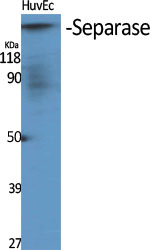
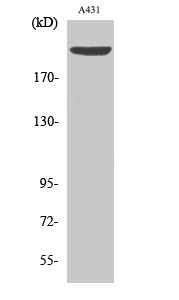Phospho SEPARASE (S801) Cell-Based Colorimetric ELISA Kit
- Catalog No.:KA1220C
- Applications:ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse
- Gene Name:
- ESPL1
- Human Gene Id:
- 9700
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- Q14674
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P60330
- Storage Stability:
- 2-8°C/6 months
- Other Name:
- Separin (EC 3.4.22.49) (Caspase-like protein ESPL1) (Extra spindle poles-like 1 protein) (Separase)
- Detection Method:
- Colorimetric
- Background:
- catalytic activity:All bonds known to be hydrolyzed by this endopeptidase have arginine in P1 and an acidic residue in P4. P6 is often occupied by an acidic residue or by an hydroxy-amino-acid residue, the phosphorylation of which enhances cleavage.,enzyme regulation:Regulated by at least two independent mechanisms. First, it is inactivated via its interaction with securin/PTTG1, which probably covers its active site. The association with PTTG1 is not only inhibitory, since PTTG1 is also required for activating it, the enzyme being inactive in cells in which PTTG1 is absent. PTTG1 degradation at anaphase, liberates it and triggers RAD21 cleavage. Second, phosphorylation at Ser-1126 inactivates it. The complete phosphorylation during mitosis, is removed when cells undergo anaphase. Activation of the enzyme at the metaphase-anaphase transition probably requires the removal of both securin and inhibitory phosphate.,function:Caspase-like protease, which plays a central role in the chromosome segregation by cleaving the SCC1/RAD21 subunit of the cohesin complex at the onset of anaphase. During most of the cell cycle, it is inactivated by different mechanisms.,PTM:Autocleaves. This function, which is not essential for its protease activity, is unknown.,PTM:Phosphorylated by CDC2. There are 8 Ser/Thr phosphorylation sites. Among them, Ser-1126 phosphorylation is the major site, which conducts to the enzyme inactivation.,similarity:Belongs to the peptidase C50 family.,subunit:Interacts with PTTG1. Interacts with RAD21.,
- Function:
- mitotic sister chromatid segregation, M phase of mitotic cell cycle, meiotic spindle organization, microtubule cytoskeleton organization, mitotic cell cycle, M phase, nuclear division, sister chromatid segregation, cytokinesis,proteolysis, apoptosis, cytoskeleton organization, microtubule-based process, cell cycle, spindle organization,chromosome segregation, regulation of sister chromatid cohesion, mitosis, regulation of mitosis, meiosis, meiosis I,regulation of mitotic cell cycle, cell death, regulation of cell cycle process, positive regulation of organelle organization,negative regulation of organelle organization, negative regulation of cell cycle process, programmed cell death, death,cell cycle process, cell cycle phase, regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition, regulation of organelle organization, regulation of chromosome organization, establishment of mitotic spindle
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs