WNT4 Polyclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YN0285
- Applications:WB;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat
- Target:
- WNT4
- Fields:
- >>mTOR signaling pathway;>>Wnt signaling pathway;>>Axon guidance;>>Hippo signaling pathway;>>Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells;>>Melanogenesis;>>Thyroid hormone signaling pathway;>>Cushing syndrome;>>Alzheimer disease;>>Pathways of neurodegeneration - multiple diseases;>>Human papillomavirus infection;>>Pathways in cancer;>>Proteoglycans in cancer;>>Basal cell carcinoma;>>Breast cancer;>>Hepatocellular carcinoma;>>Gastric cancer
- Gene Name:
- WNT4 UNQ426/PRO864
- Protein Name:
- Protein Wnt-4
- Human Gene Id:
- 54361
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P56705
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P22724
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- Q9QXQ5
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human protein . at AA range: 190-270
- Specificity:
- WNT4 Polyclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500-2000 ELISA 1:5000-20000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Observed Band(KD):
- 38kD
- Background:
- The WNT gene family consists of structurally related genes which encode secreted signaling proteins. These proteins have been implicated in oncogenesis and in several developmental processes, including regulation of cell fate and patterning during embryogenesis. This gene is a member of the WNT gene family, and is the first signaling molecule shown to influence the sex-determination cascade. It encodes a protein which shows 98% amino acid identity to the Wnt4 protein of mouse and rat. This gene and a nuclear receptor known to antagonize the testis-determining factor play a concerted role in both the control of female development and the prevention of testes formation. This gene and another two family members, WNT2 and WNT7B, may be associated with abnormal proliferation in breast tissue. Mutations in this gene can result in Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome and in SERKAL syndrome. [provided by RefSe
- Function:
- disease:Defects in WNT4 are a cause of Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome (RKH syndrome) [MIM:277000]; also called Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome (MRKH syndrome or MRKH anomaly). RKH syndrome is characterized by utero-vaginal atresia in otherwise phenotypically normal female with a normal 46,XX karyotype. Anomalies of the genital tract range from upper vaginal atresia to total Muellerian agenesis with urinary tract abnormalities. It has an incidence of approximately 1 in 5'000 newborn girls.,disease:Defects in WNT4 are the cause of female sex reversal with dysgenesis of kidneys, adrenals, and lungs (SERKAL) [MIM:611812]; also known as SERKAL syndrome.,function:Ligand for members of the frizzled family of seven transmembrane receptors.,function:Ligand for members of the frizzled family of seven transmembrane receptors. Probable developmental protein. May be a signaling molecule wh
- Subcellular Location:
- Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix.
- Expression:
- Fetal tissues,Mammary gland,Placenta,
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
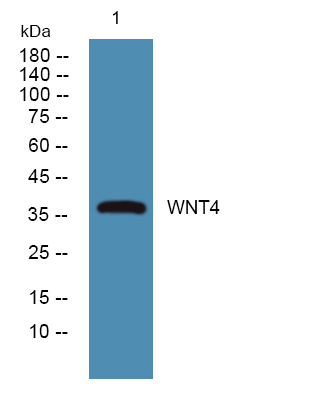
- Western blot analysis of lysates from Jurkat cells, primary antibody was diluted at 1:1000, 4°over night



