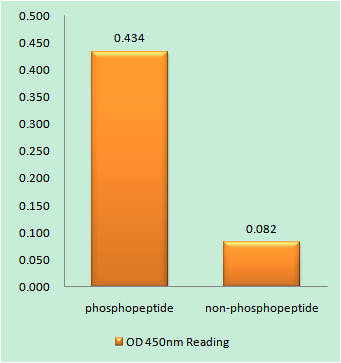
Tau (phospho Ser404) Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YP0264
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- Tau
- Fields:
- >>MAPK signaling pathway;>>Alzheimer disease;>>Parkinson disease;>>Pathways of neurodegeneration - multiple diseases
- Gene Name:
- MAPT
- Protein Name:
- Microtubule-associated protein tau
- Human Gene Id:
- 4137
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P10636
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 17762
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P10637
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P19332
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Tau around the phosphorylation site of Ser404. AA range:691-740
- Specificity:
- Phospho-Tau (S404) Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Tau protein only when phosphorylated at S404.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. ELISA: 1:20000. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- MAPT;MAPTL;MTBT1;TAU;Microtubule-associated protein tau;Neurofibrillary tangle protein;Paired helical filament-tau;PHF-tau
- Observed Band(KD):
- 50-85kD
- Background:
- This gene encodes the microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) whose transcript undergoes complex, regulated alternative splicing, giving rise to several mRNA species. MAPT transcripts are differentially expressed in the nervous system, depending on stage of neuronal maturation and neuron type. MAPT gene mutations have been associated with several neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Pick's disease, frontotemporal dementia, cortico-basal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- alternative products:Additional isoforms seem to exist. Isoforms differ from each other by the presence or absence of up to 5 of the 15 exons. One of these optional exons contains the additional tau/MAP repeat,developmental stage:Four-repeat (type II) tau is expressed in an adult-specific manner and is not found in fetal brain, whereas three-repeat (type I) tau is found in both adult and fetal brain.,disease:Defects in MAPT are a cause of corticobasal degeneration (CBD). It is marked by extrapyramidal signs and apraxia and can be associated with memory loss. Neuropathologic features may overlap Alzheimer disease, progressive supranuclear palsy, and Parkinson disease.,disease:Defects in MAPT are a cause of frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17 (FTDP17) [MIM:600274, 172700]; also called frontotemporal dementia (FTD) or historically termed Pick complex. This form
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm, cytosol . Cell membrane ; Peripheral membrane protein ; Cytoplasmic side . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton . Cell projection, axon . Cell projection, dendrite . Secreted . Mostly found in the axons of neurons, in the cytosol and in association with plasma membrane components (PubMed:10747907). Can be secreted; the secretion is dependent on protein unfolding and facilitated by the cargo receptor TMED10; it results in protein translocation from the cytoplasm into the ERGIC (endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment) followed by vesicle entry and secretion (PubMed:32272059). .
- Expression:
- Expressed in neurons. Isoform PNS-tau is expressed in the peripheral nervous system while the others are expressed in the central nervous system.
Trimethylamine N-oxide aggravated cognitive impairment from APP/PS1 mice and protective roles of voluntary exercise
Effects of Quercetin Intervention on Cognition Function in APP/PS1 Mice was Affected by Vitamin D Status. MOLECULAR NUTRITION & FOOD RESEARCH Mol Nutr Food Res. 2018 Dec;62(24):1800621 WB Mouse hippocampus , parietal cortex
Chia Seed Does Not Improve Cognitive Impairment in SAMP8 Mice Fed with High Fat Diet. Nutrients 2018 Aug 14 WB Mouse hippocampus,parietal cortex
Voluntary wheel running is capable of improving cognitive function only in the young but not the middle-aged male APPSwe/PS1De9 mice. NEUROCHEMISTRY INTERNATIONAL Neurochem Int. 2021 May;145:105010 WB Mouse Parietal-temporal cortex,hippocampus
Dietary lactoferrin has differential effects on gut microbiota in young versus middle-aged APPswe/PS1dE9 transgenic mice but no effects on cognitive function. Food & Nutrition Research Food Nutr Res. 2021; 65: 10.29219/fnr.v65.5496 WB Mouse Hippocampus, cortex
The combination of 1α,25dihydroxyvitaminD3 with resveratrol improves neuronal degeneration by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress, insulin signaling and inhibiting tau hyperphosphorylation in SH-SY5Y cells. FOOD AND CHEMICAL TOXICOLOGY 2016 Apr 28 WB Human 1:1000 SH-SY5Y total cell
Quercetin is protective against short‐term dietary advanced glycation end products intake induced cognitive dysfunction in aged ICR mice. JOURNAL OF FOOD BIOCHEMISTRY J Food Biochem. 2020 Apr;44(4):e13164 WB Mouse hippocampus,cortex
The combination of 1α, 25dihydroxyvitaminD3 with resveratrol improves neuronal degeneration by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress, insulin signaling and inhibiting tau hyperphosphorylation in SH-SY5Y cells." Food and Chemical Toxicology 93 (2016): 32-40.
Cheng, Jinbo, et al. "Vitamin D combined with resveratrol prevents cognitive decline in SAMP8 mice." Current Alzheimer Research 14.8 (2017): 820-833.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
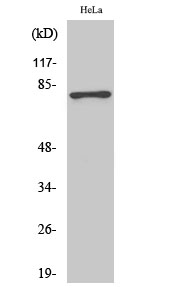
- Western Blot analysis of various cells using Phospho-Tau (S404) Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:2000

- Western blot analysis of lysates from 293 cells treated with UV, using Tau (Phospho-Ser404) Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.