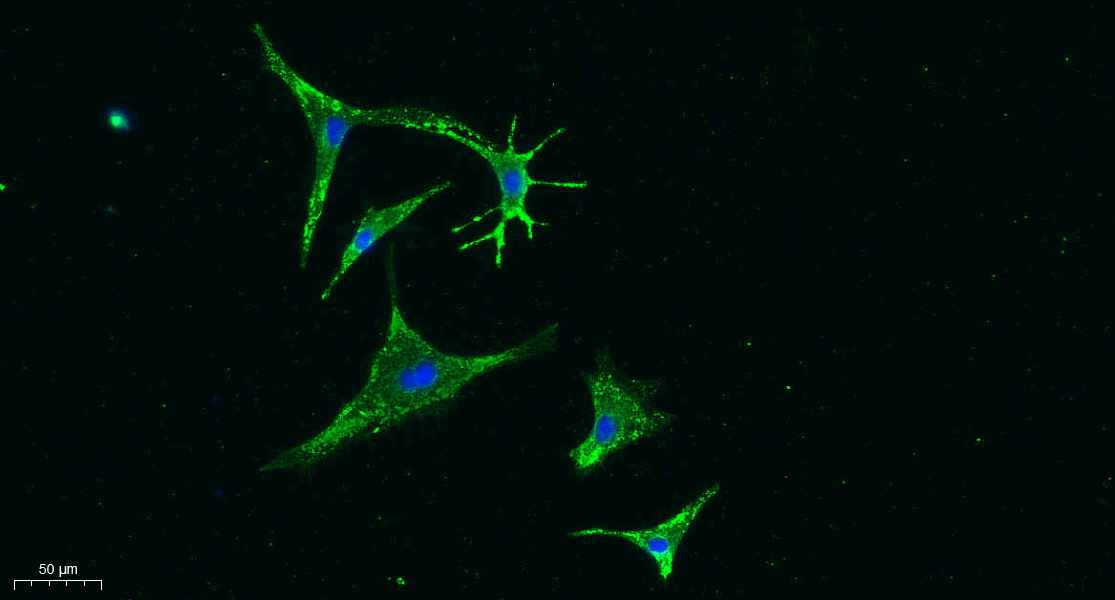
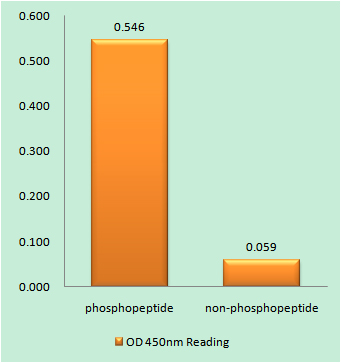
Vinculin (PT0372) Mouse mAb
- Catalog No.:YM4034
- Applications:IHC;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human (predicted: Mouse; Rat)
- Target:
- Vinculin
- Fields:
- >>Focal adhesion;>>Adherens junction;>>Leukocyte transendothelial migration;>>Regulation of actin cytoskeleton;>>Bacterial invasion of epithelial cells;>>Shigellosis;>>Amoebiasis
- Gene Name:
- VCL
- Protein Name:
- Vinculin
- Human Gene Id:
- 7414
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P18206
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 22330
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- Q64727
- Rat Gene Id:
- 305679
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- P85972
- Immunogen:
- Synthesized peptide derived from human Vinculin. AA range:786-835 AA range: 100-200
- Specificity:
- Vinculin Antibody detects endogenous levels of Vinculin protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse,IgG1
- Dilution:
- IHC 1:100-300,ELISA 1:5000-20000
- Purification:
- The antibody was affinity-purified from mouse ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- VCL;Vinculin;Metavinculin
- Observed Band(KD):
- 123kD
- Background:
- Vinculin is a cytoskeletal protein associated with cell-cell and cell-matrix junctions, where it is thought to function as one of several interacting proteins involved in anchoring F-actin to the membrane. Defects in VCL are the cause of cardiomyopathy dilated type 1W. Dilated cardiomyopathy is a disorder characterized by ventricular dilation and impaired systolic function, resulting in congestive heart failure and arrhythmia. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene, but the biological validity of some variants has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- disease:Defects in VCL are the cause of cardiomyopathy dilated type 1W (CMD1W) [MIM:611407]. Dilated cardiomyopathy is a disorder characterized by ventricular dilation and impaired systolic function, resulting in congestive heart failure and arrhythmia. Patients are at risk of premature death.,function:Involved in cell adhesion. May be involved in the attachment of the actin-based microfilaments to the plasma membrane. May also play important roles in cell morphology and locomotion.,online information:Vinculin entry,PTM:Aceylated; mainly by myristic acid but also small amount of palmitic acid.,PTM:Phosphorylated; on serines, threonines and tyrosines. Phosphorylation on Tyr-1133 in activated platelets affects head-tail interactions and cell spreading but has no effect on actin binding nor on localization to focal adhesion plaques.,similarity:Belongs to the vinculin/alpha-catenin family.,s
- Subcellular Location:
- Cell membrane ; Peripheral membrane protein ; Cytoplasmic side . Cell junction, adherens junction . Cell junction, focal adhesion . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton . Cell membrane, sarcolemma ; Peripheral membrane protein ; Cytoplasmic side . Recruitment to cell-cell junctions occurs in a myosin II-dependent manner. Interaction with CTNNB1 is necessary for its localization to the cell-cell junctions. .
- Expression:
- Metavinculin is muscle-specific.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs