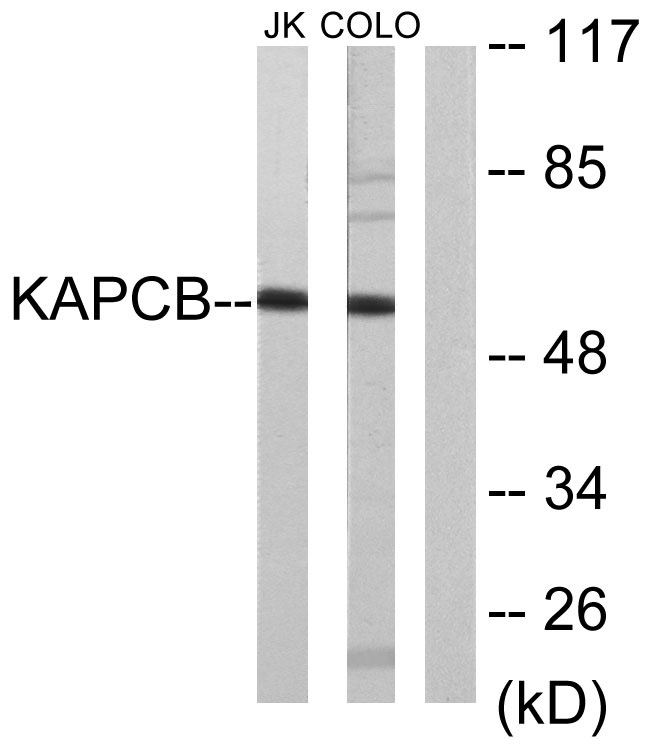
Total PKAβ cat Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA3565C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Gene Name:
- PRKACB
- Human Gene Id:
- 5567
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P22694
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P68181
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P68182
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit beta (PKA C-beta) (EC 2.7.11.11)
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- catalytic activity:ATP + a protein = ADP + a phosphoprotein.,cofactor:Magnesium.,enzyme regulation:Activated by cAMP.,function:Mediates cAMP-dependent signaling triggered by receptor binding to GPCRs. PKA activation regulates diverse cellular processes such as cell proliferation, the cell cycle, differentiation and regulation of microtubule dynamics, chromatin condensation and decondensation, nuclear envelope disassembly and reassembly, as well as regulation of intracellular transport mechanisms and ion flux.,PTM:Asn-3 is partially deaminated to Asp giving rise to 2 major isoelectric variants, called CB and CA respectively.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. AGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family. cAMP subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 AGC-kinase C-terminal domain.,similarity:Contains 1 protein kinase domain.,subcellular location:Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit) (By similarity). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm.,subunit:A number of inactive tetrameric holoenzymes are produced by the combination of homo- or heterodimers of the different regulatory subunits associated with two catalytic subunits. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits.,tissue specificity:Isoform 1 is most abundant in the brain, with low level expression in kidney. Isoform 2 is predominantly expressed in thymus, spleen and kidney. Isoforms 3 and 4 are only epxressed in the brain.,
- Function:
- protein amino acid phosphorylation, phosphorus metabolic process, phosphate metabolic process, cell surface receptor linked signal transduction, G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway, G-protein signaling, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger, G-protein signaling, coupled to cAMP nucleotide second messenger,intracellular signaling cascade, protein kinase cascade, response to endogenous stimulus, response to hormone stimulus, hormone-mediated signaling, response to organic substance, phosphorylation, regulation of phosphate metabolic process, second-messenger-mediated signaling, cAMP-mediated signaling, cyclic-nucleotide-mediated signaling, activation of protein kinase activity, cellular response to hormone stimulus, positive regulation of kinase activity, activation of protein kinase A activity, regulation of phosphorylation, positive regulation of catalytic activi
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm . Cell membrane . Membrane ; Lipid-anchor . Nucleus . Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. .
- Expression:
- Isoform 1 is most abundant in the brain, with low level expression in kidney. Isoform 2 is predominantly expressed in thymus, spleen and kidney. Isoform 3 and isoform 4 are only expressed in the brain.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs