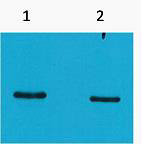
GR (Acetyl Lys494) rabbit pAb
- Catalog No.:YK0115
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- GR
- Fields:
- >>Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction
- Gene Name:
- NR3C1 GRL
- Protein Name:
- GR (Acetyl Lys494)
- Human Gene Id:
- 2908
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P04150
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P06537
- Rat Gene Id:
- 24413
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P06536
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human GR (Acetyl Lys494)
- Specificity:
- This antibody detects endogenous levels of Human,Mouse,Rat GR (Acetyl Lys494)
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:1000-2000 ELISA 1:5000-20000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit serum by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- Glucocorticoid receptor (GR;Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group C member 1)
- Observed Band(KD):
- 85kD
- Background:
- alternative products:At least 4 isoforms, Alpha (shown here), Alpha-B, Beta and Beta-B, are produced by alternative initiation at Met-1 and Met-27. The existence of isoform Alpha and isoform Alpha-B has been proved by mutagenesis. As the sequence environment of the 2 potential ATG initiator codons is the same for the other altrnatively spliced isoforms, alternative initiation of translation could also occur on these transcripts. Additional isoforms seem to exist,disease:Defects in NR3C1 are a cause of glucocorticoid resistance [MIM:138040]; also known as cortisol resistance. It is a hypertensive, hyperandrogenic disorder characterized by increased serum cortisol concentrations. Inheritance is autosomal dominant.,domain:Composed of three domains: a modulating N-terminal domain, a DNA-binding domain and a C-terminal steroid-binding domain.,function:Receptor for glucocorticoids (GC). Has a dual mode of action: as a transcription factor that binds to glucocorticoid response elements (GRE) and as a modulator of other transcription factors. Affects inflammatory responses, cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Could act as a coactivator for STAT5-dependent transcription upon growth hormone (GH) stimulation and could reveal an essential role of hepatic GR in the control of body growth. Involved in chromatin remodeling. Plays a significant role in transactivation. Involved in nuclear translocation.,miscellaneous:Can up- or down-modulate aggregation and nuclear localization of expanded polyglutamine polypeptides derived from AR and HD through specific regulation of gene expression. Aggregation and nuclear localization of expanded polyglutamine proteins are regulated cellular processes that can be modulated by this receptor, a well-characterized transcriptional regulator.,miscellaneous:High constitutive expression of isoform beta by neutrophils may provide a mechanism by which these cells escape glucocorticoid-induced cell death. Up-regulation by proinflammatory cytokines such as IL8 further enhances their survival in the presence of glucocorticoids during inflammation.,online information:Glucocorticoid receptor entry,polymorphism:Carriers of the 22-Glu-Lys-23 allele are relatively more resistant to the effects of GCs with respect to the sensitivity of the adrenal feedback mechanism than non-carriers, resulting in a better metabolic health profile. Carriers have a better survival than non-carriers, as well as lower serum CRP levels. The 22-Glu-Lys-23 polymorphism is associated with a sex-specific, beneficial body composition at young-adult age, as well as greater muscle strength in males.,PTM:Increased proteasome-mediated degradation in response to glucocorticoids.,PTM:Phosphorylated in the absence of hormone; becomes hyperphosphorylated in the presence of glucocorticoid. The Ser-203-phosphorylated form is mainly cytoplasmic, and the Ser-211-phosphorylated form is nuclear. Transcriptional activity correlates with the amount of phosphorylation at Ser-211.,PTM:Sumoylated; this reduces transcription transactivation.,PTM:Ubiquitinated; restricts glucocorticoid-mediated transcriptional signaling.,similarity:Belongs to the nuclear hormone receptor family. NR3 subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 nuclear receptor DNA-binding domain.,subcellular location:Cytoplasmic in the absence of ligand, nuclear after ligand-binding.,subunit:Heteromultimeric cytoplasmic complex with HSP90, HSP70, and FKBP5 or another immunophilin, or the immunophilin homolog PPP5C. Directly interacts with UNC45A. Upon ligand binding FKBP5 dissociates from the complex and FKBP4 takes its place, thereby linking the complex to dynein and mediating transport to the nucleus, where the complex dissociates (By similarity). Binds to DNA as a homodimer, and as a heterodimer with NR3C2 or the retinoid X receptor. Binds STAT5A and STAT5B homodimers and heterodimers. Interacts with NRIP1, POU2F1, POU2F2 and TRIM28. Interacts with NCOA1, NCOA3, SMARCA4, SMARCC1, SMARCD1, and SMARCE1 (By similarity). Interacts with several coactivator complexes, including the SMARCA4 complex, CREBBP/EP300, TADA2L and p160 coactivators such as NCOA2 and NCOA6. Interaction with BAG1 inhibits transactivation. Interacts with HEXIM1, PELP1 and TGFB1I1.,tissue specificity:Widely expressed. In the heart, detected in left and right atria, left and right ventricles, aorta, apex, intraventricular septum, and atrioventricular node as well as whole adult and fetal heart.,
- Function:
- regulation of carbohydrate metabolic process, regulation of gluconeogenesis, chromatin organization, transcription,transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, intracellular signaling cascade, steroid metabolic process, glucocorticoid metabolic process, response to organic substance, regulation of cellular ketone metabolic process, regulation of cellular carbohydrate metabolic process, regulation of hormone levels, regulation of glucose metabolic process, regulation of cell death, positive regulation of cell death, chromatin modification, regulation of lipid metabolic process, regulation of steroid metabolic process, adrenal gland development, steroid hormone receptor signaling pathway, intracellular receptor-mediated signaling pathway, regulation of glucocorticoid metabolic process, regulation of glucocorticoid
- Subcellular Location:
- [Isoform Alpha]: Cytoplasm . Nucleus . Mitochondrion . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome . After ligand activation, translocates from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. In the presence of NR1D1 shows a time-dependent subcellular localization, localizing to the cytoplasm at ZT8 and to the nucleus at ZT20 (By similarity). Lacks this diurnal pattern of localization in the absence of NR1D1, localizing to both nucleus and the cytoplasm at ZT8 and ZT20 (By similarity). .; [Isoform Beta]: Nucleus . Cytoplasm . Expressed predominantly in the nucleus with some expression also detected in the cytoplasm. .; [Isoform Alpha-B]: Nucleus . Cytoplasm . After ligand activation, translocates from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. .
- Expression:
- Widely expressed including bone, stomach, lung, liver, colon, breast, ovary, pancreas and kidney (PubMed:25847991). In the heart, detected in left and right atria, left and right ventricles, aorta, apex, intraventricular septum, and atrioventricular node as well as whole adult and fetal heart (PubMed:10902803). ; [Isoform Beta]: Widely expressed including brain, bone marrow, thymus, spleen, liver, kidney, pancreas, lung, fat, skeletal muscle, heart, placenta and blood leukocytes. ; [Isoform Alpha-2]: Widely expressed.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs