- Home
- About
- Promotions
-
Products
-
Elisa Kits
- |
-
Primary antibodies
- |
-
Secondary antibodies
- |
-
Proteins
- |
-
IHC reagents
- |
-
WB reagents
- PonceauS Staining Solution
- PBST Washing Buffer, 10X
- 1.5M Tris-HCl Buffer, pH8.8
- 1M Tris-HCl Buffer, pH6.8
- 10% SDS Solution
- Prestained Protein Marker
- TBST Washing Buffer, 10X
- SDS PAGE Loading Buffer, 5X
- Stripping Buffered Solution
- Tris Buffer, pH7.4, 10X
- Total Protein Extraction Kit
- Running Buffer, 10X
- Transfer Buffer, 10X
- 30% Acr-Bis(29:1) Solution
- Tris电泳液速溶颗粒
- PBS(1X, premixed powder)
- TBS(1X, premixed powder)
- 快速封闭液
- 转膜液速溶颗粒
- Chemical reagents
- News
- Distributor
- Resources
- Contact
- Home
- >
- Info
- >
- PPAR a protein
- >
- Go Back
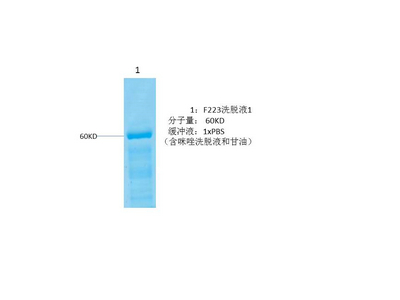
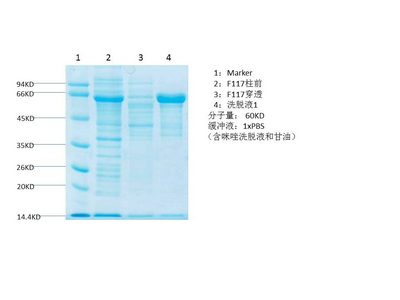
PPAR a protein
- Catalog No.:YD0085
- Applications:WB;SDS-PAGE
- Reactivity:Human
- Protein Name:
- PPAR a protein
- Sequence:
- Amino acid: 135-239, with his-MBP tag.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS
- Concentration:
- SDS-PAGE >90%
- Storage Stability:
- -20°C/6 mouth,-80°C for long storage
- Other Name:
- Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-alpha) (Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group C member 1)
- Background:
- function:Receptor that binds peroxisome proliferators such as hypolipidemic drugs and fatty acids. Once activated by a ligand, the receptor binds to a promoter element in the gene for acyl-CoA oxidase and activates its transcription. It therefore controls the peroxisomal beta-oxidation pathway of fatty acids.,online information:Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor entry,similarity:Belongs to the nuclear hormone receptor family. NR1 subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 nuclear receptor DNA-binding domain.,subunit:Heterodimer with the retinoid X receptor. Interacts with NCOA3 and NCOA6 coactivators, leading to a strong increase of transcription of target genes. Also interacts with PPARBP coactivator in vitro. Interacts with AKAP13.,tissue specificity:Skeletal muscle, liver, heart and kidney.,
- Function:
- negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, response to hypoxia, circulatory system process, transcription, transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, fatty acid metabolic process, lipid transport, ectoderm development, blood circulation, regulation of blood pressure, epidermis development, response to wounding, response to endogenous stimulus, response to hormone stimulus, negative regulation of biosynthetic process, positive regulation of biosynthetic process, regulation of catabolic process, positive regulation of catabolic process, response to extracellular stimulus, response to organic substance, regulation of specific transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, negative regulation of specific transcription from RNA p
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus.
- Expression:
- Skeletal muscle, liver, heart and kidney. Expressed in monocytes (PubMed:28167758).