associated with seizure susceptibility of common idiopathic generalized epilepsy syndromes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- function:May be responsible for potassium buffering action of glial cells in the brain. Inward rectifier potassium channels are characterized by a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into the cell rather than out of it. Their voltage dependence is regulated by the concentration of extracellular potassium; as external potassium is raised, the voltage range of the channel opening shifts to more positive voltages. The inward rectification is mainly due to the blockage of outward current by internal magnesium. Can be blocked by extracellular barium and cesium.,similarity:Belongs to the inward rectifier-type potassium channel family.,subunit:Seems to form heterodimer with Kir5.1/KCNJ16. Interacts with INADL.,
- Subcellular Location:
- Membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein. Basolateral cell membrane . In kidney distal convoluted tubules, located in the basolateral membrane where it colocalizes with KCNJ16. .
- Expression:
- Expressed in kidney (at protein level).
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
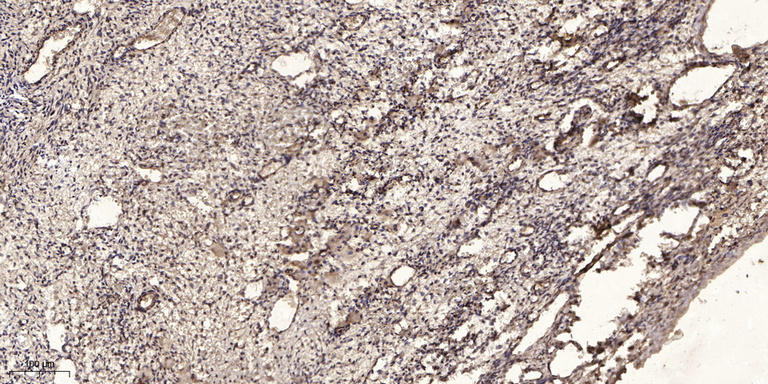
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human oophoroma. 1, Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 45min).


