Cytokeratin 16 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YT1264
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- Cytokeratin 16
- Fields:
- >>Estrogen signaling pathway;>>Staphylococcus aureus infection
- Gene Name:
- KRT16
- Protein Name:
- Keratin type I cytoskeletal 16
- Human Gene Id:
- 3868
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P08779
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 16666
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q9Z2K1
- Immunogen:
- The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Keratin 16. AA range:421-470
- Specificity:
- Cytokeratin 16 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Cytokeratin 16 protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:100 - 1:300. ELISA: 1:10000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- KRT16;KRT16A;Keratin; type I cytoskeletal 16;Cytokeratin-16;CK-16;Keratin-16;K16
- Observed Band(KD):
- 52kD
- Background:
- The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the keratin gene family. The keratins are intermediate filament proteins responsible for the structural integrity of epithelial cells and are subdivided into cytokeratins and hair keratins. Most of the type I cytokeratins consist of acidic proteins which are arranged in pairs of heterotypic keratin chains and are clustered in a region of chromosome 17q12-q21. This keratin has been coexpressed with keratin 14 in a number of epithelial tissues, including esophagus, tongue, and hair follicles. Mutations in this gene are associated with type 1 pachyonychia congenita, non-epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma and unilateral palmoplantar verrucous nevus. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in KRT16 are a cause of pachyonychia congenita type 1 (PC1) [MIM:167200]; also known as Jadassohn-Lewandowsky syndrome. PC1 is an autosomal dominant ectodermal dysplasia characterized by hypertrophic nail dystrophy resulting in onchyogryposis (thickening and increase in curvature of the nail), palmoplantar keratoderma, follicular hyperkeratosis, and oral leukokeratosis. Hyperhidrosis of the hands and feet is usually present.,disease:Defects in KRT16 are a cause of unilateral palmoplantar verrucous nevus (UPVN) [MIM:144200]. UPVN is characterized by a localized thickening of the skin in parts of the right palm and the right sole.,disease:Defects in KRT16 are the cause of palmoplantar keratoderma non-epidermolytic (NEPPK) [MIM:600962]. NEPKK is a dermatological disorder characterized by focal palmoplantar keratoderma with oral, genital, and follicular lesions.,disease:KRT16
- Subcellular Location:
- nucleus,cytoskeleton,intermediate filament,extracellular exosome,
- Expression:
- Expressed in the corneal epithelium (at protein level).
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Western Blot analysis of various cells using Cytokeratin 16 Polyclonal Antibody
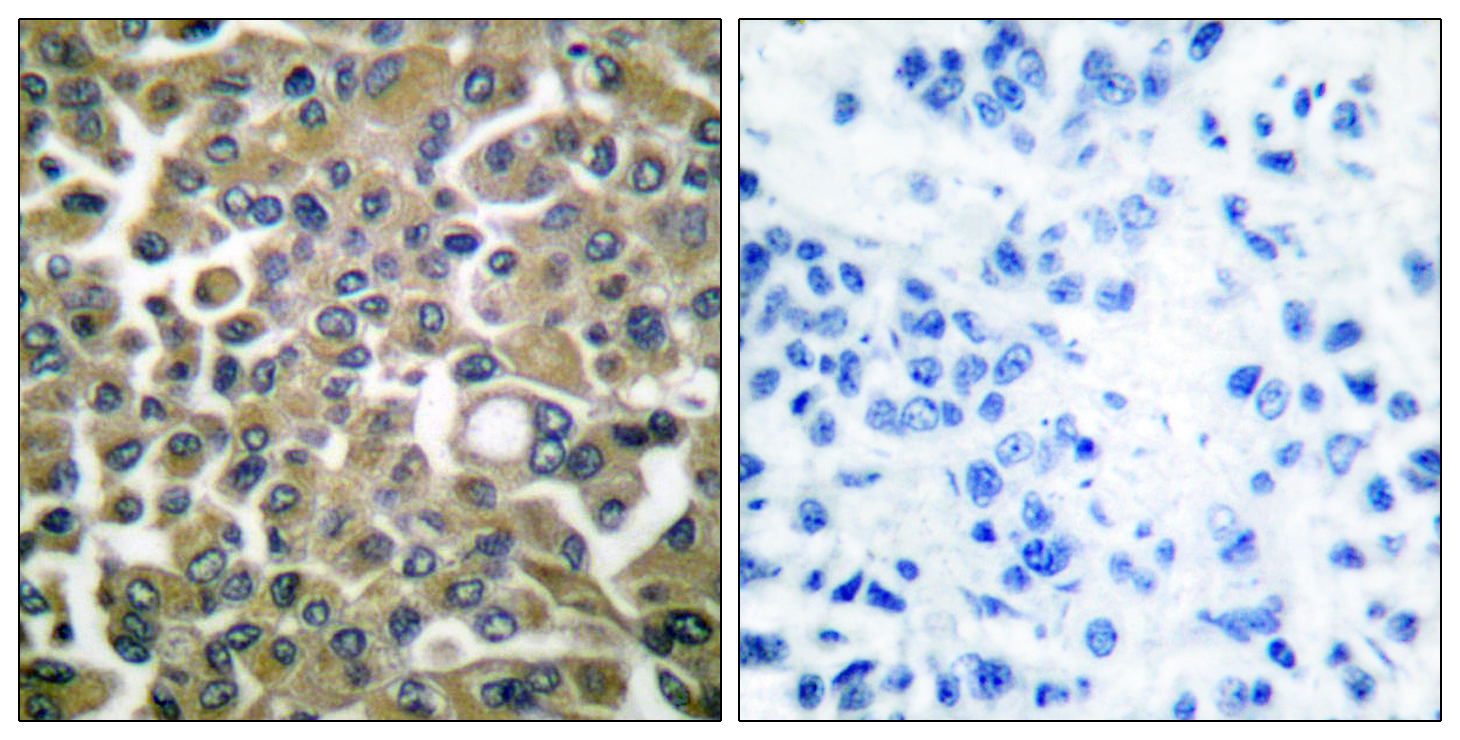
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma tissue, using Keratin 16 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
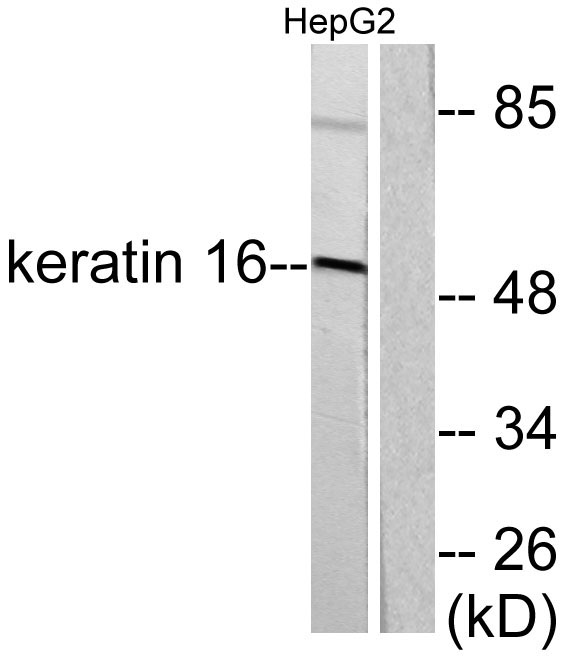
- Western blot analysis of lysates from HepG2 cells, using Keratin 16 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.



