- Home
- About
- Promotions
-
Products
-
Elisa Kits
- |
-
Primary antibodies
- |
-
Secondary antibodies
- |
-
Proteins
- |
-
IHC reagents
- |
-
WB reagents
- PonceauS Staining Solution
- PBST Washing Buffer, 10X
- 1.5M Tris-HCl Buffer, pH8.8
- 1M Tris-HCl Buffer, pH6.8
- 10% SDS Solution
- Prestained Protein Marker
- TBST Washing Buffer, 10X
- SDS PAGE Loading Buffer, 5X
- Stripping Buffered Solution
- Tris Buffer, pH7.4, 10X
- Total Protein Extraction Kit
- Running Buffer, 10X
- Transfer Buffer, 10X
- 30% Acr-Bis(29:1) Solution
- Tris电泳液速溶颗粒
- PBS(1X, premixed powder)
- TBS(1X, premixed powder)
- 快速封闭液
- 转膜液速溶颗粒
- Chemical reagents
- News
- Distributor
- Resources
- Contact
- Home
- >
- Info
- >
- SOD1 protein
- >
- Go Back
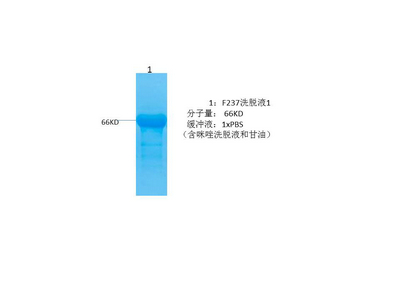
SOD1 protein
- Catalog No.:YD0094
- Applications:WB;SDS-PAGE
- Reactivity:Human
- Protein Name:
- SOD1 protein
- Sequence:
- Amino acid: full length, with his-MBP tag.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS
- Concentration:
- SDS-PAGE >90%
- Storage Stability:
- -20°C/6 mouth,-80°C for long storage
- Other Name:
- Superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] (EC 1.15.1.1) (Superoxide dismutase 1) (hSod1)
- Background:
- catalytic activity:2 superoxide + 2 H(+) = O(2) + H(2)O(2).,cofactor:Binds 1 copper ion per subunit.,cofactor:Binds 1 zinc ion per subunit.,disease:Defects in SOD1 are the cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis type 1 (ALS1) [MIM:105400]. ALS1 is a familial form of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, a neurodegenerative disorder affecting upper and lower motor neurons and resulting in fatal paralysis. Sensory abnormalities are absent. Death usually occurs within 2 to 5 years. The etiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is likely to be multifactorial, involving both genetic and environmental factors. The disease is inherited in 5-10% of cases leading to familial forms.,function:Destroys radicals which are normally produced within the cells and which are toxic to biological systems.,miscellaneous:The protein (both wild-type and ALS1 variants) has a tendency to form fibrillar aggregates in the absence of the intramolecular disulfide bond or of bound zinc ions. These aggregates may have cytotoxic effects. Zinc binding promotes dimerization and stabilizes the native form.,online information:ALS genetic mutations db,online information:Superoxide dismutase entry,PTM:Unlike wild-type protein, the pathogenics variants ALS1 Arg-38, Arg-47, Arg-86 and Ala-94 are polyubiquitinated by RNF19A; which leads to their proteasomal degradation.,similarity:Belongs to the Cu-Zn superoxide dismutase family.,subunit:Homodimer. The pathogenics variants ALS1 Arg-38, Arg-47, Arg-86 and Ala-94 interact with RNF19A, whereas wild-type protein does not.,
- Function:
- MAPKKK cascade, activation of MAPK activity, response to reactive oxygen species, response to superoxide, response to oxygen radical, DNA catabolic process, endonucleolytic, cell morphogenesis, cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation, regulation of action potential, ovarian follicle development, leukocyte homeostasis, regulation of cytokine production, positive regulation of cytokine production, placenta development, tissue homeostasis, retina homeostasis, auditory receptor cell morphogenesis, myeloid cell homeostasis, immune system development,regulation of leukocyte activation, reproductive developmental process, muscle system process, circulatory system process, heart process, vascular process in circulatory system, DNA metabolic process, DNA repair, double-strand break repair, DNA catabolic process, DNA fragmentation involved in apoptosis, protein amino acid phosphorylation,pe
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm . Mitochondrion . Nucleus . Predominantly cytoplasmic; the pathogenic variants ALS1 Arg-86 and Ala-94 gradually aggregates and accumulates in mitochondria. .