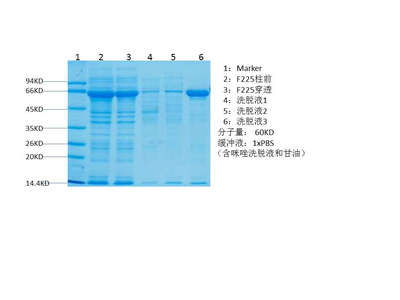
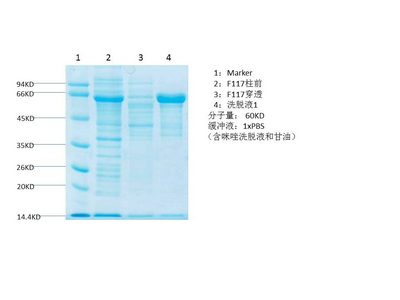
PPAR delta protein
- Catalog No.:YD0086
- Applications:WB;SDS-PAGE
- Reactivity:Human
- Gene Name:
- PPARD NR1C2 PPARB
- Protein Name:
- PPAR delta protein
- Sequence:
- Amino acid: 287-441, with his-MBP tag.
- Human Gene Id:
- 5467
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q03181
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P35396
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS
- Concentration:
- SDS-PAGE >90%
- Storage Stability:
- -20°C/6 mouth,-80°C for long storage
- Other Name:
- Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta (PPAR-delta) (NUCI) (Nuclear hormone receptor 1) (NUC1) (Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group C member 2) (Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor beta) (PPAR-beta)
- Background:
- function:Receptor that binds peroxisome proliferators such as hypolipidemic drugs and fatty acids. Once activated by a ligand, the receptor binds to a promoter element in the gene for acyl-CoA oxidase and activates its transcription. It therefore controls the peroxisomal beta-oxidation pathway of fatty acids. Decreases expression of NPC1L1 once activated by a ligand.,online information:Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor entry,similarity:Belongs to the nuclear hormone receptor family. NR1 subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 nuclear receptor DNA-binding domain.,subunit:Heterodimer with the retinoid X receptor.,tissue specificity:Ubiquitous with maximal levels in placenta and skeletal muscle.,
- Function:
- negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, regulation of action potential, placenta development, maternal placenta development, hair follicle development, reproductive developmental process,monosaccharide metabolic process, glucose metabolic process, generation of precursor metabolites and energy,transcription, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter,fatty acid metabolic process, fatty acid beta-oxidation, isoprenoid metabolic process, vitamin metabolic process, fat-soluble vitamin metabolic process, vitamin A metabolic process, lipid transport, cellular ion homeostasis, apoptosis, cell motion, cell adhesion, ensheathment of neurons, ectoderm development, female pregnancy, embryo implantation,steroid metabolic process, cholesterol metabolic process, cell death, cell proliferation, positive regulati
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus.
- Expression:
- Ubiquitous with maximal levels in placenta and skeletal muscle.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images